What is a Mental Status Assessment?
A mental status assessment (MSA) is a systematic assessment that allows care providers to observe and describe a patient’s behaviour in an objective non-judgmental manner. It provides information about a patient's emotional, mental, and behavioural functioning at the time of interaction.
What group of medications treat various psychiatric disorders?
Psychotropics
List 3 physical symptoms of anxiety.
Shortness of Breath
Dizzy
Shaking
Chest Pain
Cold / Clammy
Aches and Pains
Poor Sleep
What were institutions for the mentally ill originally called?
Asylum
The symptoms below indicate what type of emergency:
Unconscious
Unresponsive
Pin point pupils
Blue lips / Finger nails
Shallow Breathing
Cold / Clammy Skin
Gurgling sounds coming from the mouth
Opioid Overdose
What are the 6 assessment areas of a MSA?
General Observation
Emotional Status
Sensorium & Cognitive Functioning
Thought Process
Perception
Risk Assessment
Antipsychotics are available in what administrations forms?
Oral (PO)
Sublingual (SL)
Intramuscular Injection (IM)
What is the difference between Schizophrenia and Schizoaffective Disorder?
Schizophrenia: Psychotic disorder that can cause positive and negative symptoms.
Schizoaffective: Psychotic disorder that can cause positive and negative symptoms + mood symptoms.
When was the defence of mental disorder introduced?
1985
You are administering 300mg of Haldol Decanoate IM 100mg/ml. The patient is a 32yr old male with a BMI of 30. What injection site will you use? What size needle (gauge and length) will you use?
Ventrogluteal
21-23 gauge
2 inch
A fixed false belief.
Delusion
How many generations of antipsychotics are there?
3
What are negative symptoms?
Negative: Absence or reduction of usual experiences and behaviors; blunted / flat affect, social withdrawal, anhedonia.
What was the first "antipsychotic"?
Antipsychotics were discovered in the late 1950s. The first antipsychotic drug, chlorpromazine, was first developed as a “tranquilizer.” Its usefulness for treating psychosis was recognized by accident. It was found to decrease positive symptoms such as hallucinations, delusions, and thought disorder.
Chlorpromazine is a phenothiazine that is used to treat psychotic disorders such as schizophrenia or manic-depression in adults.
Chlorpromazine is also used in adults to treat nausea and vomiting, anxiety before surgery, chronic hiccups, acute intermittent porphyria, and symptoms of tetanus.
What muscle, commonly used for IM injections is pictured below:
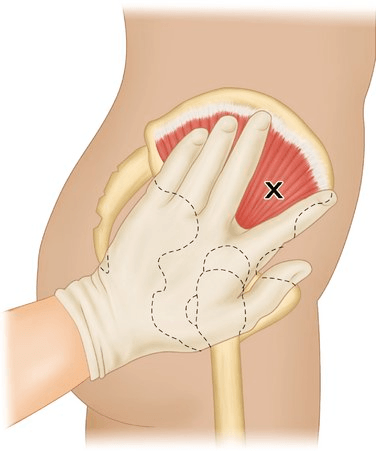
Ventrogluteal
A false experience involving the 7 senses.
Hallucination
What are the 5 classes of psychotropics?
Antidepressant
Antipsychotic
Sedative
Mood Stabilizer
Psychostimulant
What is the difference between Bipolar type 1 and Bipolar type 2?
Bipolar type 1: Mania & Depressive episodes. Can develop delusions and paranoia.
Bipolar type 2: Hypomania & Depressive episodes. No delusions or paranoia.
What are the origins of the Royal Ottawa Hospital:
When did it originally open?
What was it originally for?
When did it start admitting the mentally ill?
The hospital was established as the Lady Grey Hospital in February 1910 and known in the early days as “the San.” Over the first 60 years, the hospital admitted 11,000 tuberculosis patients from all over Eastern Ontario. The last tuberculosis ward in the facility closed in 1970. It was renamed the Royal Ottawa Hospital at around that time.
