Define the follicular phase
First day of menses until ovulation
The corpus luteum primarily secretes which hormone?
Progesterone (to a lesser extent estrogen)
The final maturation of the preovulatory oocyte is induced by a surge of:
a. Activin
b. FSH
c. GnRH
d. Luteinizing hormone (LH)
What is the D - LH
LH stimulates the resumption of meiosis 1 at mid-cycle
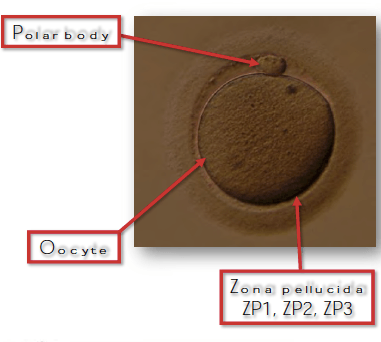
BONUS: What phase do they arrest in after ovulation?
Describe the changes in cervical mucous during the menstrual cycle
Immediately after menstruation: scant and thin
Follicular phase: clear, copious, and elastic, increased quantity - "ferning" appearance
Luteal phase: thick, viscous, opaque, decreased quantity
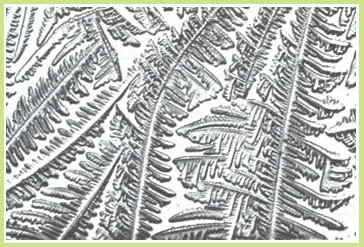
Example of ferning above
BONUS: What is the name of the cervical mucous at midcycle?
The two phases of the menstrual cycle are
What are the follicular (proliferative) and luteal (secretory) phases
In a spontaneous menstrual cycle, the follicle that is most sensitive to FSH becomes the:
a. Preantral follicle
b. Primary follicle
c. Antral follicle
d. Dominant follicle
What is D - dominant follicle
The primary hormone produced by the hypothalamus is:
a. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
b. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
c. Inhibin
d. Prolactin
What is B - GnRH
BONUS: Lupron is an example of a:
a. GnRH agonist
b. GnRH antagonist
Secreted from which portion of the hypothalamus?
FSH receptors exist on the cell membranes of which type of cell in the ovary?
What are granulosa cell membranes
What is the typical length of the luteal phase?
What is 14 days.
The LH surge proceeds ovulation by approximately how many hours?
What is 34-36 hours
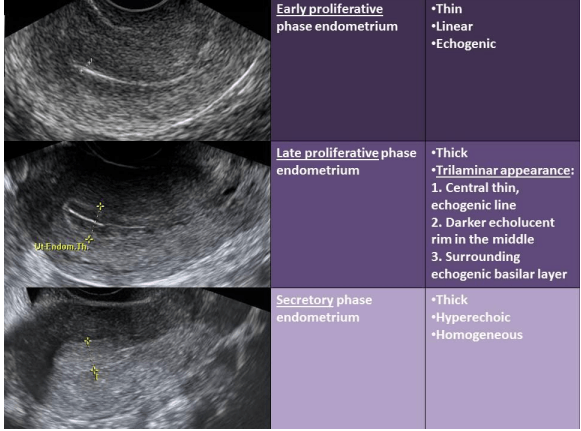
Correctly identify which phases of the menstrual cycle these sonographic images correspond to. 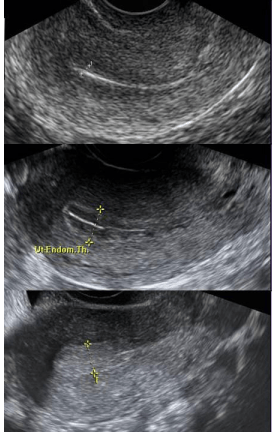
BONUS: What are the two layers of endometrium? Which one is responsive to hormones?
What is the length of a normal menstrual cycle?
25-35 days
During fetal development, oocytes become enveloped with granulosa cells and enter meiosis but arrest early in the first phase.
Meiosis resumes at:
a. Birth
b. Puberty
c. Conception
d. Menopause
What is B - puberty (ovulation)
When do they complete the second meiotic division?
