Atoms prefer to have ____ electrons in the valence shell.
What is Eight.
Definition of the Octet Rule.
The term used to describe all of the chemical reactions inside a cell is __________.
What is metabolism.
DNA is the acronym for this.
What is Deoxyribonucleic Acid.
After touching the surface of a surgical table with pathogens present the subjects hand is covered in this.
What is transient microbes.
A patient describes how they are feeling to you in a very subjective format.
"My headache is horrible and I can't get the ringing out of my ears."
What is a Symptom.
A sign is considered to be an objective measure of their symptoms such as a fever, or any other change in their vital signs.
Granulocytes are this type of cell.
What is Leukocytes.
Molecules with the same atomic makeup but different structural arrangement of atoms are called this.
What is Isomers.
Slight changes in the structural arrangements of the atoms can lead to very different properties.
When small molecules are assembled into larger ones, using energy.
What is an Anabolic reaction or Anabolism.
Catabolism: Large molecules are broken down into smaller ones, releasing energy.
The nucleotide that is present in RNA that is not present in DNA.
What is Uracil.
RNA does not have Thymine.
A process that destroys all viable microbes, including viruses and endospores.
What is Sterilization.
After being on antibiotics for a while a provider recommends taking these to introduce microbes back into the body.
What is Probiotics.
When someone is deliberately exposed to material that is antigenic but not pathogenic.
What is Vaccination.
The byproduct of H2O and OH occurs during this type of synthesis reaction.
What is a Dehydration Synthesis reaction.
Organisms that obtain their for electron transfer through breaking chemical bonds.