In 1961, the ROH was designated as a hospital for the care and treatment of emotional and psychiatric disorders.
Below are what type of adverse side effect:
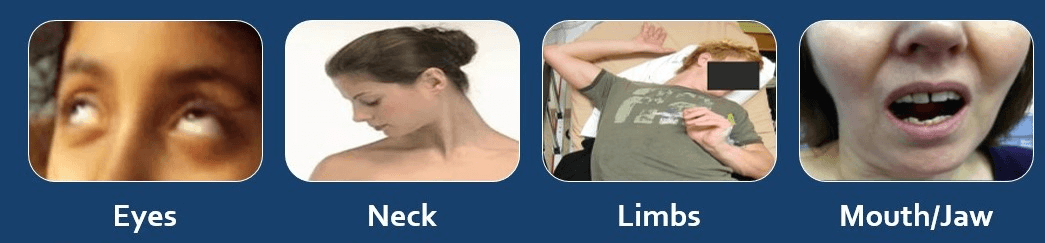
Extrapyramidal Symptoms
"I am the King of Canada! The government is after me! Cant you hear the spy's over the radio?"
What MSA findings are in this patient quote?
Grandiose Delusion
Paranoid Delusion
Auditory Hallucination
Your 36yr old female client is presenting with a temp of 38.3 C, abdominal cramping, loose stool q 2hrs, and shivering. You review their MAR. They are prescribed Fluoxetine (Prozac), with the dose recently being increased. What are you concerned about?
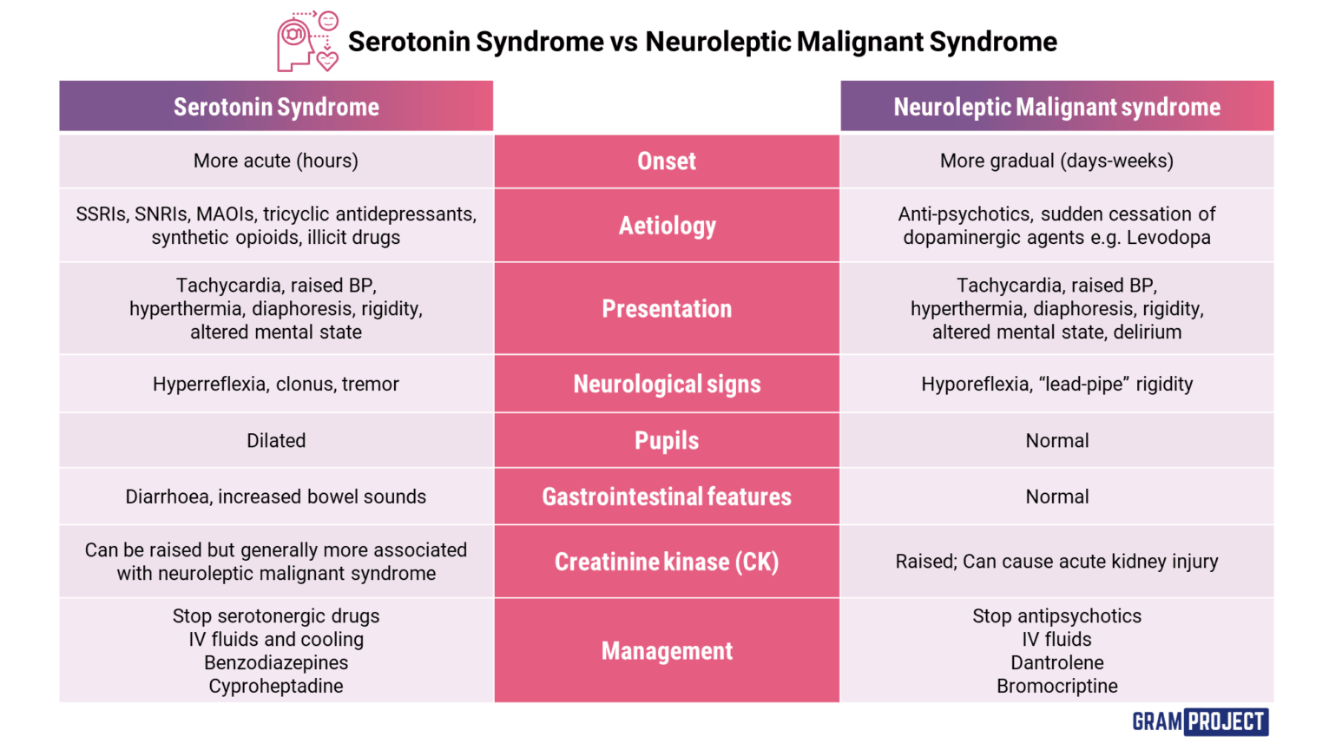
SEROTONIN SYNDROME.
