List the stages of mitosis
Prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase and cytokinesis
- Control points that regulate the cell cycle
What are the two types of cell cycle regulators?
Internal and external regulators
What does uncontrollable growth of cancer cells lead to?
Tumors
What are somatic cells and what are gametes? Which one undergoes mitosis?
- Somatic cells are body cells, gametes are reproductive cells
- Somatic cells undergo mitosis
Metaphase
Which checkpoint checks for cell size, growth factors and DNA damage?
G1 checkpoint
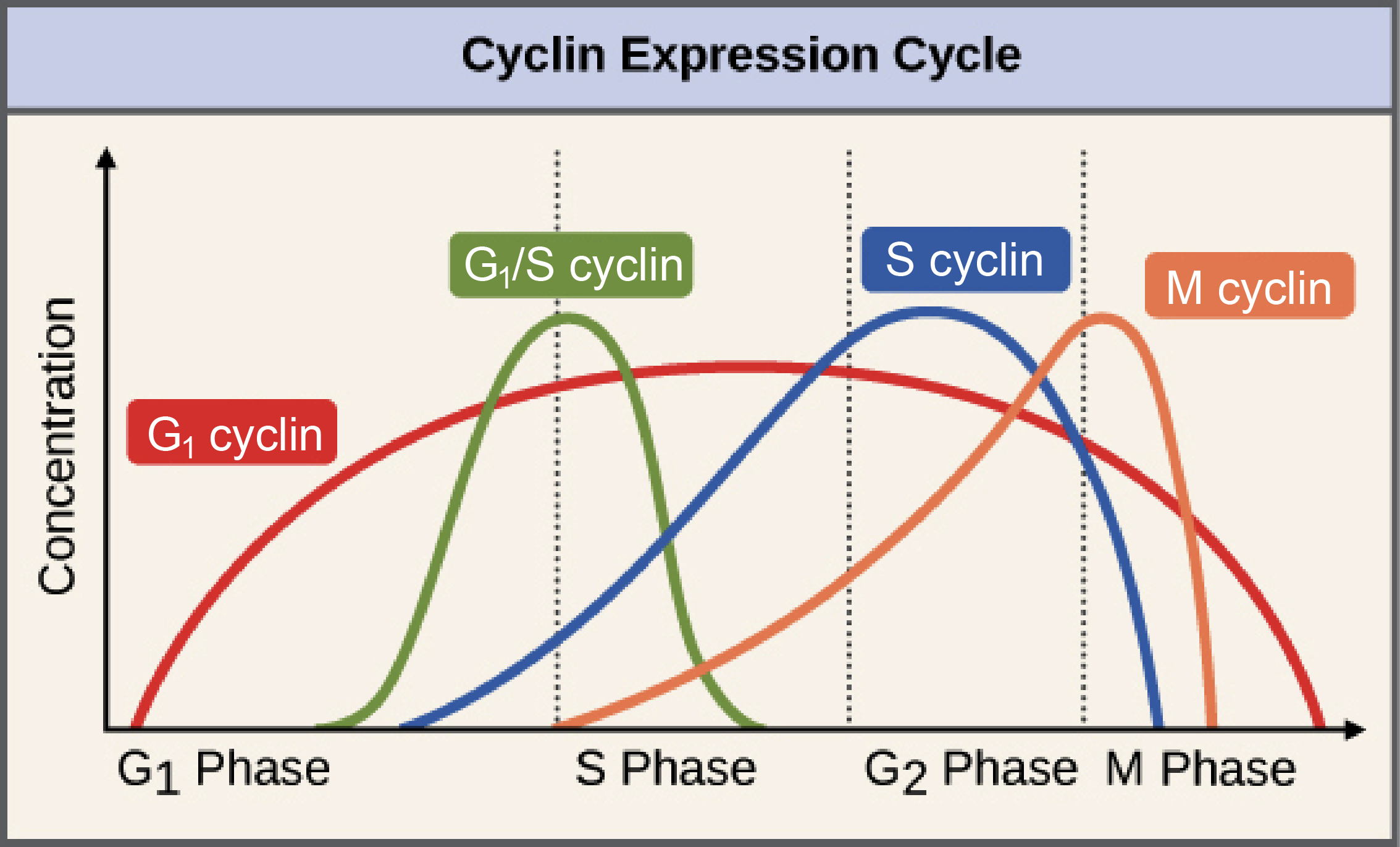 In which phase is Cyclin A at its peak?
In which phase is Cyclin A at its peak?
G2 phase
Name the two types of tumors
Benign tumor and Malignant tumor
In a somatic cell, mice have 40 chromosomes. Explain why and how many chromosomes the mice inherited from each parent
The mice inherited 20 from each since a somatic cell is 2n number of total chromosomes
In which stage do two daughter nuclei form?
Telophase
What does the G2 checkpoint check for?
DNA replication and DNA damage
Which enzymes and proteins do internal cell cycle regulators use?
Proteins known as cyclins, enzymes known as cyclin-dependent kinases
List three ways to prevent cancer
1. Do not smoke
2. Eat healthy and drink water
3. Protect your skin
You perform a karyotype on a human cell and find that it has 23 chromosomes. Is this a somatic cell or a gamete? how do you know?
This is a gamete because somatic cells have 2n number of chromosomes (46) while gametes only have 1n which would be 23
What stage is this?
Anaphase
Why would a cell go through apoptosis? (programmed cell death)
If damage cannot be repaired at the stop signal of a G2 checkpoint
What are the three types of external cell cycle regulators?
Growth factors, contact (or density) inhibition, and anchorage dependence
What is metastasis?
When cells separate from the tumor and spread elsewhere in the body
A cell has 50 chromosomes. After mitosis and cell divisiom, you find that one daughter cell has 49 chromosomes and the other has 51. Predict one way that this could happen
In anaphase, the chromatin did not separate. The microtubules could have not been long enough and didn't attach
Whats the difference between cytokinesis in plants vs animals?
Animals - A cleavage furrow appears due to a contractile ring of actin filaments
Plants - Vesicles produced by the golgi travel to the middle of the cell and form a cell plate
What does the M(spindle checkpoint) Check for?
microtubule attachment to chromosomes at kinetochores at metaphase
What is anchorage dependence?
Cells rely on attachment to other cell or the extracellular matrix to divide
What makes a cancer cell different from a normal cell?
- They don't follow checkpoints
- They divide infinitely when in culture ("immortal")
- They evade apoptosis and continue diving even w/ errors
Vinablastine is a chemotherapeutic drug often administered to patients suffering from Hodgkins lymphoma, lung cancer and bladder cancer. Vinblastine enters cancer cells and binds to tubulin, which is a protein that forms microtubules and proper formation of the mitotic spindle. The cell cycle then arrests.
A- identify two phases of the cell cycle most affected by vinblastine
B- identify the checkpoint that is most responsible for arresting the cell cycle
A - anaphase, metaphase
B - the M (spindle) checkpoint