What does dematiaceous mean?
darkly pigmented produce melanin
What organism is this? How are the macroconidia different from the other spp.? How are the macroconidia described?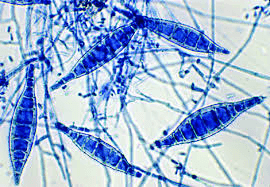
Microsporum canis (tinea capitis)
Thicker cell walls
multicelled, pointed, thick spiny (echinulate) wall with cross-septations
What is this organism? What disease does it cause? Where is it found? Who does it infect? What is its unique morphology called?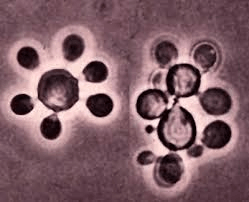
Paracoccidiodes brasiliensis
progressive, subacute to chronic granulomatous infection
primarily Central and south america
HIV patients
mariner's wheel or Mickey mouse cap
What organism is this? What does it cause? What morphology does it have? What color reverse does it have? 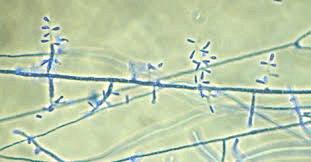
Trichophyton rubrum
tinea capitis
birds on a fence
cherry red reverse
What are the differences between arthroconidia, microconidia, and macroconidia?
arthroconidia: fragmentation of fertile hyphae
macroconidia: large fruiting structures
microconidia: small fruiting structures
What do cutaneous mycoses infect?
skin hair and nails
What organism is this? What disease does it cause? Who does it infect?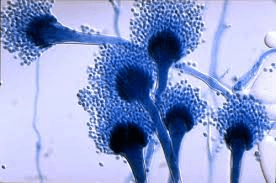
Aspergillus fumigatus
death in immunocompromised
What organism is this? What disease does it cause? What are two key features of this fungi? What are the microconidia described as?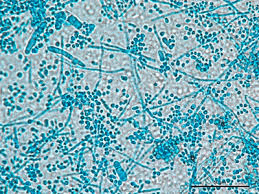
Trichophyton mentagrophytes
Tinea capitis
perforates hair and is rapid growing
grape-like clusters
What organism is this? What disease does it cause? Who does it normally infect? What is the second most common species of it? How do you tell them apart?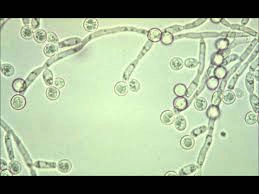
Candida albicans
Thrush leading to systemic infections
Babies and immunocompromised
C. krusei
albicans is large and krsuei is small budding yeast
What does dimorphic mean in relation to fungi?
mold at room temperature
and yeast at body temperature
What are ascospores?
contained in a saclike structure (ascus)
What organism is this? What disease does it cause? How is it spread? Where is it commonly found?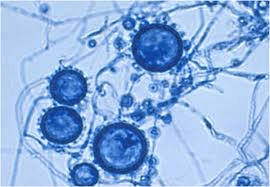
Histoplasma capsulatum
Cave or spelunker's disease (Reticuloendothilial cytomycosis) darlings disease
Inhaling spores from dried chicken or bat excrement
North American River basin (St. Lawrence, Ohio, Mississippi, and Missouri river valleys)
What organism is this? What disease does it cause?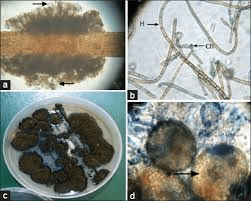
Piedraia hortae
black piedra
What organism is this? What disease does it cause? What is it morphologically referred to as? 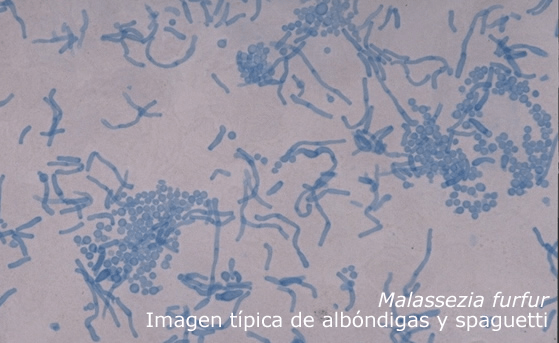
Malassezia furfur
tinea versicolor (dandruff possibly)
spaghetti and meatballs morphology
What are rhizoids?