What is Chemotrophs.
Those that get their energy for electron transfer from light are phototrophs.
The nitrogenous bases present in DNA.
Cytosine, Guanine, Thymine, and Adenine
Betadine is an example of this that can be applied directly to exposed body surfaces prior to surgery.
What is an Antiseptic.
Disinfection - a process to destroy vegetative pathogens, not endospores; done to inanimate objects
An infectious agent.
What is a Pathogen.
A mother passing antibodies through her breastmilk to her child is an example of this.
What is natural form of Passive Immunity.
The macromolecule known for energy storage, receptors, food, structural role in plants, fungal cell walls, and exoskeletons of insects.
What is Carbohydrates.
Other Macromolecules:
Lipids, Nucleic acids, Proteins
The energy used after its release through catabolism.
What is ATP - adenosine triphosphate.
The expression of the genotype creates this observable trait.
What is phenotype.
All types of genes constitute the genetic makeup - genotype.
An example of the highest resistant microbes.
What is Prions, or bacterial endospores.
•Moderate resistance
–Pseudomonas sp.
–Mycobacterium tuberculosis
–Staphylococcus aureus
–Protozoan cysts
•Least resistance
–Most bacterial vegetative cells
–Fungal spores and hyphae, yeast
–Enveloped viruses
Protozoan trophozoites
Portal of entry > Adhesion > Invasion > _______ > Infection of Target > Disease > Portal of exit
What is Multiplication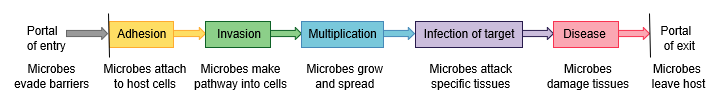
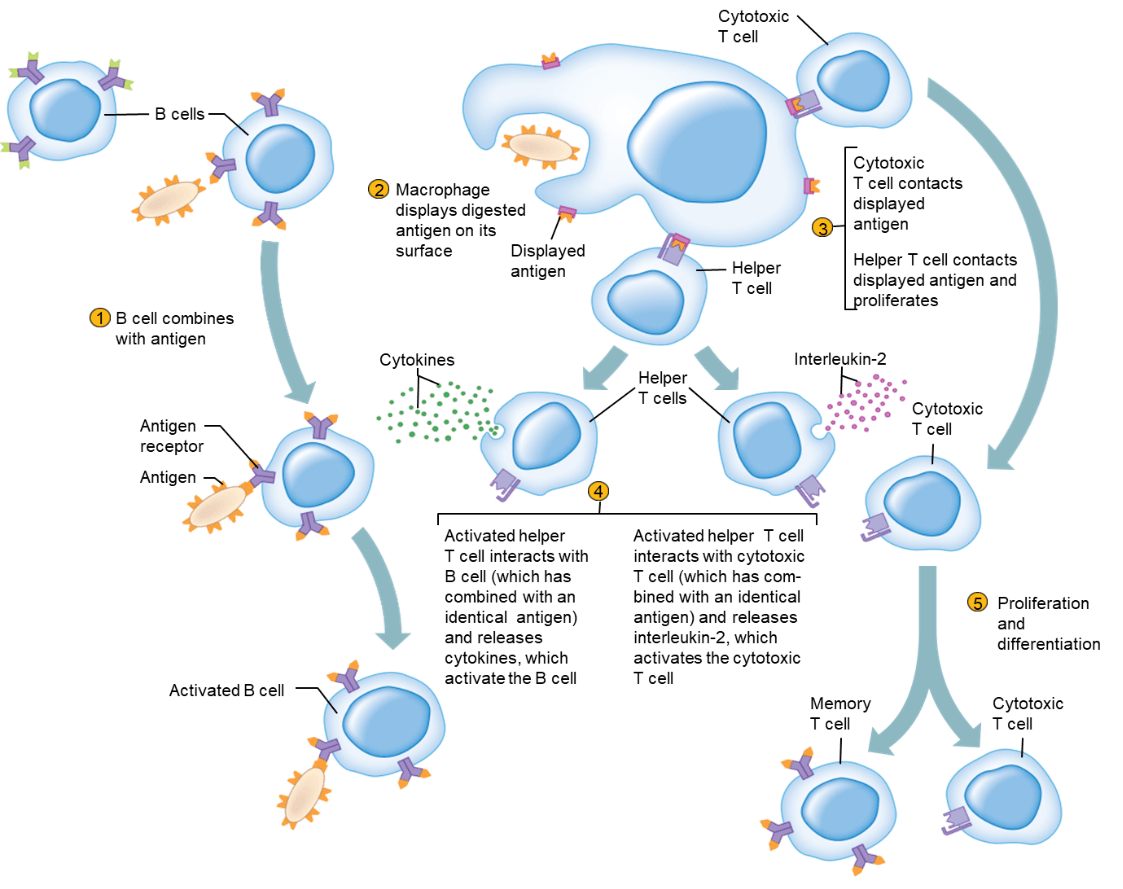
White Blood Cells
What is Leukocytes.
This is demonstrated in the image below. 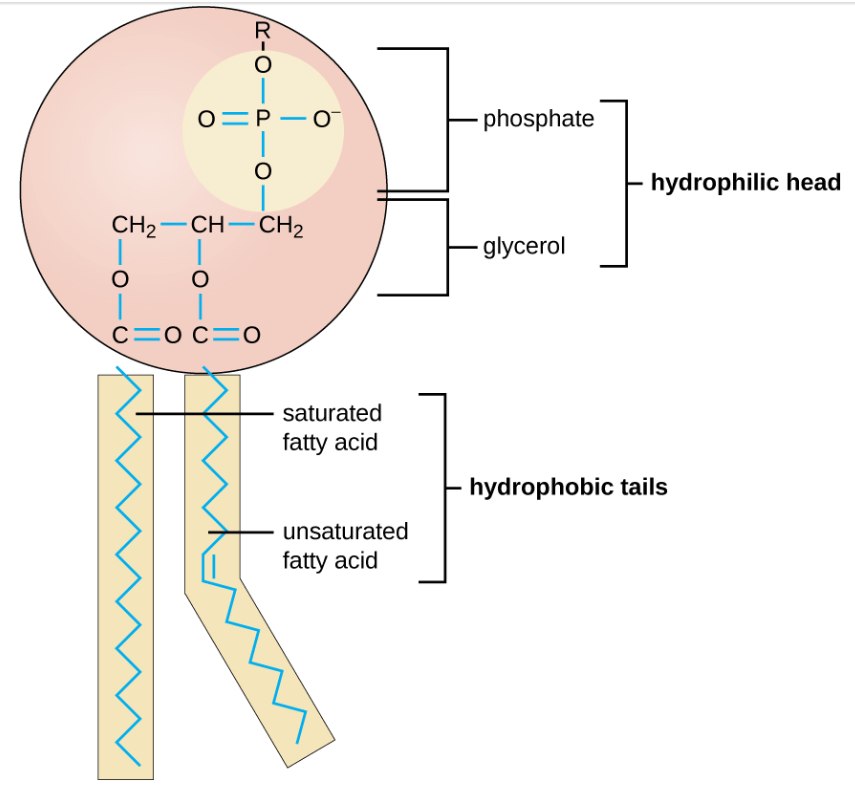
What is a Phospholipid.
The proteins used as a catalyst for biochemical reactions within the cell.
What is Enzymes.
