What is the correct order of the following objects, descending in size from largest to smallest: star, galaxy, planet, solar system, moon, universe
Universe, galaxy, solar system, star, planet, moon
what is the minimum number of seismic stations needed to find an earthquake's epicenter?
3
What type of rock is most likely to contain fossils?
Sedimentary
What is the difference between heliocentric and geocentric models of the universe?
heliocentric - sun centered
geocentric - earth centered
Which seismic waves travel slower, pressure (P) waves or shear (S) waves?
shear waves
what is the correct order of the following processes: cementation, erosion, deposition, weathering, compaction
weathering, erosion, deposition, compaction, cementation
what movement of the Earth causes night and day?
rotation
what is a barycenter?
it is the point around which 2 orbiting bodies revolve
What drives the motion of tectonic plates?
mantle convection
what type of weathering is oxidation an example of?
chemical weathering
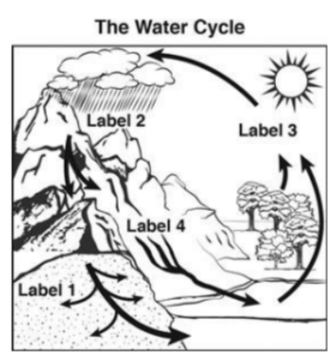 Which one shows infiltration?
Which one shows infiltration?
Label 1
What causes the seasons and how?
tilt of the axis changes the amount of direct solar energy received at different regions of the earth
what law states that the shape of planetary orbits is an ellipse?
Kepler's 1st Law
what is the name of the point from which seismic waves originate during an earthquake?
the focus
what type of soil is found in NC? Pedocal, pedalfer, or laterite?
pedalfer
What is the force that drives the water cycle?
the Sun
What is the length of one Earth's revolution?
1 year (365.25 days) to complete Earth's revolution around the Sun
What are Spring Tides and what causes them?
The highest high tide and the low tide caused by the alignment of the Moon, Earth and Sun (new moon and full moon)
Identify one piece of evidence that the seafloor is spreading
record of magnetic polarity reversal, carbon-dating of oceanic crust
warm and moist climates
30% clay, 60% silt, 10% sand?
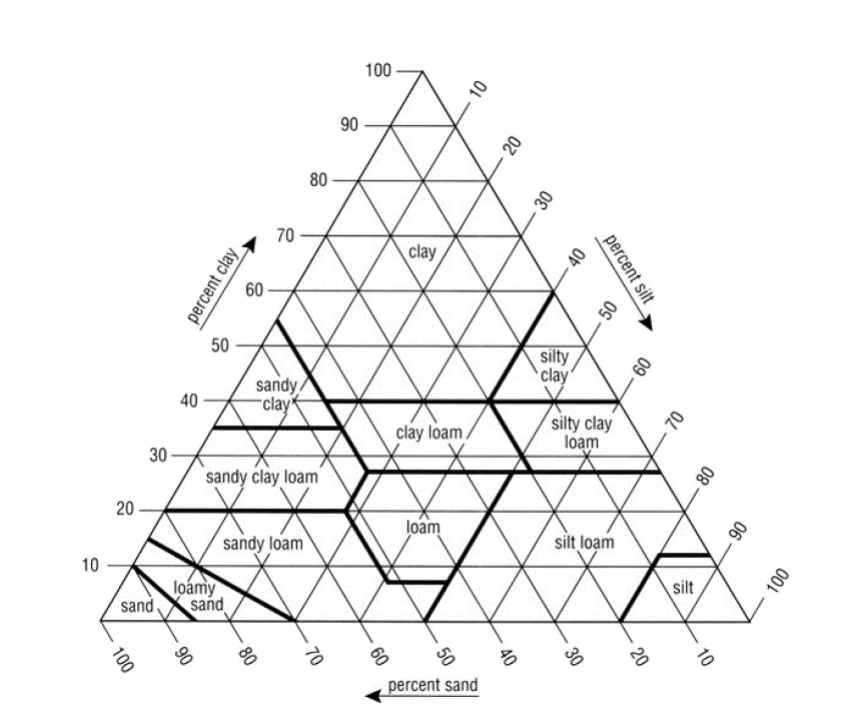
silty clay loam