Serotonin is good! But too much serotonin causes signs and symptoms that can range from mild (shivering and diarrhea) to severe (muscle rigidity, fever and seizures). Severe serotonin syndrome can cause death if not treated.
Serotonin syndrome can occur when you increase the dose of certain medications or start taking a new drug. It's most often caused by combining medications that contain serotonin, such as a migraine medication and an antidepressant.
What treatment is the image below? And what does it treat?
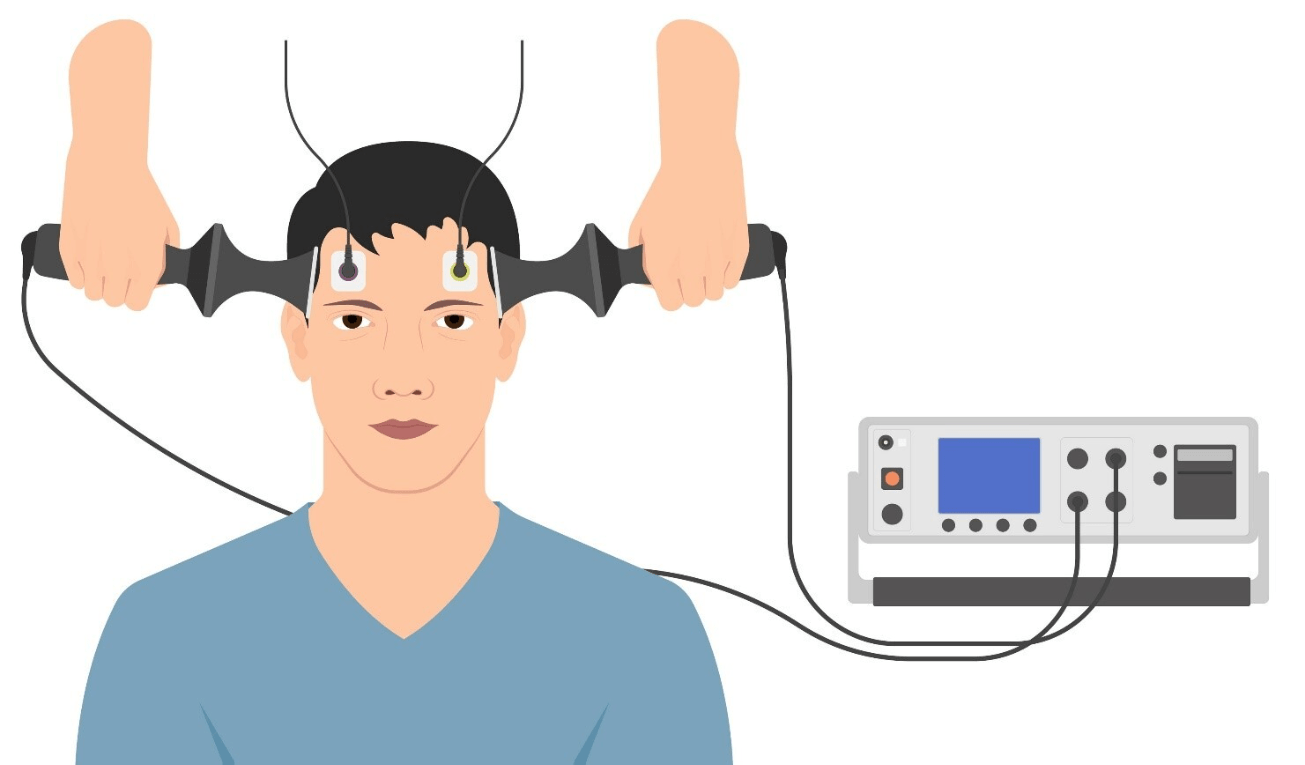
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a medical treatment most commonly used in patients with severe major depression or bipolar disorder that has not responded to other treatments. ECT involves a brief electrical stimulation of the brain while the patient is under anesthesia.