Which of the following are reproductive impacts of estrogen?
a. Thin endometrium, thin cervical mucus
b. Thick endometrium, thin cervical mucus
c. Thick endometrium, thick cervical mucus
d. Thin endometrium, thick cervical mucus
What is B - thick endometrium, thin cervical mucous
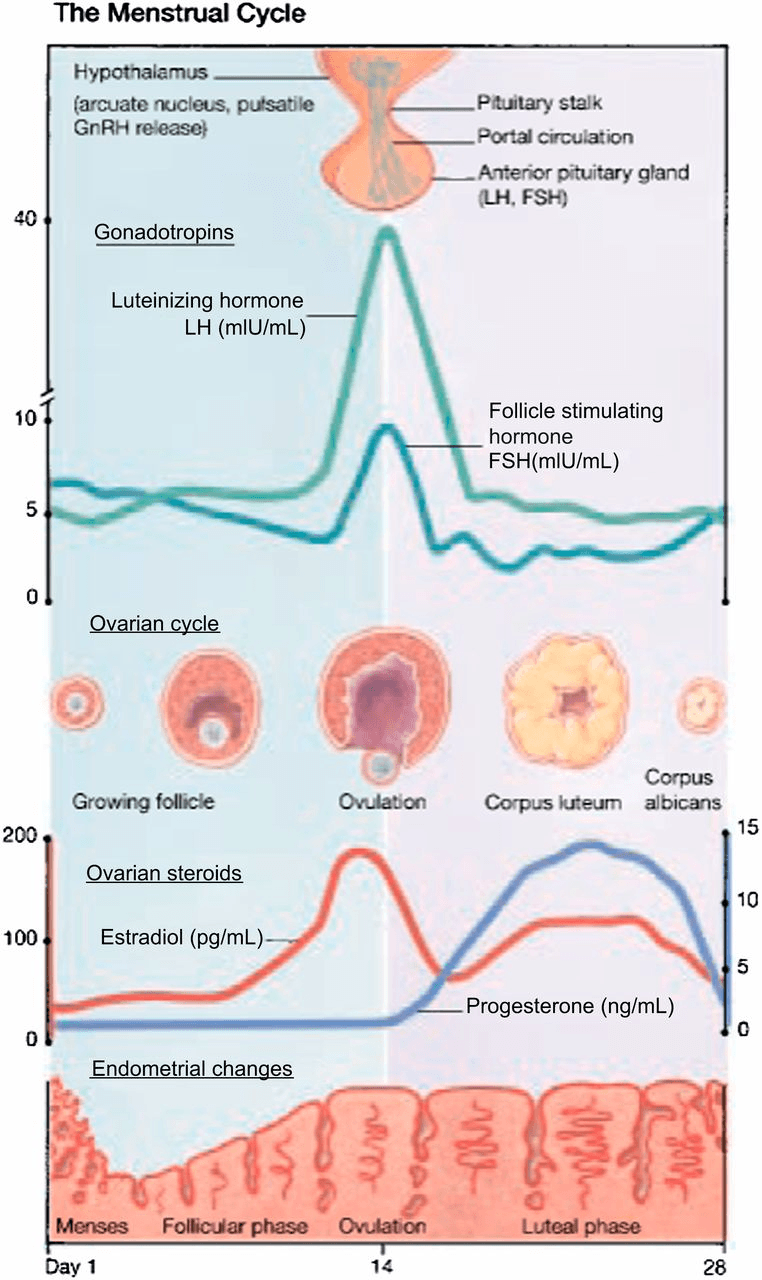
Describe the hormonal changes taking place during this phase of the menstrual cycle (i.e. which hormones are increasing and which are decreasing)
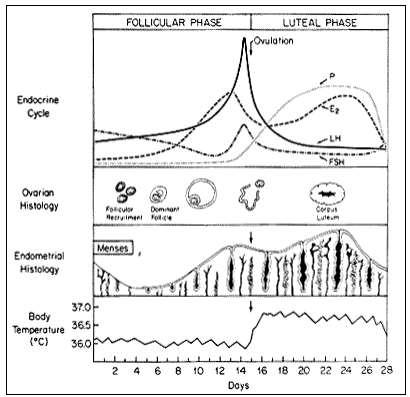 Anterior pituitary: FSH is decreasing secondary to negative feedback from E2 and inhibin B from developing follicles. Rise in LH from positive feedback of Estrogen.
Anterior pituitary: FSH is decreasing secondary to negative feedback from E2 and inhibin B from developing follicles. Rise in LH from positive feedback of Estrogen.
