What shape is spirillium?
Spiral
How to viruses reproduce?
Host Cell
Organisms without a nucleus
Prokaryote
What is the tail part of a bacteria? (D)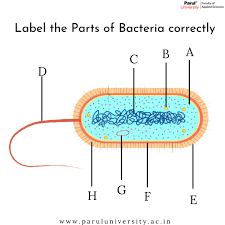
flagellum
What is B? ...A cell structure that synthesizes proteins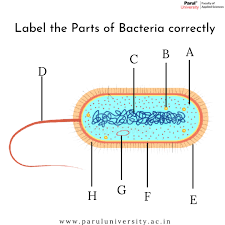
Ribosomes
What shape is coccus?
round/spherical
Do antibiotics affect viruses?
No
Organisms with a nucleus
Eukaryotes
What is C?
DNA
short, hair-like protein structures found on the surface of bacterial cells, primarily used for attachment to other cells or surfaces
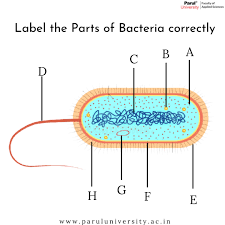
pilli
How can you get rid of bacteria?
Antibiotics
Do viruses have cells?
No, They are non-living
The two kingdoms of bacteria are....
Eubacteria and Archaea
What is G? (typically a small circular DNA strand in the cytoplasm)
Plasmid
The gelatinous liquid that fills the inside of a cell?
Cytoplasm
Eubacteria
What can prevent viruses?
Vaccines
What is a heterotroph?
An organism which is not able to produce its own food and must obtain it from another source
What is F? (the inside lining) 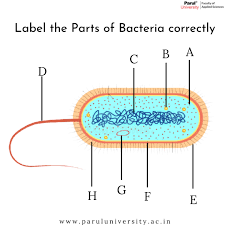
Cell membrane
What kind of cell is this?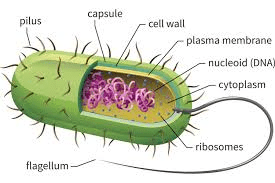
Bacterial/Prokaryote
Bacteria that live in harsh environments
Archaebacteria
How can antibiotic resistance develop?
Taking antibiotics when they are not needed or not finishing a perscription
What is an autotroph?
An organism which can produce its own nourishment (ex. photosynthesis)
What is E? A rigid, non-living layer that surrounds certain types of cells, primarily plant cells, providing structural support, protection, and maintaining the cell's shape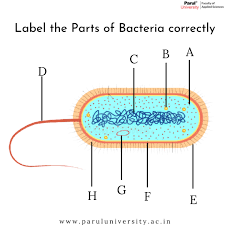
Cell Wall
What are the two types of cells that all organisms fall into?
Prokaryote and Eukaryote