These are the connected points of a network
What are nodes/vertices?
We generally try to achieve this when working with time-series data
What is stationarity?
This system aims to match users to new [nouns]
What is a Recommendation Engine?
What is a neuron?
Perceptrons and similar models emulate this biological entity
What is the largest O time complexity noted on the Big O table?
| O(N!) |
These connect the elements of a network
What are edges/links?
What does ARIMA stand for?
Auto Regressive Integrated Moving Average
This modeling language attempts to simply the syntax of machine learning
Patsy
A multi-layer perceptron contains an input layer, an output layer and at least one what?
Hidden layer
What two parts of a Big O notation do we drop when calculating time complexity representative of that function?
Constants and Non-Dominant Terms
Ex. O(N^2 + 2N) = O(N^2)
What is shortest path?
This is the fastest route between two non-adjacent nodes.
What is Heteroscedasticity?
Heteroscedasticity (also spelled heteroskedasticity) refers to the circumstance in which the variability of a variable is unequal across the range of values of a second variable that predicts it
[DAILY DOUBLE] Which non stationary time series displays Non-constant covariance?
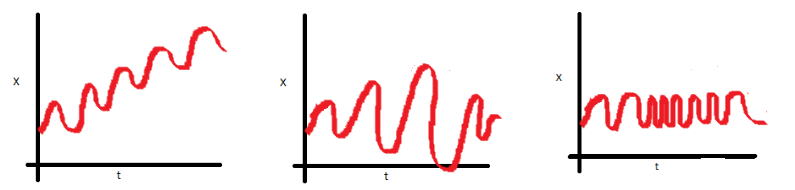
The 3rd
This is one method by which we iteratively optimize the loss function of a machine learning algorithm.
What is Gridsearch or gradient descent?
What is the O notation for:
O(n)
What is centrality?
A measure of a nodes importance to the network
What does a Dickey Fuller Test test for?
In statistics and econometrics, an augmented Dickey–Fuller test (ADF) tests the null hypothesis that a unit root is present in a time series sample. The alternative hypothesis is different depending on which version of the test is used, but is usually stationarity or trend-stationarity.
How are Moving Average models different from Autoregressive models?
Moving average models, as opposed to autoregressive models, do not take the previous outputs (or values) as inputs, but instead take the previous error terms. We will attempt to predict the next value based on the overall average and how incorrect our previous predictions were.
What is an activation function?
Given an input, the activation function determines the output of a neural network node. In simplest terms, it is on (activated) or off (not activated) depending on the value of the input.
What is the Big O notation for:

O(N2)
Define 'robustness' in the context of network science.
Robustness is the resilience of a network to attack or change. That is, how many nodes can be removed before the whole network collapses.
What do (p,d,q) parameters mean with ARIMA
- p indicates how many prior time periods we’re taking into consideration for explained autocorrelation. Increasing p would increase the dependency on previous values further (longer lag).
- q indicates how many prior time periods we’re considering for observing sudden trend changes.
- d indicates what difference we are anticipating predicting. d=1 may cause stationarity for us; d=2 may capture exponential movements
Define the Markov Property
A random (stochastic) process has the Markov Property iff the future state of the process (t+1) depends only on the present state (t).
In the context of a neural network, what is backpropagation?
Backpropagation ("backprop") is a method for determining the gradient that is used to calculate the weights of inputs. It feeds errors back the layers of a network to 'train' the optimal weights.
Binary Search is what time complexity?
O(log N)