Ovary: increasing E2 levels and inhibin B levels
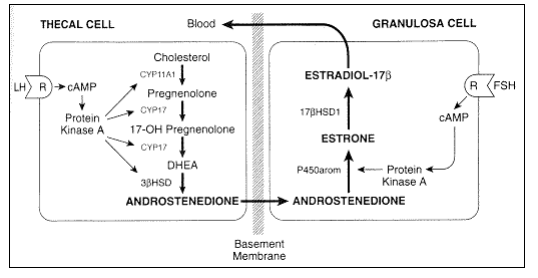
LH acts on receptors on this type of cell to produce this steroid hormone?
Thecal cell; androstenedione
Ovulation occurs more commonly from the right or left ovary?
What is the right ovary.
If pregnancy does not occur, a drop in this hormone and a rise in this compound cause the lining to shed (menstruation)
What is a drop in progesterone and a rise in prostaglandins
BONUS: this is due to degeneration in this ovarian structure?
What is considered a typical amount of blood loss during menses? AND What amount is considered abnormal?
Typical = 30mL
Abnormal = 80mL
Which of the following cells will divide mitotically in the ovary?
a. Spermatogonia
b. Secondary oocyte
c. Primary oocyte
d. Oogonia
What is D - oogonia
BONUS: At what stage in a females life does this occur?
From which portion of the pituitary gland are the gonadotropins FSH and LH released from?
a. anterior pituitary
b. posterior pituitary
What is anterior pituitary
What is the name of the enzyme that converts androgens to estrogens in the granulosa cell?
What is aromatase.
Describe what happens to the corpus luteum if pregnancy does not occur?
If pregnancy does not occur, the corpus luteum undergoes luteolysis under the influence of estradiol and prostaglandins, and forms a scar tissue called the corpus albicans
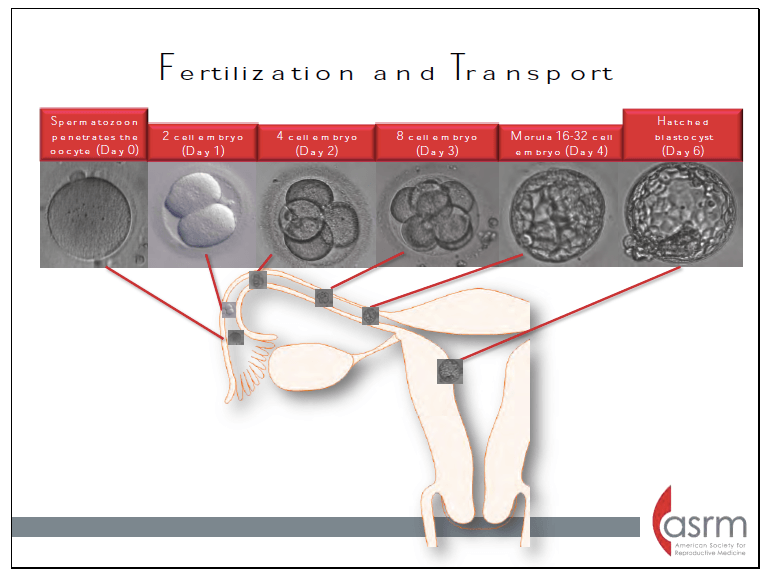
Fertilization typically occurs in this portion of the fallopian tube?
What is the distal third (ampulla) adjacent to the ovary
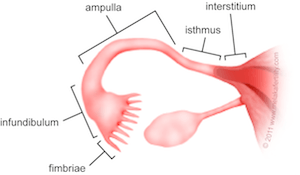
BONUS: What is the usual diameter of a fallopian tube?
Does your basal body temperature increase or decrease after ovulation?
