This is the region of a chromosome that joins sister chromatids.
What is a centromere?
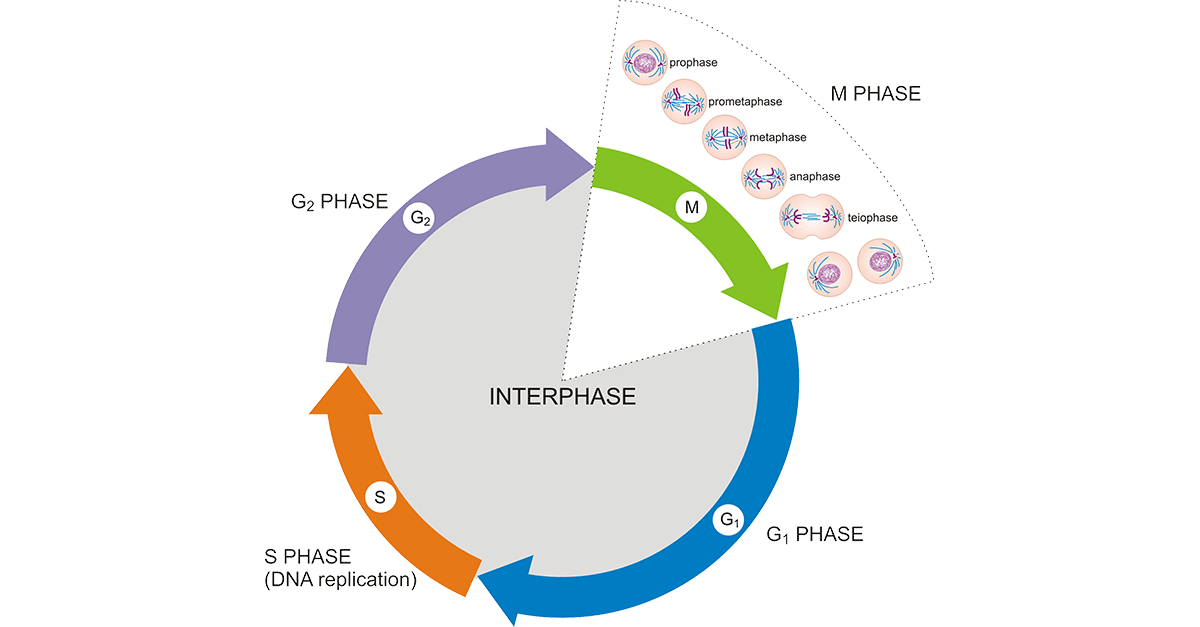
The stage of the cell cycle when a cell grows and copies its DNA.
What is interphase?
A pair of chromosomes that are similar in size and gene position, with one inherited from each parent.
What are homologous chromosomes?

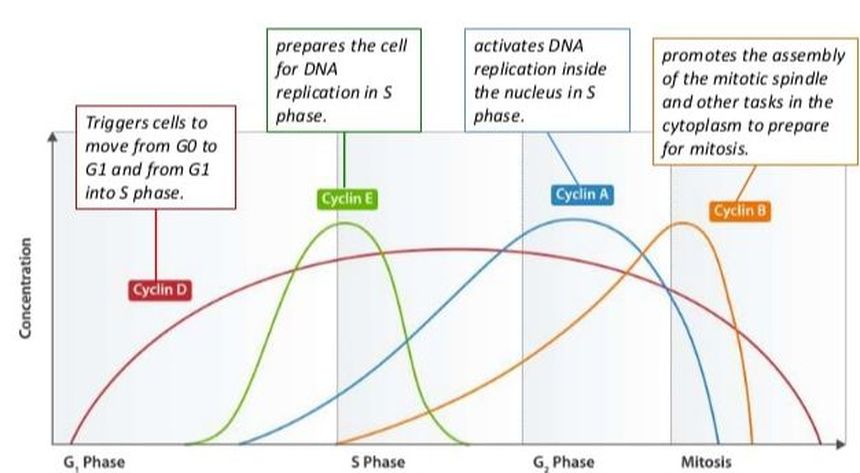
The cell cycle is regulated by the fluctuating concentration of these proteins
What are cyclins?
860 × 473
This is the ratio of cells undergoing mitosis to the total number of cells in a population.
What is the mitotic index?

