Substances that nonfermenters fail to ferment in traditional media
What are carbohydrates?
The disease most commonly associated with newborns passing through a birth canal infected with Neisseria gonorrhoeae
What is ophthalmia neonatorum?
NAD and hemin, two requirements necessary for Haemophilus influenzae to grow, are most commonly known by these terms
What are X and V factors?
Method by which Bordetella pertussis is spread?
What is respiratory droplets?
Common causative agent of pharyngitis that is universally susceptible to penicillin
What is Group A streptococcus?
Causative agent of pseudomembranous colitis.
What is Clostridium difficile?
The yeast most commonly found in a clinical laboratory and is germ tube positive
What is Candida albicans?
Causative agent of chicken pox
What is Varicella zoster?
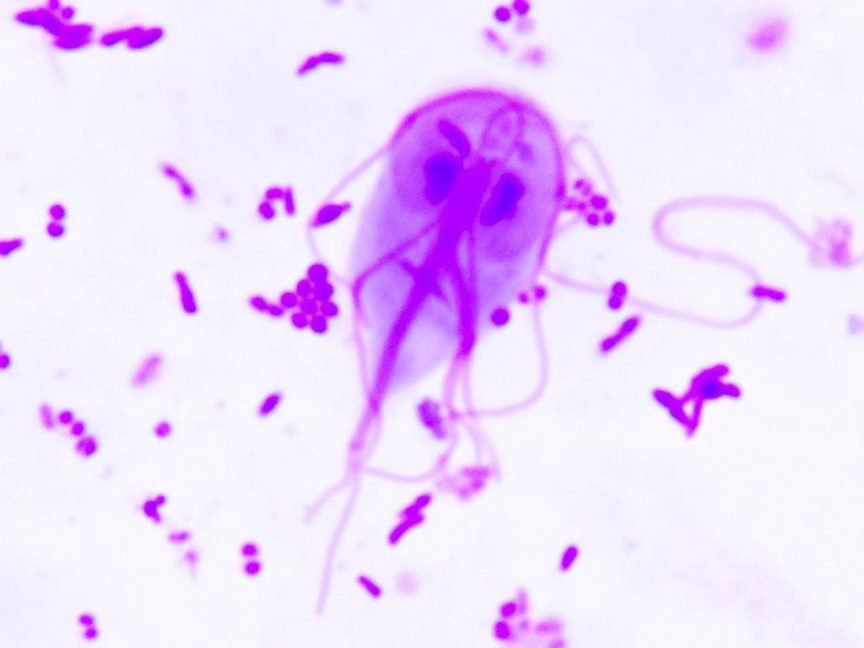
What is Giardia duodenalis?
This organism is a common cause of pulmonary disease among individuals with cystic fibrosis
What is Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
All Neisseria spp. possess all of the following characteristics but this one: oxidase positive, catalase positive, motile and aerobic
What is motile?
Tiny pleomorphic gram negative rod that does not grow on sheep blood agar and has "mousy" odor
What is Haemophilus influenzae?
The following are biochemical characteristics of Vibrio spp., except for this one: ferments glucose, is halophilic, is oxidase negative and reduces nitrates to nitrites
What is oxidase negative?
Antibacterial activity is significantly greater with two antibiotics used together than if the agents were used alone.
What is synergism?
A gram positive rod that demonstrates double zone hemolysis on an anaerobic sheep blood plate
Fungi that cause infection in skin, hair and nails.
What are dermatophytes?
Means by which hepatitis is spread
What is blood and body fluids?
Parasite seen in this biopsy of an arm nodule
What is Trichinella spiralis?
The nonfermenter not included in the list of the majority of isolates routinely seen in clinical laboratory: Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, Pseudomonas putida and Acinetobacter.
What is Pseudomonas putida?
The most likely organism when intra- and extracellular gram negative diplococci are seen on a CSF gram stain
What is Neisseria meningitidis?
What is satellitism?
The causative agent of undulant fever
What is Brucella?
On a breakpoint panel, how the result is interpreted when there is growth in both wells
What is resistant?
An organism that grows only in the absence of molecular oxygen
What is an obligate anaerobe?
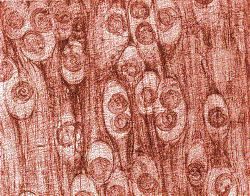
Specimen taken from an infected nail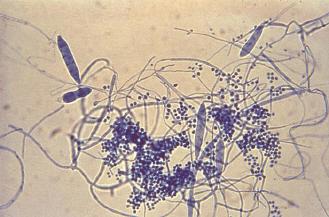
What is Trichophyton mentagrophytes?
Type of cancer is associated with human papilloma virus (HPV)?
What is cervical cancer?
