This is the variable that is thought to be affected by the manipulations of the I.V.
Dependent variable
This is an individual’s unique constellation of consistent behavioral traits
Personality
This is any circumstances that threaten or are perceived to threaten one’s well-being and thereby tax one’s coping abilities.
Stress
Your text defines this as poor impulse control
self-indulgence
This is an organized collection of beliefs about the self... also called self-
schemas.
Self-concept
Widely held beliefs that people have certain characteristics because of their membership in a particular group
Stereotypes
largely unconscious reactions that protect a person from unpleasant emotions such as anxiety and guilt
Defense mechanisms
In an experimental design, this group consists of similar subjects
who do not receive the special
treatment given to the
experimental group...
The control group
A type of learning in which a neutral stimulus acquires the capacity to evoke a response that was originally evoked by another stimulus
Classical Conditioning
Behavioral responses to stress usually refer to this... or active efforts to master, reduce, or tolerate the demands created by stress
Coping
People who act out toward others who had nothing to do with their frustration are engaging in what type of defense mechanism?
Displacement
This component of Type A behavior has the strongest link to coronary disease
Anger or Hostility
The process of directing and controlling one’s behavior
Self-regulation
As we engage in this... we rely on appearance, verbal behavior, actions, nonverbal messages, and situations
Person Perception
(the process of forming impressions of others)
Passive behavior produced by exposure to unavoidable aversive events
Learned helplessness
This is EMPIRICISM.
The premise that knowledge should be acquired through observation.
This is an estimate of the proportion of trait variability in a population that is determined by variations in genetic inheritance.
Heritability ratio
These are powerful, largely uncontrollable feelings, accompanied by physiological changes.
Emotions
Unrealistic appraisals of stress that exaggerate the magnitude of one’s problems.
Catastrophic Thinking
Roughly 1 in 5 Americans do this, and approximately 16 million of them live with a chronic disease tied to the habit.
Smoking
Refers to one’s overall assessment of one’s worth as a person.
Self-esteem
These are inferences that people draw about the causes of their own behavior, others' behaviors, and events
Attributions
bonus: what are the 2 types of attributions?
This model holds that physical health is influenced by a complex network of biological, psychological, and sociocultural factors.
Biopsychosocial model

this would indicate what type of correlation...
Positive correlation
This is the common tendency to mold one’s interpretation of the past to fit how events actually turned out
Hindsight bias
This is a physiological reaction to a threat that mobilizes an organism...
Fight-or-flight response
The generation of as many ideas as possible while withholding criticism and evaluation.
Brainstorming
This can impair driving, cause various types of accidents, and increase the likelihood of aggressive interactions or reckless sexual behavior. In the long term, chronic, excessive consumption increases one’s risk for numerous health problems, including cirrhosis of the liver, heart disease, hypertension, stroke, and cancer.
Drinking
Inferences that people draw about the causes of their own behavior.
Self-attributions
This is when we seek information that support's our beliefs while not pursuing refuting information
Confirmation bias
This perspective on theories of human personality is considred the most optimistic.
Humanistic
These variables are, surprisingly, not strongly correlated to happiness.
Money, Age, Gender, Parenthood, Intelligence, and Attractiveness.
Individualism involves putting personal goals ahead of group goals and defining one’s identity in terms of personal attributes rather than group memberships.
In contrast, collectivism involves putting group goals ahead of personal goals and defining one’s identity in terms of the groups to which one belongs
This is a model of the body’s stress response, consisting of three stages: alarm, resistance, and exhaustion.
General Adaptation Syndrome
This consists of the ability to perceive and express emotion, use emotions to facilitate thought, understand and reason with emotion, and regulate emotion.
Emotional Intelligence (EQ)
Is influenced by genetic endowment, eating and exercise habits, and perhaps a set point or settling point.
Body weight
Refers to usually conscious efforts by people to influence how others think of them.
Impression Management
This is a negative attitude toward members of a group
Prejudice
To avoid being overwhelmed with information, people tend to use this type of processing, but for important decisions, they shift to a controlled version.
Automatic processing
These are emotionally charged images and thought forms that have universal meaning, according to Jung
Archetypes
The formation of new neurons
Neurogensis
Involves counteracting the natural tendencies to seek vengeance or avoid an offender, thereby releasing this person from further liability for his or her transgression.
Forgiveness
A person may be considered this if they have an inflated sense of self-importance, are sensitive to criticism, and are more likely to engage in violence
Narcissistic, a narcissist, to have narcissism
This is when people yield to real or imagined social pressure
Conformity
This involves the communication of arguments and information intended to change another person’s attitudes
Persuasion
This hypothesis states that: Strong emotions may hamper or enhance our ability to cope with stress, depending on our level of arousal and the task complexity. 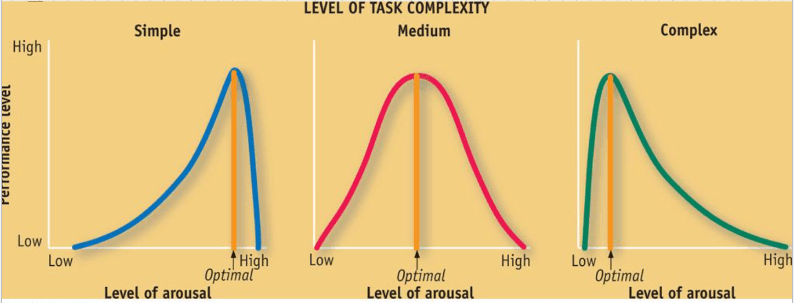
Inverted-U Hypothesis
The tendency to delay tackling tasks until the last minute.
Procrastination
This is a form of compliance that occurs when people follow commands, usually from someone in a position of authority
Obedience
This is the tendency for individuals to be less likely to provide help when others are present than when they are alone
The bystander effect