The chemical reactants to which an enzyme binds are called substrates, and the location within the enzyme where the substrate binds is called the enzyme's active site.
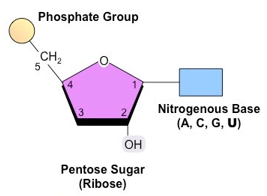
What is an RNA Nucleotide.
DNA Nucleotide 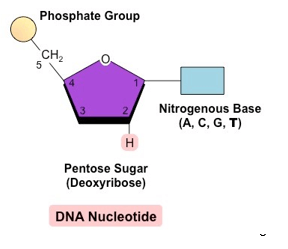
When categorizing clinical cleanliness a stethoscope is an example of this.
What is a noncritical item.
•Critical Items – must be sterile because they will be used inside the body, and penetrating sterile tissues
•Semi-critical Items – they may contact mucous membranes or nonintact skin but do not penetrate tissues
When the host's defenses are compromised these bacteria or microbes can cause infection.
What is an Opportunistic Pathogen.
Antigens produce a response in this system of the human body.
What is the Immune system.
_______ is the fundamental element of life.
What is Carbon.
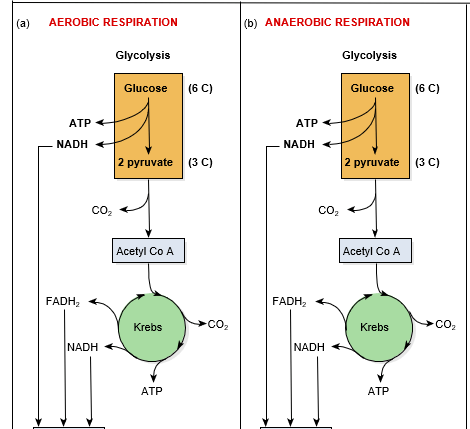 The end point of glucose catabolism is.
The end point of glucose catabolism is.
What is Electron Transport Chain.
Glycolysis > Acetyl CoA > Pyruvate > Krebs Cycle
..... > Electron Transport Chain
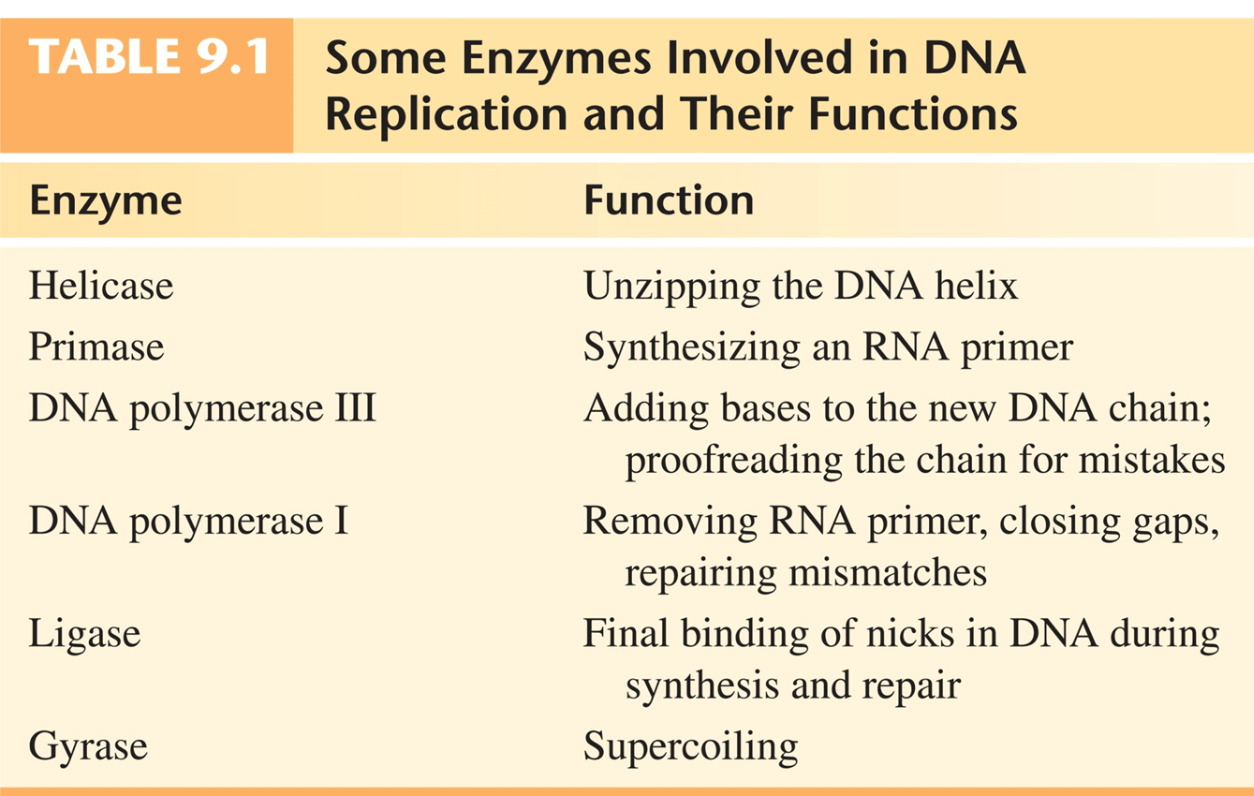
The enzyme that unzips the DNA.