Increases
This phase of the menstrual cycle remains relatively constant in all women, while this phase of the menstrual cycle is more variable
Constant = luteal (14 days)
Variable = follicular (10-16 days)
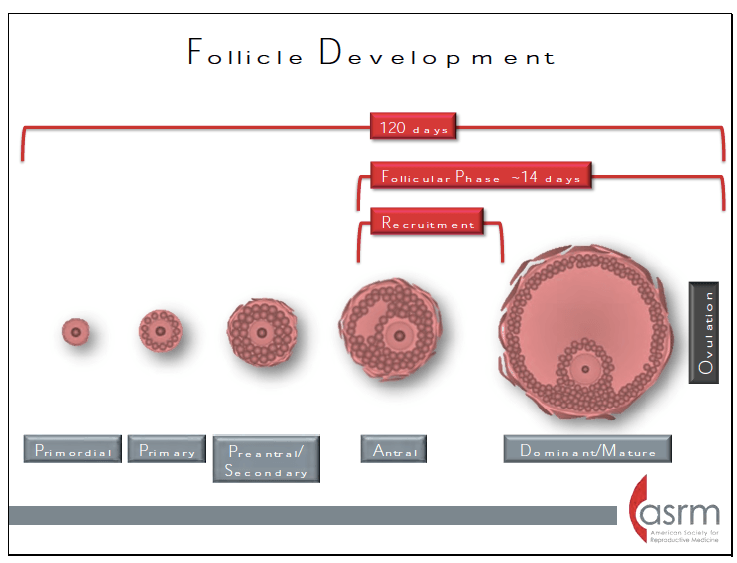
Development from a primordial follicle to a preovulatory follicle takes approximately:
a. 1 menstrual cycle
b. 3 weeks
c. 4 months
d. 3 to 4 years
What is C - 4 months
What are the four functional compartments involved in reproduction?
What are hypothalamus, pituitary (anterior), ovary, endometrium
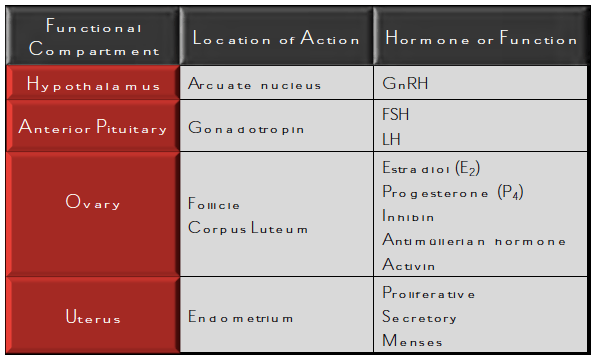
BONUS: Estrogen and progesterone exert negative feedback on which portion of the H-P-O axis?
In the ovary, the primordial follicles are arrested in which stage of Meiosis?
What is prophase of Meiosis 1
BONUS: what stage of prophase?
In the absence of a pregnancy, steroid hormone levels begin to fall due to declining corpus luteum function. Progesterone withdrawal results in what changes in the endometrium causing menstruation?
Increased coiling and constriction of the spiral arterioles. This eventually results in tissue ischemia due to decreased blood flow to the superficial endometrial layers, the spongiosa and compacta. The endometrium releases prostaglandins that cause contractions of the uterine smooth muscle and sloughing of the degraded endometrial tissue.
Describe the chemical process of ovulation in the ovary?
Proteolytic enzymes and prostaglandins are activated and digest collagen in the follicular wall, leading to an explosive release of the oocyte-cumulus complex Prostaglandins may also stimulate ovum release by stimulation of smooth muscle within the ovary. The point of the dominant follicle closest to the ovarian surface where this digestion occurs is called the stigma.
Describe the endometrial glands in the two phases of the menstrual cycle
Proliferative: narrow, tubular, and some mitosis and pseudostratification is present.
Secretory: tortuous and dilated, more vacuoles, more stromal edema 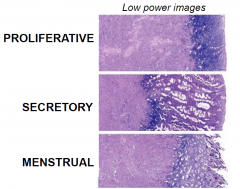
Describe the image in the handout provided
The developing ovarian follicles/oocytes are found in which portion of the ovary?
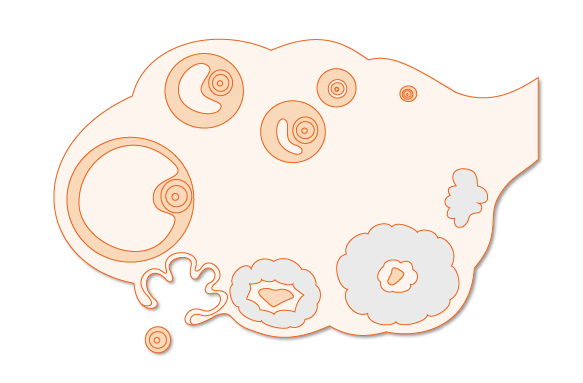 What is the outer cortex
What is the outer cortex
What is the half life of FSH and LH secretion?
What is 3-4 hours for FSH and 20 mins for LH
BONUS: Which has a long half life Lupron or hCG? How do these stimulate ovulation?