A duplicated chromosome that consists of two identical copies joined at the centromere.
What is a sister chromatid?

The process of forming new allele combinations by exchanging genetic material between non-sister chromatids.
What is crossing over?

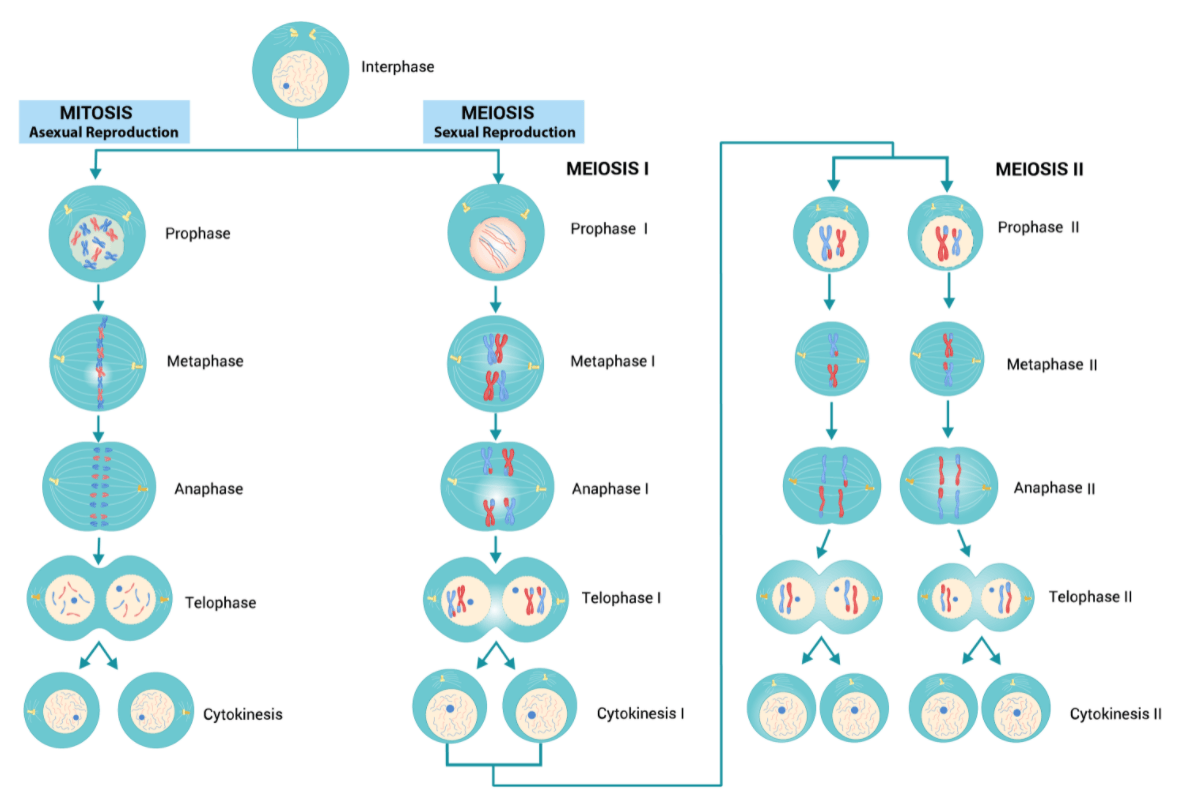
This type of cell division results in two identical daughter cells, essential for growth and repair.
What is mitosis?
A cell must reach this minimum level of a specific cyclin to pass a checkpoint.
What is a threshold level?

A high mitotic index indicates this about the rate of cell division in a population.
What is a rapid rate of cell division?
The structure formed when two homologous chromosomes are paired up during Prophase I of meiosis.
What is a bivalent (or tetrad)?

The failure of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate properly during meiosis.
What is nondisjunction?
This term describes a cell that contains only a single set of chromosomes, such as a gamete.
What is haploid?

When mutated, this type of gene can be converted into a cancer-causing gene (oncogene).
What is a proto-oncogene?