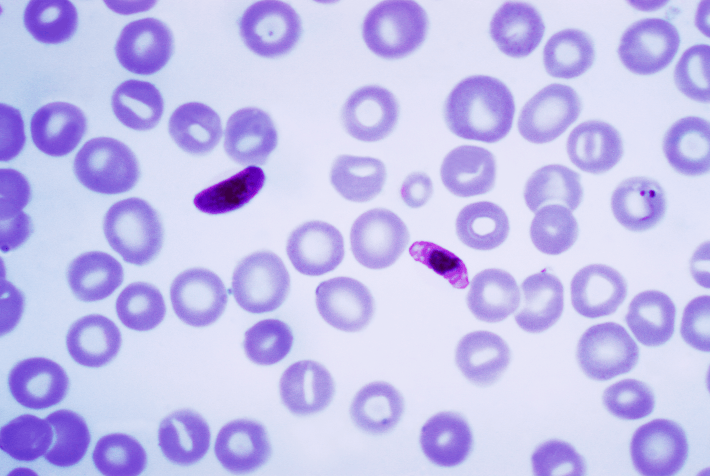 The plasmodium species seen here:
The plasmodium species seen here:
What is falciparum?
The characteristic from the following list that is not true of Pseudomonas: oxidase positive, indole positive, thin gram-negative rods, resistant to many antibiotics
What is indole positive?
35° C and 3% to 5% carbon dioxide
What are the conditions under which Neisseria gonorrhoeae culture be incubated?
All of the following are all characteristics of the HACEK group of organisms except for this one: normal oral flora, cause endocarditis, gram positive rod and possess fastidious nutritional requirements.
What is gram positive rod?
The virulence factor associated with Haemophilus spp. plays the most significant role in the invasiveness of the organism?
What is the capsule?
The patient’s infecting organism is likely to require the maximum amount of antimicrobial or more than can be achieved when this susceptibility result is reached.
What is an intermediate MIC or zone size?
Growth on the anaerobic BBE plate shows dark brown colonies that stain as gram-negative coccobacilli
What is Bacteroides fragilis?
This fungus grew in a sputum from a cave explorer.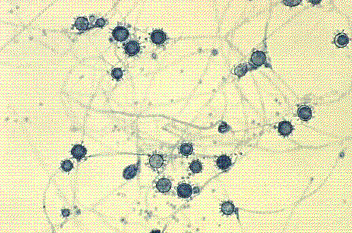
What is Histoplasma capsulatum?
Most commonly isolated virus from children with gastroenteritis
What is Rotavirus?

What is Schistosoma mansoni?
The pigment that is only produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa
What is pyocyanin?
The way Neisseria meningitidis is most commonly is spread
What is respiratory droplets?
A fastidious gram negative rod is isolated frequently from a human bite wound whose colonies can pit the agar and possess a chlorine bleach-like odor.
The name of the organism that is responsible for “summer diarrhea” in Japan?
What is Vibrio parahaemolyticus?
The lowest antibiotic concentration to inhibit the growth of an organism
What is an MIC (minimal inhibitory concentration?)
The appearance of Clostridium perfringens colonies on egg-yolk agar
What is off-white precipitate around the colonies?
Specimen taken from a scaly patch on a leg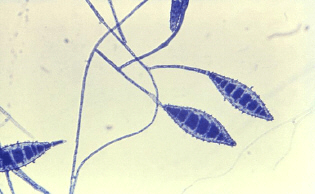
What is Microsporum canis?
Requirement for viruses to be able to replicate
What is be inside a living cell?
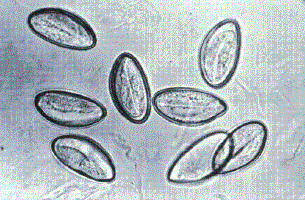
What is pinworm (Enterobius vermicularis)?
The single situation when Stenotrophomonas maltophilia typically produce disease
What is nosocomial?
In a carbohydrate substrate test, this gram-negative diplococcus produces acid only from glucose.
What is Neisseria gonorrhoeae?
The organism represented by the "K" in HACEK?
What is Kingella?
What is Campylobacter?
The most critical step in any susceptibility test
What is inoculum preparation?
The anaerobic gram negative rod that characteristically is long, slender and has pointed, tapered ends?
What is Fusobacterium?
This organism was isolated from a diabetic patient with a sinus infection and revealed wide sparsely septate (aseptate) hyphae without rhizoids.
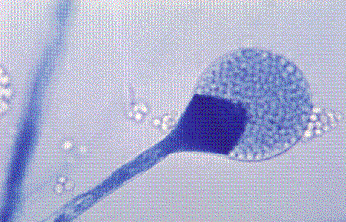
What is Mucor?
The visual changes produced in an infected cell by a virus
What is the cytopathic effect?
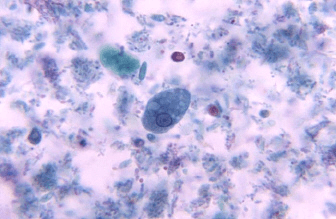
What is Entamoeba histolytica?