What treatment is the image below? What did it treat? What area of the brain was effected? Is it still practiced?
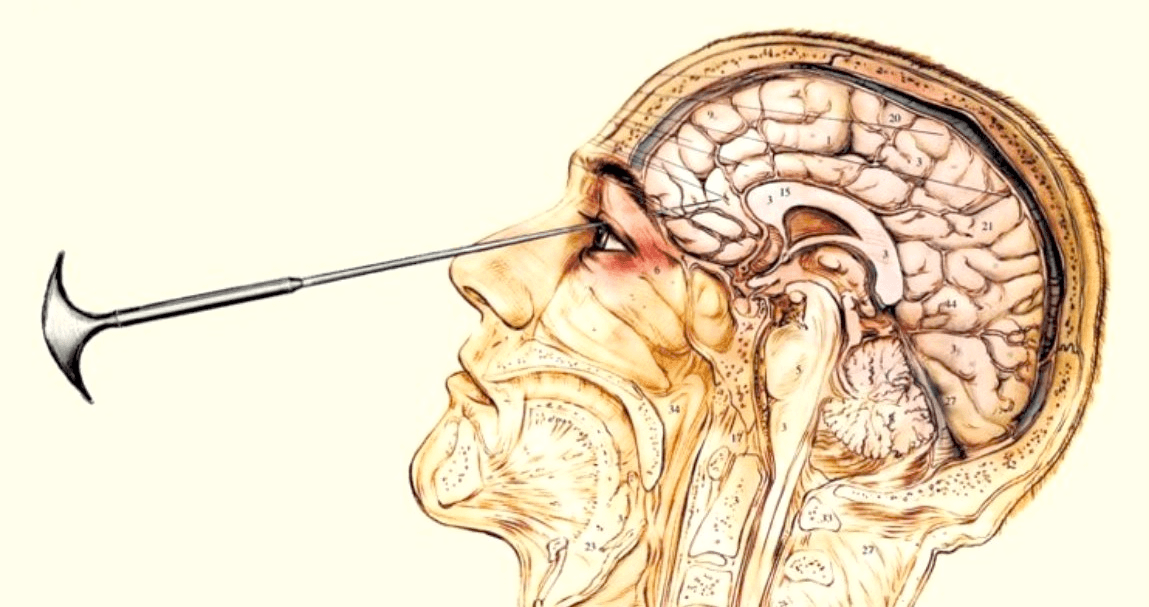
A lobotomy is a type of psychosurgery that was used to treat mental health conditions such as mood disorders and schizophrenia.
The frontal lobe was the part of the brain targeted in the standard lobotomy operations practiced in the 1940s and 1950s. This surgery consisted of making holes in the skull, removing some brain tissue, and severing the connections between the frontal lobe and the thalamus.
How does serotonin syndrome present?
How does neuroleptic malignant syndrome present?