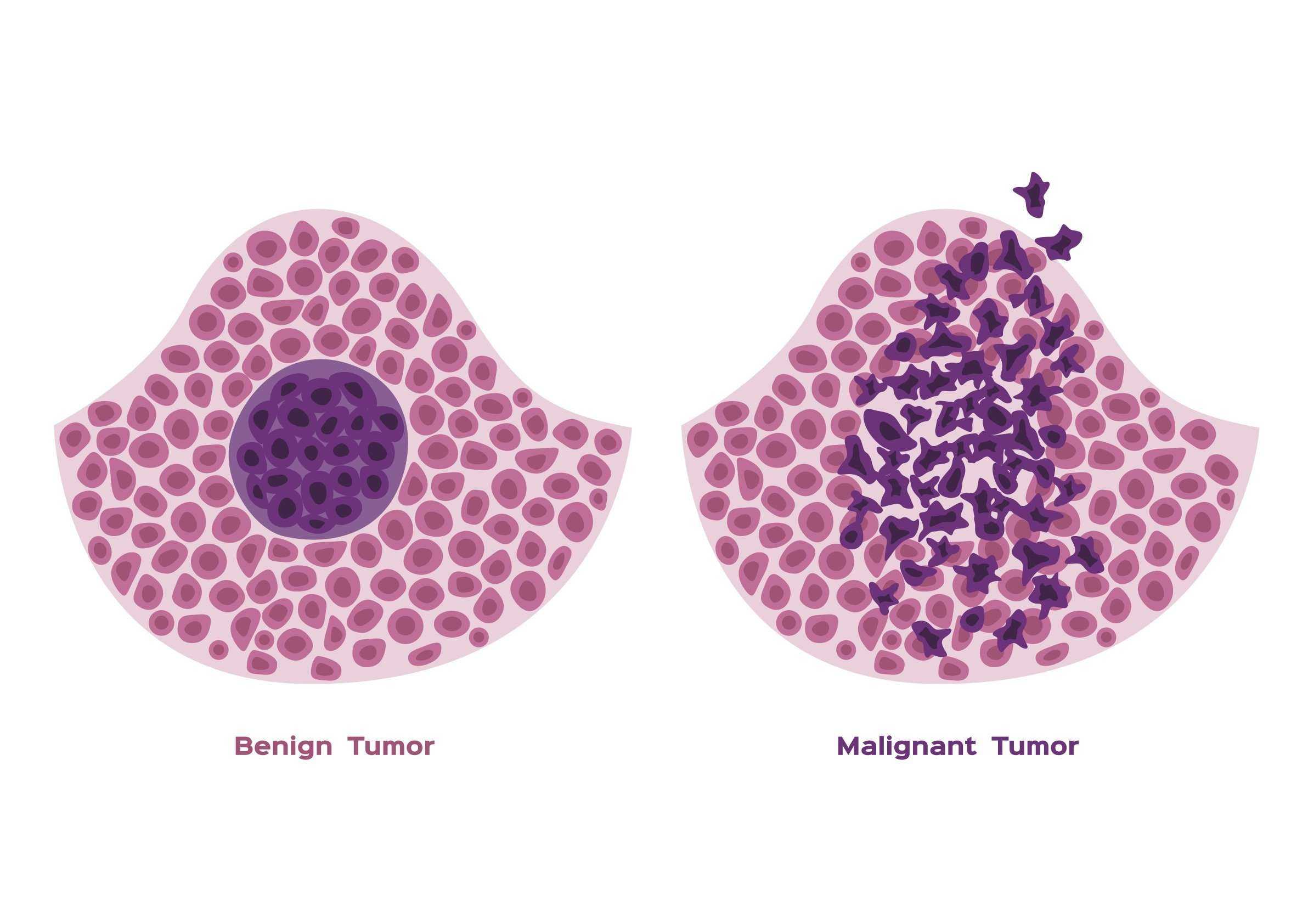
This is the term for a tumor that is not cancerous and does not spread to other tissues.
What is a benign tumor?
This is the stage of mitosis where sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
What is anaphase?

The random orientation and separation of homologous chromosomes during Meiosis I, which increases genetic diversity.
What is independent assortment?

This stage of mitosis is characterized by the alignment of chromosomes along the cell's equator.
What is metaphase?

