How do enzymes work?
They stabilize transition products to lower activation energy
Where does glycolysis occur
In the cytoplasm
What is the role of chlorophyll in photosynthesis?
When light strikes chlorophyll, it excites chlorophyll's electrons, releasing them to move through the electron transport chain
Which atoms are present in 1.) Carbohydrates; 2.) Lipids; 3.) Proteins; 4.) Carbohydrates
Carbs: C, H, O
Lipids: C, H, O
Proteins: C, H, O, N (sometimes S)
Nucleic Acids: C, H, O, N, P
Definition of Apoptosis
Organized, programmed cell death
Describe two types of enzyme inhibition
Competitive inhibition: inhibitor binds to active site. Non-competitive inhibition: inhibitor binds to allosteric site, causing active site to change shape and lose affinity for substrate.
Oxygen consumption would increase, since more electron flow would be required to maintain the H+ gradient. ATP production would decline, since the H+ ions could cross into the mitochondrial matrix without passing through ATP synthase
Why do the "light independent reactions" still mostly happen during the day?
They require ATP and NADPH, which are produced by the light-dependent reactions
Describe the endomembrane system. Include the roles of at least 3 organelles
Proteins are made by bound ribosomes in rough ER, sent to the Golgi for distribution. Golgi forms vesicles which merge with the cell membrane for export, or with lysosome for digestion.
What are spindle fibers, and what is their role in the cell cycle?
Spindle fibers are long protein "cables" that enable sister chromatids to separate to opposing poles of the cell during mitosis. They are also important for the process of cytokinesis
An exergonic process such as ATP hydrolysis or the oxidation of an electron carrier is used to drive endergonic processes like building large, complex molecules from simpler ones.
Why is lactic acid produced when oxygen is not present?
Fermentation must be used to supply NAD+ to glycolysis, which is how ATP is generated in the absence of oxygen
What is the role of Rubisco in the Calvin Cycle?
Rubisco performs "carbon fixation" by attaching inorganic CO2 from the atmosphere to an organic molecule (RUBP) in the plant.
Describe the molecular basis of cohesion, and explain how cohesion leads to at least one physical property of water.
Hydrogen bonding between water molecules causes them to be attracted to each other, resulting in surface tension.
How does the amplification step occur in cell signaling
Any of the below are correct
1.) Activated kinases can phosphorylate multiple enzymes (phosphorylation cascade)
2.) A secondary messenger can activate multiple kinases
3.) A signal transduction cascade can run multiple times after an initial activation
Explain why high substrate concentration is can overcome competitive inhibition, but not non-competitive inhibition
high substrate concentration means there is a greater likelihood that a substrate, and not a competitive inhibitor, will bind to the enzyme's active site. This has little effect on non-competitive inhibition because if the active site is "shut down" by a non-competitive inhibitor, the substrate cannot bind, no matter how much is present.
What is the purpose of electron flow in the electron transport chain
to pump hydrogen ions (protons) into the mitochondria's intermembrane space, creating electrochemical gradient that will later be used to power ATP synthase
Describe the electron transport chain in photosynthesis
(1) When light strikes the chlorophyll in photosystem 1, it donates an electron to NADP+, reducing it to NADPH. (2) The electrons lost by PS1 chlorophyll are replenished by light striking PS2 chlorophyll. (3) the electrons lost by PS2 chlorophyl are replenished by H2O being stripped of electrons and converted to O2 by PS2. (4) Electron flow from PS2 to PS1 powers an H+ pump that pumps H+ ions into the thylakoid, creating a concentration gradient (5) These ions flow down the concentration gradient into the stroma through ATP synthase, generating ATP. In the end ATP and NADPH are produced, which are necessary for the Calvin Cycle.
What is polarity? How is polarity important in biological systems (give 2 examples)
Polarity is an uneven distribution of charge or partial charge in a molecule. Examples include:
-Cell membrane has nonpolar interior and polar exterior - only permeable to nonpolar
-Proteins and nucleic acids rely on polarity to form their shapes (through hydrogen and ionic bonds)
-Water's polarity enables its properties, including cohesion, adhesion, and its ability to dissolve polar molecules
Role of p53
P53 checks DNA for damage during G1. If there is damage, P53 initiates a signaling cascade that leads to cell cycle arrest (G0), preventing the cell from replicating
(1) shape (2) negative charge and/or polarity
What is the "purpose" of the krebs (citric acid) cycle?
To "charge up" the electron carriers NAD+ and FAD to NADH and FADH2, so that they can donate electrons to the electron transport chain
Why are ATP and NADPH necessary for photosynthesis?
They transfer energy from the light-dependent reactions to the calvin cycle
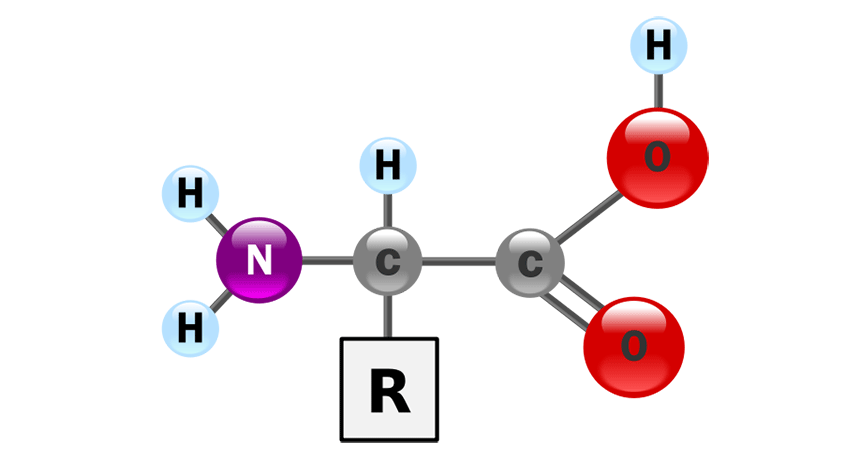
Describe an amino acid, and explain how the properties of amino acids lead to the primary, secondary, and tertiary structure of a protein.
One end is NH3 (amino group), one end is COOH (carboxyl group). In the middle is a variable R-group. COOH binds to NH3 in covalent "peptide" bond to form the primary structure. Hydrogen bonds between backbone forms secondary structure. Interactions between R-groups (ionic, covalent, hydrogen) form tertiary structure
All phases and sub-phases of cell cycle, including description
1.) Interphase: (G1- organelles are duplicated. S [synthesis] - DNA is duplicated. G2 -Duplicated DNA is double checked)
2.) Mitosis: (PMAT) - (Prophase - DNA condenses from spaghetti to chromosomes, Metaphase - Chromosomes line up in middle of cell; Anaphase - sister chromatids separate and travel to opposite sides of cell; Telophase - Nuclear envelope reforms)
3.) Cytokinesis: Cell divides