Type of reproduction that occurs in mitosis.
Asexual reproduction (pictured on the left)
Type of reproduction that occurs in meiosis.
Sexual reproduction (pictured on the right)
The phase in which chromosomes align in the centre, or middle, of the cell.
Metaphase
Explain why chromosome replication has to occur before mitosis, during interphase.
Chromosome replication is necessary to ensure each daughter cell receives a complete set of identical chromosomes after mitosis.
Cells that divide to form eggs are germ cells.
True
The type of cells that undergo mitosis.
Somatic cells (pictured on the right)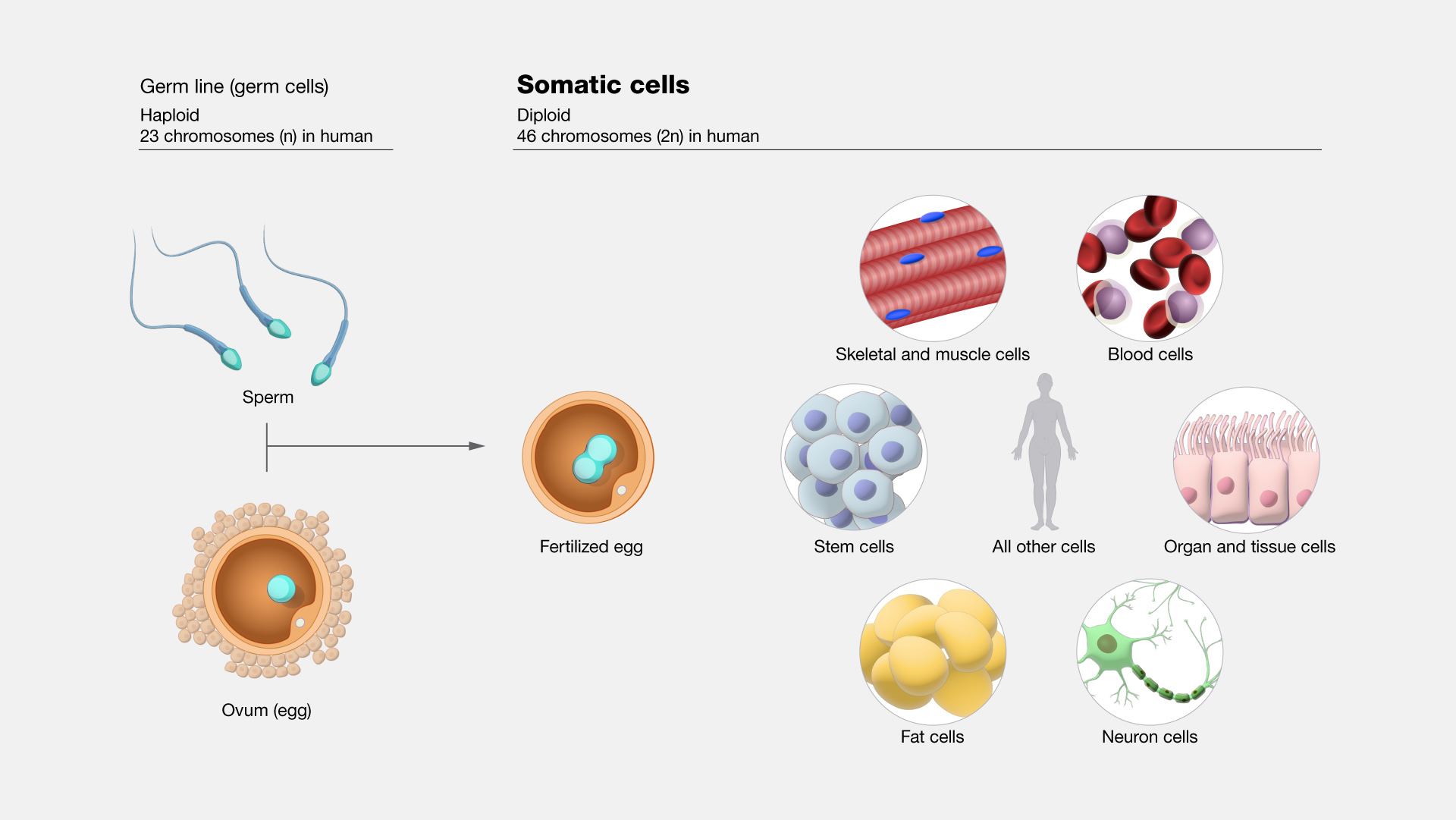
The type of cell that undergo meiosis.
Germ cells (pictured on the left)
The phase in which replicated chromosomes condense into visible structures, becoming shorter and thicker.
Prophase
Explain the differences between somatic cells and germ cells, and describe the outcomes of cell division between these two categories of cells.
Somatic cells divide by mitosis and result in two genetically identical diploid cells. Germ cells undergo meiosis, producing four non-identical haploid cells for sexual reproduction.
Cells that divide to form sperm are somatic cells.
False
(They are Germ Cells)
Centrioles duplicate and migrate to opposite poles of the cell, initiating the formation of _____.
