Behavioral and cognitive process of selectively concentrating on a single thing while ignoring other things.
What is attention?
Memory is static, true or false?
FALSE
Founder of Cognitive Psychology.
Who is Ulric Neisser?
What is social psychology?
A bias that occurs when we focus on information that confirms existing beliefs.
What is confirmation bias?
The brain's ability to attend to two different things at the same time.
What is divided attention?
Autobiographical memories, stories.
What are episodic memories?
The ability to produce and comprehend, spoken and written, or signed words.
What is language?
We compare ourselves to others around us to see where we stand. We care more about the people who are close to us.
What is Social Comparison Theory?
What is a memory palace?
A memory tool. You envision your self walking around a place you know and place the numbers or objects you need to remember in odd places.
When you can focus on a single conversation in a loud room.
What is the cocktail party effect?
Acts and knowledge that we learn but don't directly involve our own experience.
What are semantic memories?
When the intended use of an object gets in the way of you seeing other potential uses.
What is functional fixedness?
Making a mistake impacts what other people think about us. Competent - more likable. Incompetent - evidence for why we don't like someone.
What is the Pratfall Effect?
Snap judgment of other people - less than 30 seconds.
Attention is limited, true or false.
TRUE
What is the difference between implicit and explicit memories?
Explicit - consciously work to remember
Implicit - unconscious remembering
Rule of thumb, strategy, mental shortcut.
What is a heuristic?
What happened in the Stanford Prison Experiment?
Students were taken into a mock prison in the basement of the psychology lab at Stanford and divided into groups of guards and prisoners. The researchers observed the behavior of the guards and prisoners and had to end the experiment early due to the mistreatment of the prisoners.
The active and conscious effort to change an attitude by sending a message.
What is persuasion?
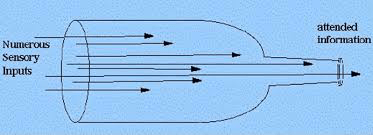
The bottleneck theory of attention suggests that we take in a lot more information than we can process.
When presented with misinformation in the form of leading questions, a witness may create false memories.
What is the misinformation effect?
Series of steps for solving a problem.
What is an algorithm?
What happened in the Asch Conformity studies?
Line tests. See if the participants would continue to give the correct answer or conform to the group.
What happened in the Milgram Obedience studies?
The research participant was set up in front of a box designed to give electric shocks to someone else. Despite hearing the person cry and scream the participant was told to continue on. The researchers were curious to see how far people would go or if they would challenge the authority of the researcher.