What's the difference between toxic and hazardous?
Toxic substances are poisonous and can kill/damage organisms by reacting with their cellular components to interfere with normal metabolic functions. Toxic substances are dangerous even at very low concentrations. Similarly, hazardous substances can be very dangerous but for different reasons (flammable, explosive, irritant, etc) than toxins. Also, through physical treatments (e.g. dilution, neutralization), hazardous substances can be made much less harmful.
Describe factors that result in natural variations in climate….e.g. past glacial and interglacial periods
include ocean currents (distribution of cold and warm water around Earth), ocean-atmospheric oscillations, intensity of the sun, time of year, and volcanic eruptions. Long term variability can be explained by the 3 Milankovitch cycles. The first involves the elliptical orbit stretching and shortening (100,000 years). The next cycle entails the angle of tilt of earth’s axis shifting (40,000 years). And lastly, the earth “wobbles” on the axis (26,000 years) (p. 210-213).
These non-native species can cause environmental harm when introduced to a new area, often outcompeting local species.
What are invasive species?
What groups of people are more at risk for mercury toxicity?
Children, pregnant women, elderly, the immune comprimised
What subjects does Molly tutor?
Reading, Writing, and Environmental Science
What are the two kinds of toxicity/toxicity exposure?
Acute toxicity is characterized by affecting the organism immediately from a single exposure but can potentially be reversed if swift action is taken. While chronic toxicity causes long lasting negative effects from a single, high dose exposure or lower, repeated exposures
which month had the highest precipitation?

March
This type of symbiotic relationship benefits both species involved, such as bees pollinating flowers while collecting nectar.
What is Mutualism?
Describe how mercury gets into fish
Pollution (mainly from coal plants) flows into the air, the mercury falls to Earth as rain or it just falls, then bacteria turn it into methylmercury, then it bioaccumulates and and biomagnification moves it up the food chain
What is Molly's favorite Environmental Science topic?
Evolution
Describe your bioassay lab. Points to consider: How did you measure toxicity? What was the point/term where 50% of your test samples (RIP Daphnia, let's pour one out for the homeboys) died? How do toxic substances affect different demographics?
Dose/response study – Where response includes the biological changes caused by exposure to a chemical. Bioassay is a standardized method to determine chemical toxicity. LD50 is where half of the test subjects die. The same dose of a chemical (eg: 5mg of cyanide) will affect children differently than it will affect an adult. Pregnant women and the elderly may also be affected differently.
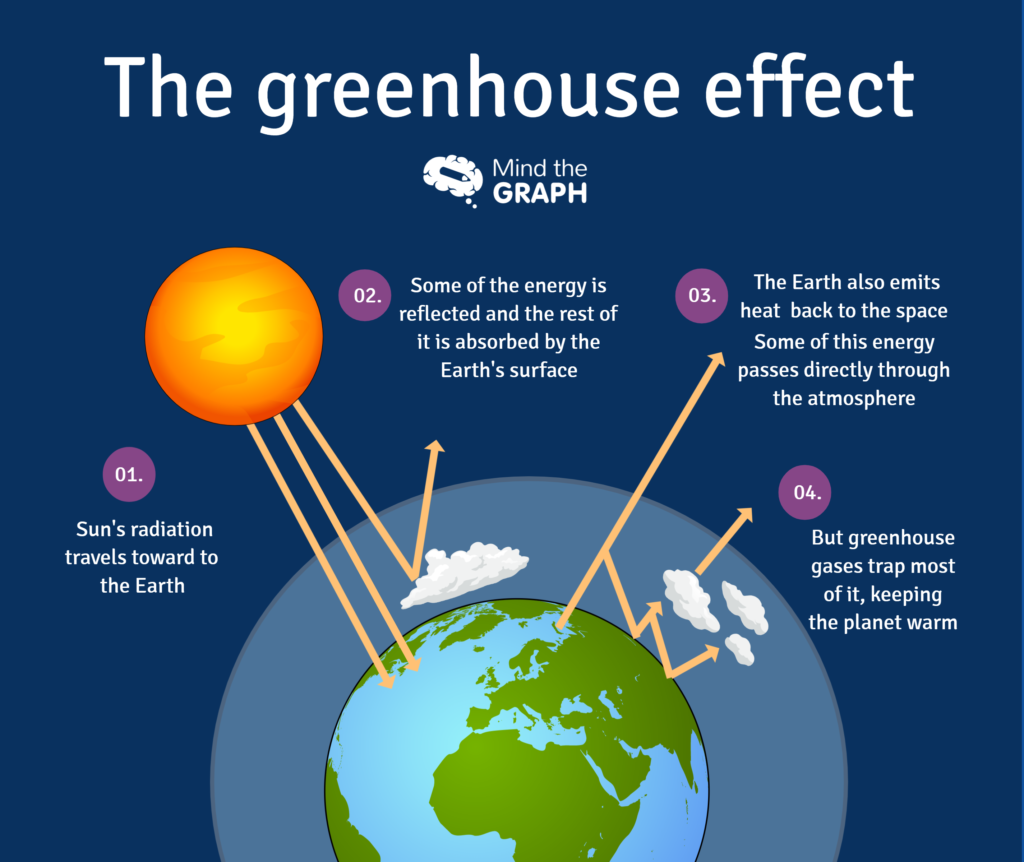