Mitotic spindles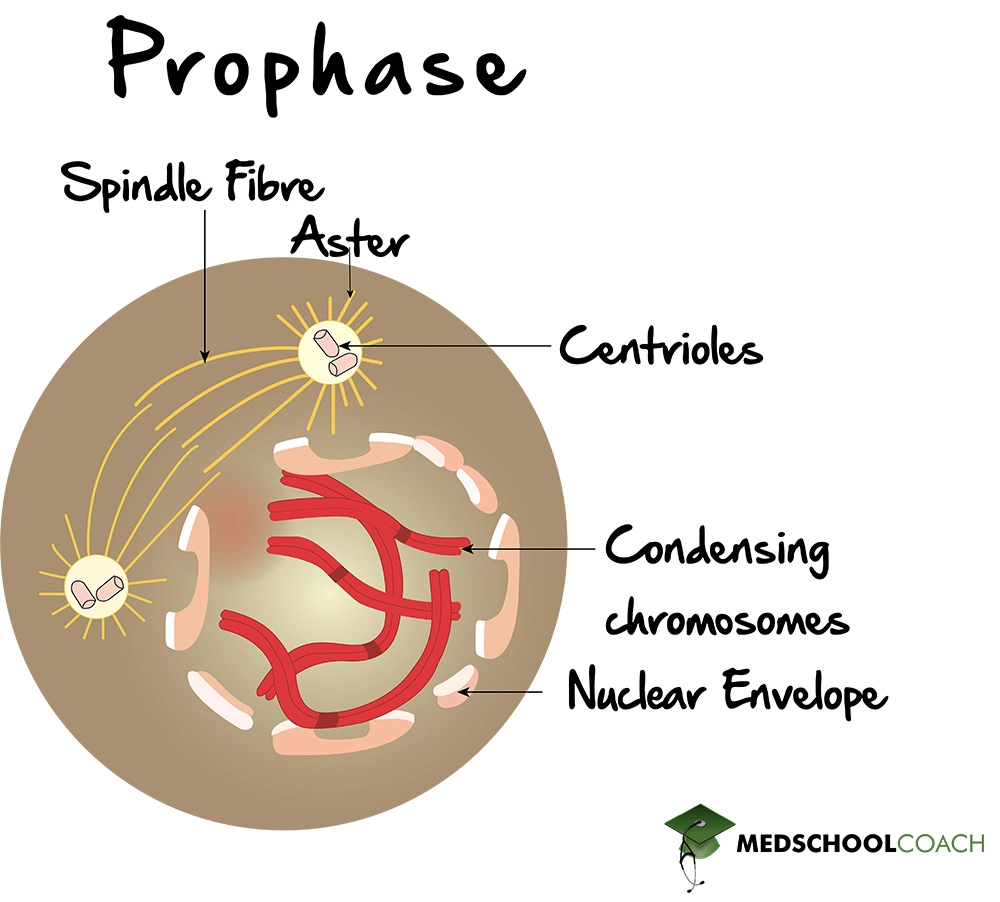
The five stages that take place in meiosis I/II.
Prophase I/II, prometaphase I/II, metaphase I/II, anaphase I/II, and telophase I/II
The phase in which the sister chromatids separate as spindle fibers, pull them toward opposite poles of the cell & ensures each pole receives an identical set of chromosomes.
Anaphase
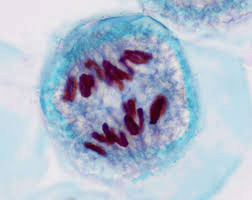
Given a micrograph of a cell undergoing mitosis, explain what is happening to the chromosomes.
Chromosomes condense, align at the metaphase plate, separate at the centromere, and move to opposite poles during different stages of mitosis.
Humans contain 22 pairs of chromosomes.
False
(23 pairs, 46 total)
After the completion of telophase which transitions into cytokinesis, each daughter cell is genetically ____.
Identical -hence "daughter" and not "sister"-
The process in meiosis that ensures genetic variation.
A crossover

The phase in which homologous chromosomes pair up in a process called synapsis, forming tetrads. This allows for crossing over, where genetic material is exchanged between homologs, increasing genetic diversity.
Early in prophase I in meiosis I:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Meiosis-Metaphase-I-58dc0b205f9b584683325d8b.jpg)
Explain why the segregation of homologous chromosomes in meiosis I leads to a reduction in ploidy.
Homologous chromosomes are separated during meiosis I, reducing the chromosome number from diploid (2n) to haploid (n), as each new cell receives only one chromosome from each pair.
Bacteria and archaea undergo mitosis.
False
(Through binary fission, they reproduce asexually.)
Occurring before the initiation of mitosis -in S-, one copy of each chromosome is duplicated in order to prepare for the formation of another daughter cell upon completion of mitosis; this is a process referred to as _______.
DNA replication
During meiosis I, the separation of homologous chromosomes permits each daughter cell to receive one chromosome from each pair, thus having transitioned the cell from diploid to __.
Haploid
The phase in which the cell grows, performs normal functions, and prepares for division. It includes G1 (growth), S (DNA replication), and G2 (preparation for mitosis)
Interphase
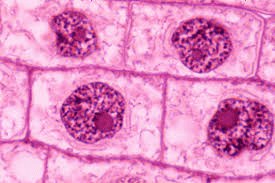
Explain why no two haploid cells that result from meiosis are alike in terms of genotype, and why this is important for offspring fitness.
Genetic variation occurs due to independent assortment and crossing over during meiosis, increasing offspring fitness by creating unique combinations of alleles that may improve survival.
Recombination happens in the Anaphase.
False.
It does not occur in Mitosis, only Meiosis.
