Although scientific experiments and other kinds of investigations can be very different, they all start the same way with this step.
What is forming or asking a question?
Put the states of matter in order from most tightly packed to least tightly packed particles. (Density)
Solid, Liquid, Gas
What is the difference between potential energy and kinetic energy?
Potential Energy: stored energy that an object has because of its position or condition.
Kinetic Energy: Energy an object has because of motion.
Heat always flows in this direction.
What is from the hot object to the colder object?
Raoul threw a ball into the air and watched it go up. Then it started to fall back toward him. What force caused the ball to start to move downward?
gravity
Students look out a window for 5 minutes. They record the number, the type, and the color of vehicles that pass. What skill are the students using?
They are making observations.
What is the difference between a chemical change and a physical change?
Chemical change: cannot be changed back. changes a substance or material into a new one.
Physical change: can be changed back. Only changes appearance or state, still the same substance or material.
The sun gives off light energy. What other forms of energy does it give off?
Thermal energy
Heat will flow from one object to another until this happens.
What is until they are the same temperature?
What is the difference between a balanced and unbalanced force?
Unbalanced forces cause motion, balanced forces do not.
What is the difference between evidence and an opinion?
Opinions are beliefs or judgements that are not based on facts.
Evidence is information that is collected, such as measurements or observations.
What condition has the greatest effect on how quickly a substance changes from one state of matter to another?
Temperature
What happens when something that is has a positive charge comes near something that has a negative charge?
It attracts. Because opposite charges attract.
Name and describe the 3 types of heat transfer.
Conduction: heat transfer through touching.
Convection: heat transfer through the movement of air or water.
Radiation: heat transfer through space.
Gravity is a force that pulls objects toward Earth's center. Which claim tells how the gravitational force on a 1-kg block of wood compares to the gravitational force on a 5-kg block of steel, if both are on the ground?
The force exerted on the steel block is greater than the force exerted on the wooden block.
What is always an important part of an EXPERIMENT?
identifying and controlling variables
What are the 3 conditions that speed of dissolving.
Temperature of water (hot water)
Stirring
Making the solid into smaller pieces (crushing)
What is the energy transformation that occurs when a fan is plugged into a wall?
electrical energy into mechanical energy or energy of motion
When this is on the circuit is closed allowing electricity to flow. When this is off the circuit is open stopping the flow of electricity.
What is a switch?
What do you need to know to find the speed of an object?
Distance and time
Name and describe 3 different types of scientific investigations.
1. Making observations: use your five senses to observe the natural world.
2. Making models: good for when things are too big, too expensive or too far away.
3. Experiments: control for variables. Change only one thing!
Describe the properties of each state of matter. (Shape, volume, and mass).
Solid: Definite shape, volume, and mass
Liquid: Definite volume and mass. Can change shape.
Gas: Definite mass. Can change shape and volume.
Name as describe the 6 forms of energy we reviewed in class for double the points.
Light energy: the energy we can see as light.
Sound energy: energy we can hear. Comes from vibration.
Mechanical energy: the total potential and kinetic energy. The energy of motion
Chemical: potential energy that is released by a chemical reaction.
Thermal: the total kinetic energy of the particles. Has to do with heat.
Electrical: the energy caused by the movement of electrons.
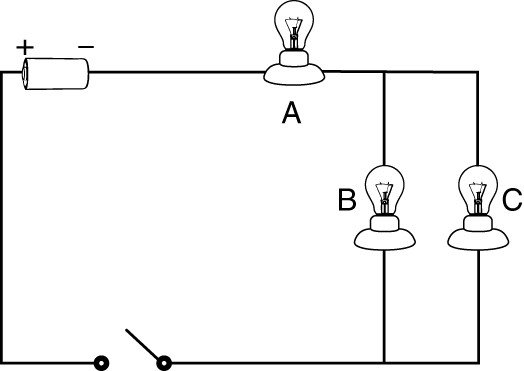
When the switch is closed, and light B goes out this will happen to the other light bulbs because it is this type of circuit.
Light bulbs B and C will stay lit because it is a parallel circuit.
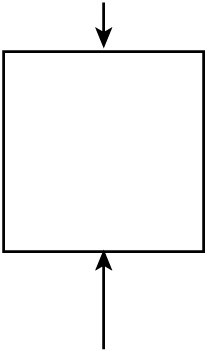
Arrows represent the forces applied to an object. A longer arrow means greater force. Draw an object with two forces acting on it that move upward.