Property that shows how a mineral reflects light
Luster
This property is not typically useful when identifying minerals
Color
Sediment forms from this process
Weathering and Erosion
This rock type
Foliated Metamorphic
The main advantage of using renewable resources
No pollution
Property that refers to the minerals ability to scratch something or be scratched
Hardness
The hardest mineral on the Moh's Hardness Scale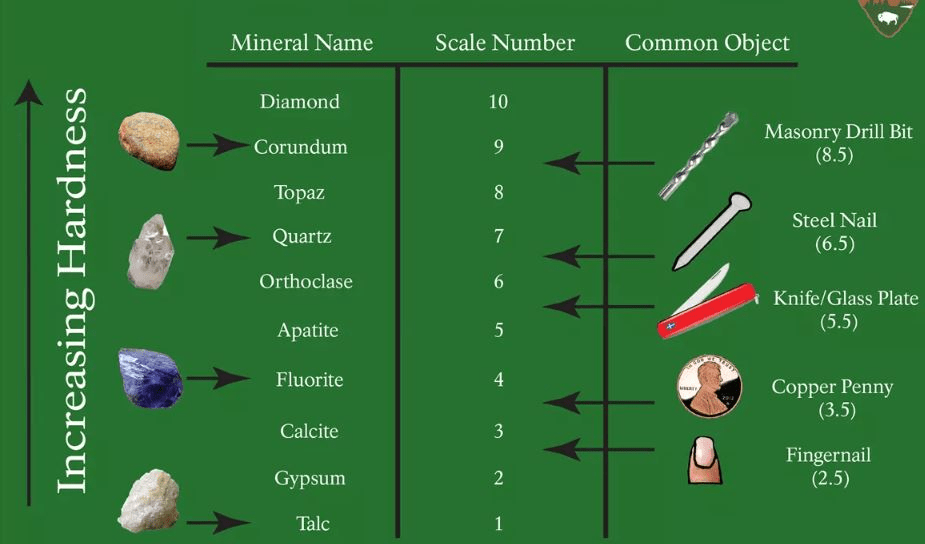
Diamond
The process that would turn any type of rock into magma
Melting
This rock type
Clastic Sedimentary
Main advantage of using nonrenewble resources
They are cheap
Property that refers the mineral in powdered form
Streak
This flat mineral has one plane of mineral cleavage
Mica
The process that forms igneous rocks
Cooling of Magma/Lava
This rock type
Intrusive Igneous
Two major disadvantages of using nuclear energy
Toxic waste and nuclear meltdowns
Property that refers to minerals breaking into jagged pieces
Fracture
This mineral has rhombohedral cleavage
The process that forms sedimentary rock
Cementation and Compaction
These three textures are related to extrusive igneous rocks
Fine, Glassy, Vesicular
Main disadvantage of using renewable energy sources
They are expensive
Property that refers to minerals breaking along a clean plane of weakness
Cleavage
This mineral fizzes when exposed to dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl)
The process that will change any rock type into a metamorphic rock
Heat and Pressure
The parent rock to Marble
Limestone
The major disadvantage to using fossil fuels
CO2 Pollution