Uncontrolled cell division is associated with mutations in proto-oncogenes and these other genes.
What are tumour suppressor genes?
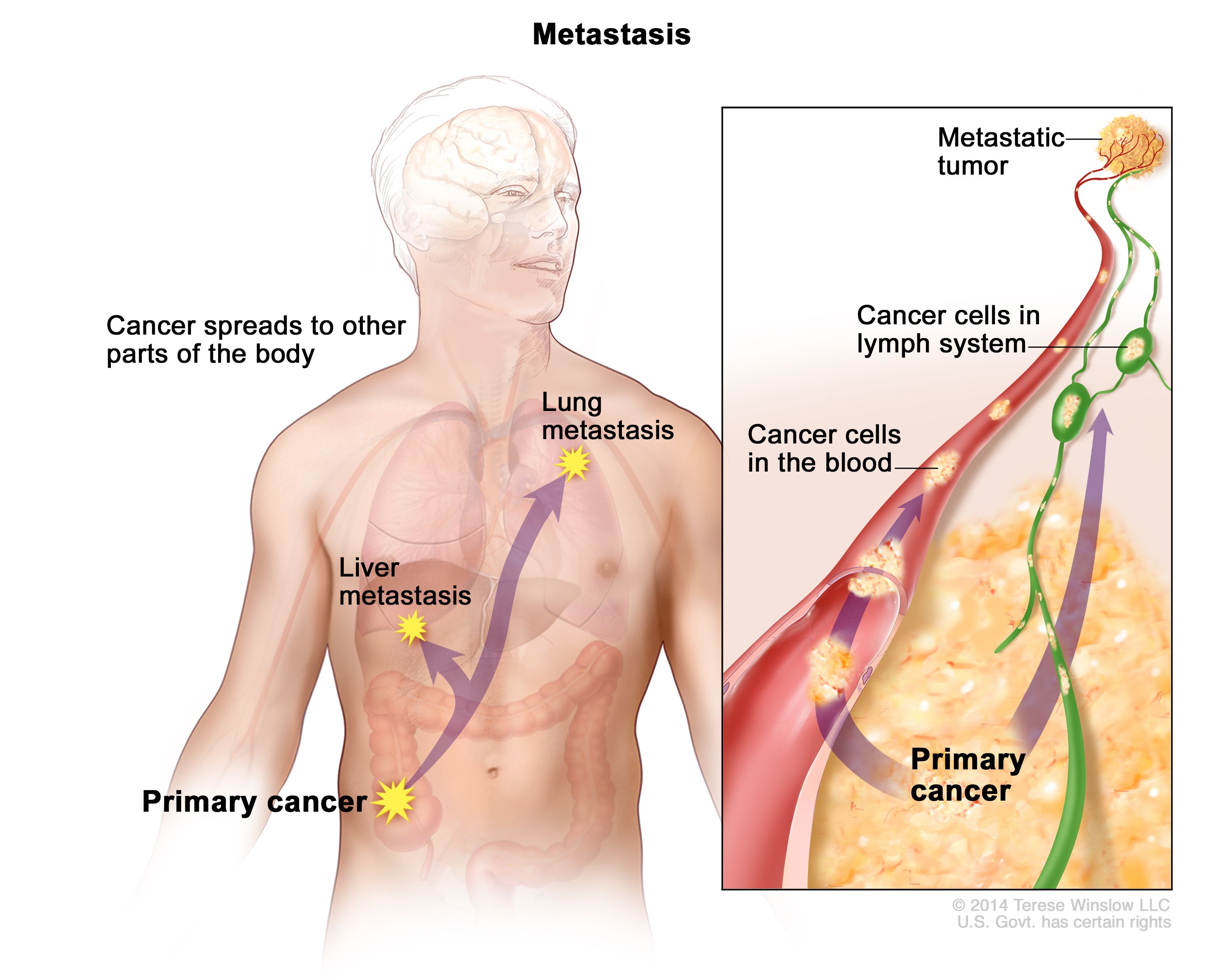
The process of a malignant tumor spreading to form a secondary tumor is known as this.
What is metastasis?
This is the stage of meiosis where sister chromatids separate, resulting in four haploid cells.
What is anaphase II?

The key event that happens in prophase I of meiosis that does not happen in prophase of mitosis.
What is synapsis (the pairing of homologous chromosomes)?