Draw a diagram illustrating the greenhouse effect
This occurs when individuals of different species compete for the same resource in an ecosystem, such as food or space.
What is interspecific competition?
What are the effects of mercury? How/why is it harmful?
Mercury builds up in fish/other organisms, leading to neurological damage, cognitive impairments, and reproductive issues in both animals and humans.
What is Molly's favorite animal?
Sloths
Describe the difference(s) between bioaccumulation and biomagnification
Bioaccumulation is defined as the selective absorption and concentration of molecules by the cells of an organism because the external environment has a higher concentration of the substance than the organism does and it cannot be excreted as fast as it is being absorbed. But biomagnification is the substance having increased concentrations in organisms in higher trophic levels than those below
list 5 effects of climate change
5 effects of climate change are (p. 219):
In 50 years there has been an 8 inch rise in global sea level from thermal expansion, melting glaciers, and melting ice sheets.
An increase in the frequency of wildfires as well as pests.
Earlier springs lead to early flowering, migration, and hotter summers from the onset of warm weather.
Heavier storms from the increased energetic atmospheric circulation.
- Cumulative costs for damaged infrastructure, lost property values, and health costs due to climate change.
These long-term changes in the Earth’s orbit and tilt are believed to be a significant factor in triggering ice ages.
What are Milankovitch Cycles?
What is the point of the Dragonfly Mercury Project?
- Find out where there are potential mercury risks.
- Improve tools for understanding and managing mercury risks.
- See how well mercury emission reduction programs and policies are working.
- Get people involved in learning about mercury.
- Spread the word about mercury issues.
What is Molly's favorite type of car?
Mazda Miata NA
Name some toxic chemicals in your household, and use info from the course to explain why or why not you'd ever be able to use completely non-toxic substances
No right or wrong answer
What are some conclusions you can draw from this graph?

Keeling curve, increase since industrial revolution from anthropogenic activity
This type of factor, such as food or disease, limits population growth more significantly as population density increases.
What is a density dependent factor?
Why does the DMP test for mercury specifically in dragonfly larvae?
Dragonflies thrive in far more arid areas than most fish and birds, who serve as researchers’ traditional mercury-carrying sample pools. Their larvae are also much easier to harvest, plentiful, and cheaper to analyze. Because of this, examining the insects are already providing new insights into the toxic contaminant.
Who are Molly's favorite F1 drivers (there are 2)
Niki Lauda and Sebastian Vettel