What is Helicase.
Machinery required to denature proteins, and destroy membranes including DNA through moist heat.
What is an Autoclave.
The acronym that is used for pathogens that infect during pregnancy.
What is STORCH.
Syphilis, Toxoplasmosis, Other diseases (hepatitis B, AIDS and chlamydia), Rubella, Cytomegalovirus and Herpes simplex virus
This type of cell matures in the thymus gland and has three specializations including: helper, cytotoxic, and memory.
What is T-cells.
List the 4 biological macromolecules.
What is Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids.
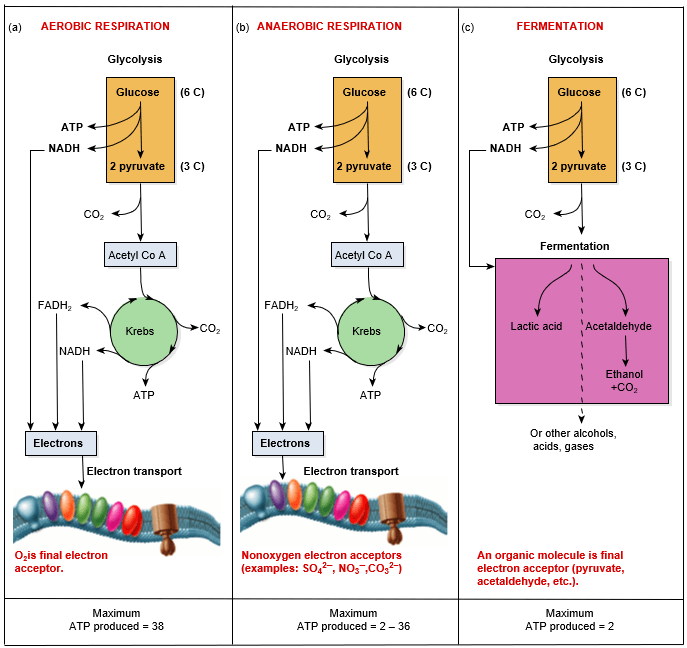
The number of ATP produced through aerobic cellular respiration.
What is 38 ATP.
Give the mRNA codons for the following sequence.
TAC CAG ATA
What is AUG GUC UAU.
mRNA transcripts include the following code:
Adenine - Uracil; Thymine - Adenine; Guanine - Cytosine
Lysol is an example of the germicidal category.
What is Phenolics.
Phenolics - Disrupt cell walls and membranes and precipitate proteins
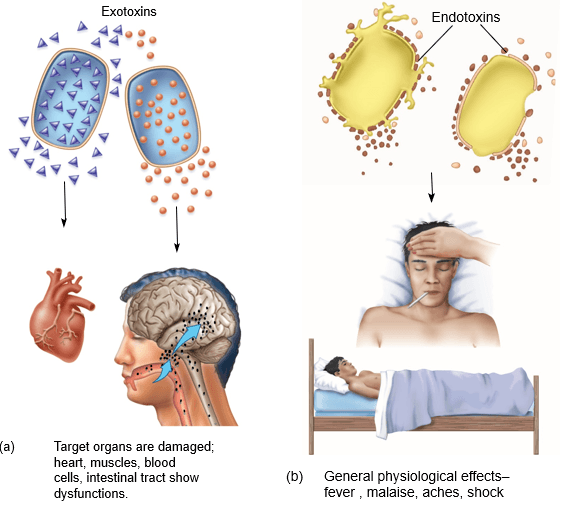
The general effects of this bacterial toxin results in fever, malaise, aches, and shock.
What is Endototoxins.
Cytokines (chemical mediators) are needed in the proliferation of this cell.
What is B-cells.