DNA replicates to form sister chromatids during this phase of the cell cycle.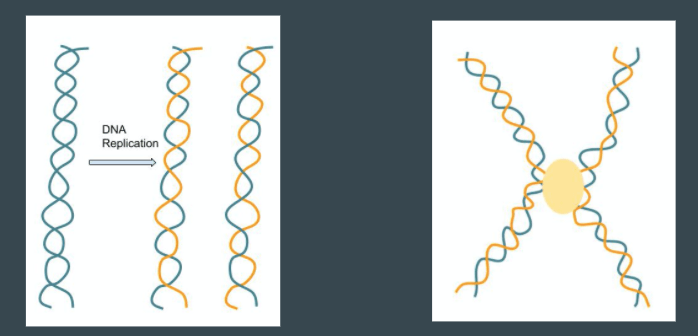
What is "S" phase?
The goal of mitosis AND the reason an organism would need to undergo mitosis.
What is to create two identical daughter cells? What is to grow and repair injury?
The goal of meiosis.
What is to make gametes (eggs and sperm)?
The phase of meiosis II shown below.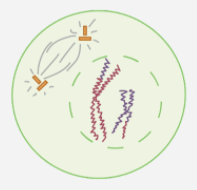
What is prophase II?
A fertilized egg splits in two and two different babies develop in a women's uterus. What type of twins is this?
What is identical twins?
This is the reason that these chromosomes are partly red and partly green.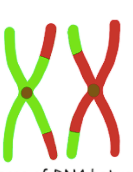
What is crossing over?
Cells grow and prepare for cell division during these two phases of the cell cycle.
What are G1 and G2?
The level of similarity between daughter cells created during mitosis.
What is identical?
What the black dot is indicating.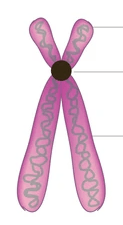
What is a centromere?
The term used to describe the amount of DNA in a somatic cell (like liver, kidney, muscle, lung, skin, etc.).
What is diploid (2n)? (Because somatic cells have two sets of chromosomes...two #1 chromosomes, two #2 chromosomes, two #3 chromosomes, etc.)
If the checkpoints of the cell cycle are not followed, cells may uncontrollably replicate with damaged or missing DNA. This disease may develop as a result.
What is cancer?
Homologous chromosome pairs line up independently of each other. This is the name of that process. 
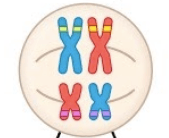
What is independent assortment?
The phase of the cell cycle in which the nucleus and DNA are divided is called this. (Note: This question is not discussing the division of cytoplasm.)
What is mitosis?
Nuclear envelope disintegrates, spindle fibers form, chromosomes condense during this phase.
What is prophase?
What the two sides of the "x" are called.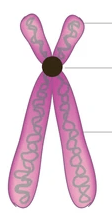
What are sister chromatids?
The term used to describe the amount of DNA in gametes (n), which contain only one set of chromosomes.
What is haploid?
White fish embryos are sometimes used in biology classes to look at mitosis for this reason.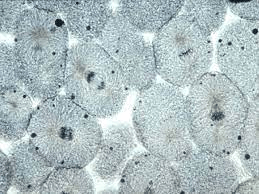
What is the fact that embryos are in rapid development and there would be a large number of cells undergoing mitosis?
This is the difference between asexual and sexual reproduction in terms of genetic diversity.
Sexual reproduction creates more genetic diversity because two parents contribute DNA to create genetically unique offspring. Asexual reproduction leads to offspring that have the same DNA as the parent.
The phase of the cell cycle when cytoplasm splits to finally form two new cells.
What is cytokinesis?
The phase of mitosis shown here.
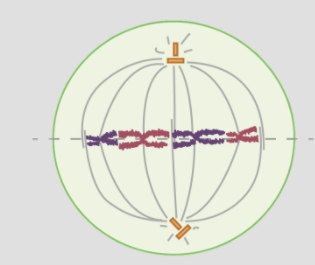
What is metaphase?
The phases of meiosis shown here.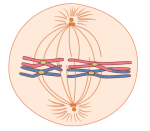
What are metaphase I and anaphase I?
When a sperm fertilizes an egg, this forms.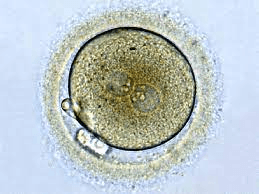
What is a zygote?
The reason for the size difference between eggs and sperm.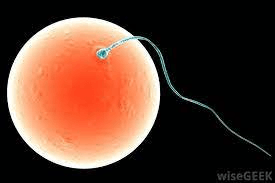
Does crossing over occur between sister chromatids?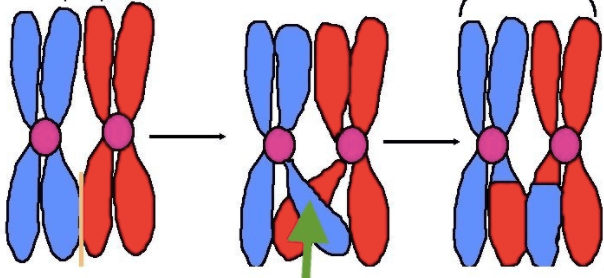
No, crossing over occurs between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes.
This is what a scientist might see if they were to look at cancer cells under a microscope.
What is many cells that are in cell division or many rapidly dividing cells. (Because cancer is caused by uncontrolled cell division.)
This phase has to do with the creation of new nuclei in two daughter cells, while this other phase has to do with the final division of cytoplasm and organelles. (Name the two phases.)
What are telophase and cytokinesis?
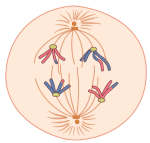
The phase of meiosis shown below AND the number of tetrads shown.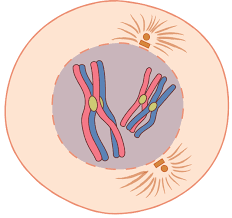
What is prophase I and 2 tetrads.
The term used for the cells that are discarded during egg production (oogenesis).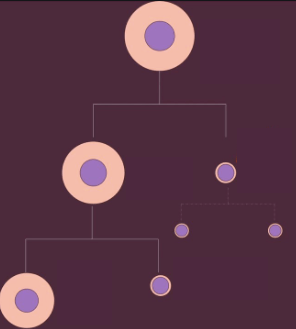
What are polar bodies?
If nondisjunction of homologous chromosomes takes place during meiosis, then the resulting gametes may have this issue. 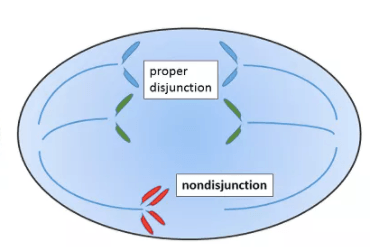
What is too much or too little DNA?
Bob has the chromosomes on the right in his reproductive organs. He creates sperm through meiosis. Does the sperm have to carry the chromosomes in the picture on the left?
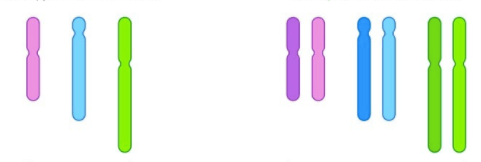
No, Bob just needs to have one purple, one blue, and one green chromosome in the sperm he creates. It doesn't matter if they are dark purple, dark blue, or dark green. Think of these as chromosome pairs #1, #2, #3. He just needs to put a #1, #2, #3 chromosome into the haploid sperm.