little anchors that make the fungus harder to kill
What organism is this? What is the pacman looking thing? 
pseudallescheria boydii
sexual structure: cleistothecia containing ascospores
What organism is this? Who does it infect?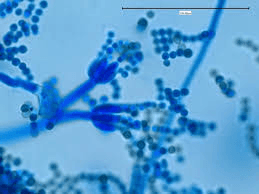
Penicillium marneffei HIV patients
What organism is this? What disease does it cause? Who is most likely to get it? How are its macroconidia described?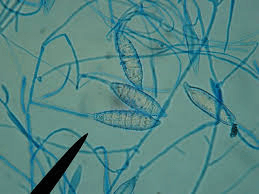
Microsporum gypseum
tinea capitis (dermatophytes)
kidney transplant patients and immunocompromised
abundant with long and rounded tips, echinulate wall with less thick septations
What is this organism? What does it cause? Where is it found? What causes the distinctive appearance? What saying do we have about this culture and why?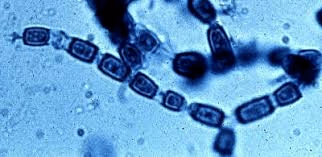
Coccoides immitis
Valley Fever, or spherule form (non-yeast forming) can cause Sweet syndrome on skin
endemic in Southwest US
hyphae are delicate and break up into barrel-shaped arthroconidia
Fluffy and white keep the lid tight! Highly infectious!!!
What does tinea capitis affect?
Favosa?
Barbae?
Corporis?
manuum?
unguium?
cruris?
pedis?
imbricate?
capitis: head
Favosa: head distinctive pathology
barbae: beard
corporis: body (glabrous skin, esp. hairless)
manuum: hand
unguium: nails
cruris: groin
pedis: feet
imbricate: body (distinctive lesion)
What organism is this? What does it cause? What patients are especially susceptible? What are the macroconidia typically described as? 
Fusarium
high fiver with disseminated skin lesions
bone marrow transplant patients
canoes or bananas
What organism is this? What disease does it cause? 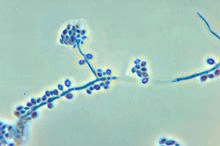
Sporothrix schenckii
rose pickers disease
What diseases does it cause? What does its yeast form look like? What is its morphology described as in mold form?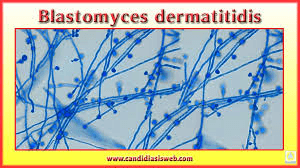
Blastomycosis: Fulminant infectious acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) OR Gilchrist's disease OR Chicago disease
yeast form single bud attached by broad base
lollipop structure
What organism is this? What disease does it cause? Where does it show up on the body?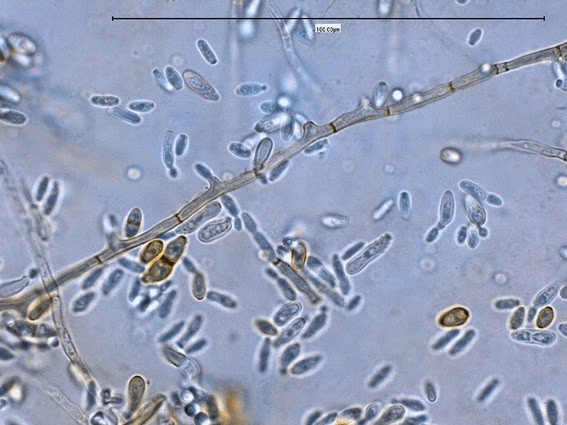
Hortaea werneckii
tinea nigra
soles of feet and palms
What organism is this? What does it cause? If it is in CNS what do you do? What animal carries it? What reagent do you use to ID it? How do you tell it apart from Candida albicans?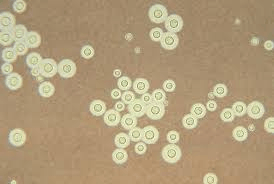
Cryptococcus neoformans
meningitis, pneumonia, septicemia
take it to the hood
pigeons
India ink
Capsule in neoformans