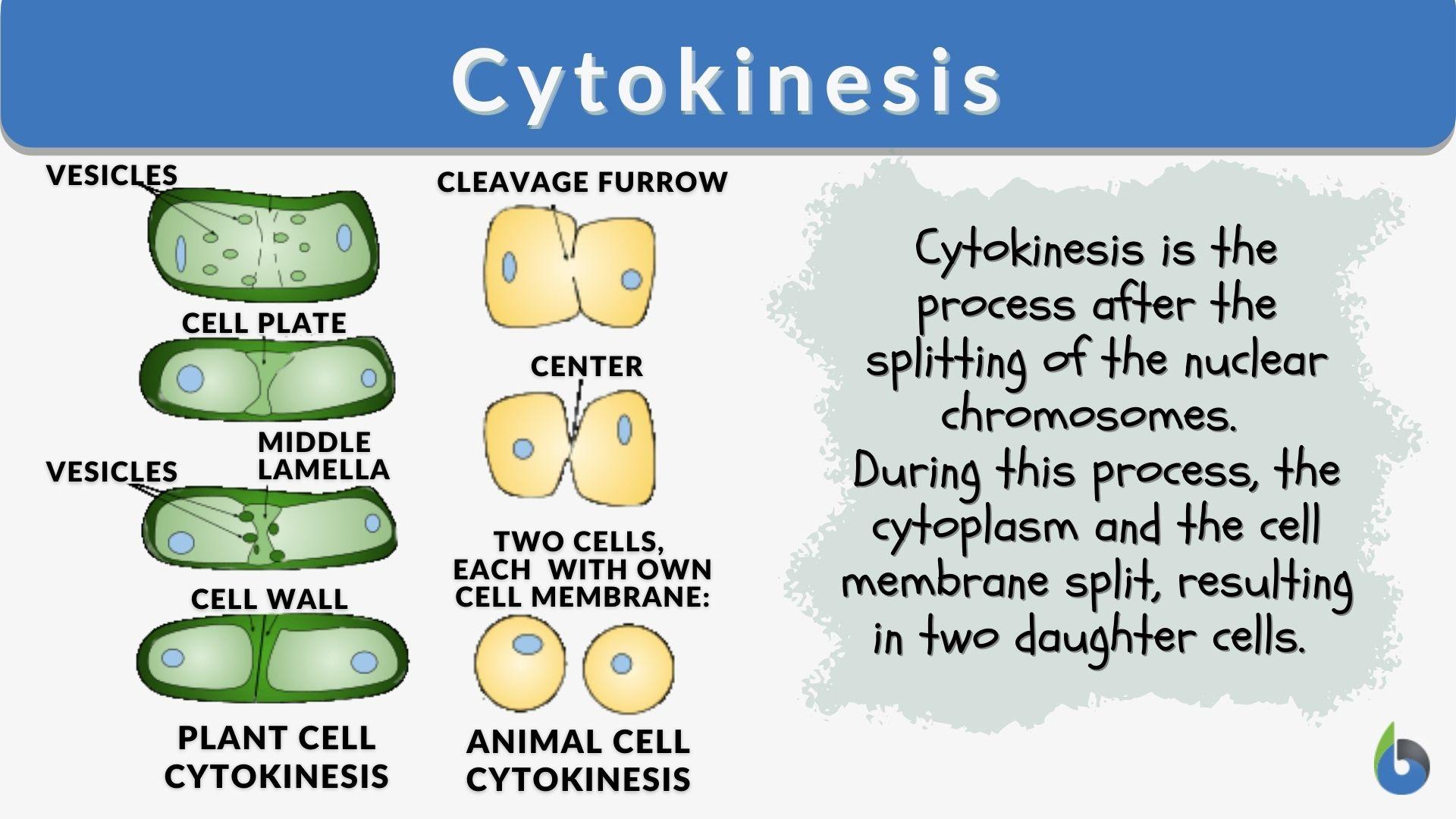
The formal name for the division of the cytoplasm that follows mitosis or meiosis.
What is cytokinesis?
A tumor that can invade neighboring tissues and metastasize is classified as this.
What is a malignant tumor?

A mutation in a tumor suppressor gene leads to this specific event in the cell cycle.
What is uncontrolled cell division?