Consideration
What are the five categories of insulins
1. RAPID ACTING: lispro(Humalog) aspart ( Novolog) glulisine ( Apidra)
2. SHORT ACTING: regular (Humulin R) novolin R lletin II
3. INTERMEDIATE ACTING: NPH(neutral protamin hagedom) Humulin N Novolin N (NPH)
4. VERY LONG ACTING: glargin (Lantus) detemir ( Levemir ) glargin (Toujeo)
5. RAPID ACTING INHALED INSULIN: afreza
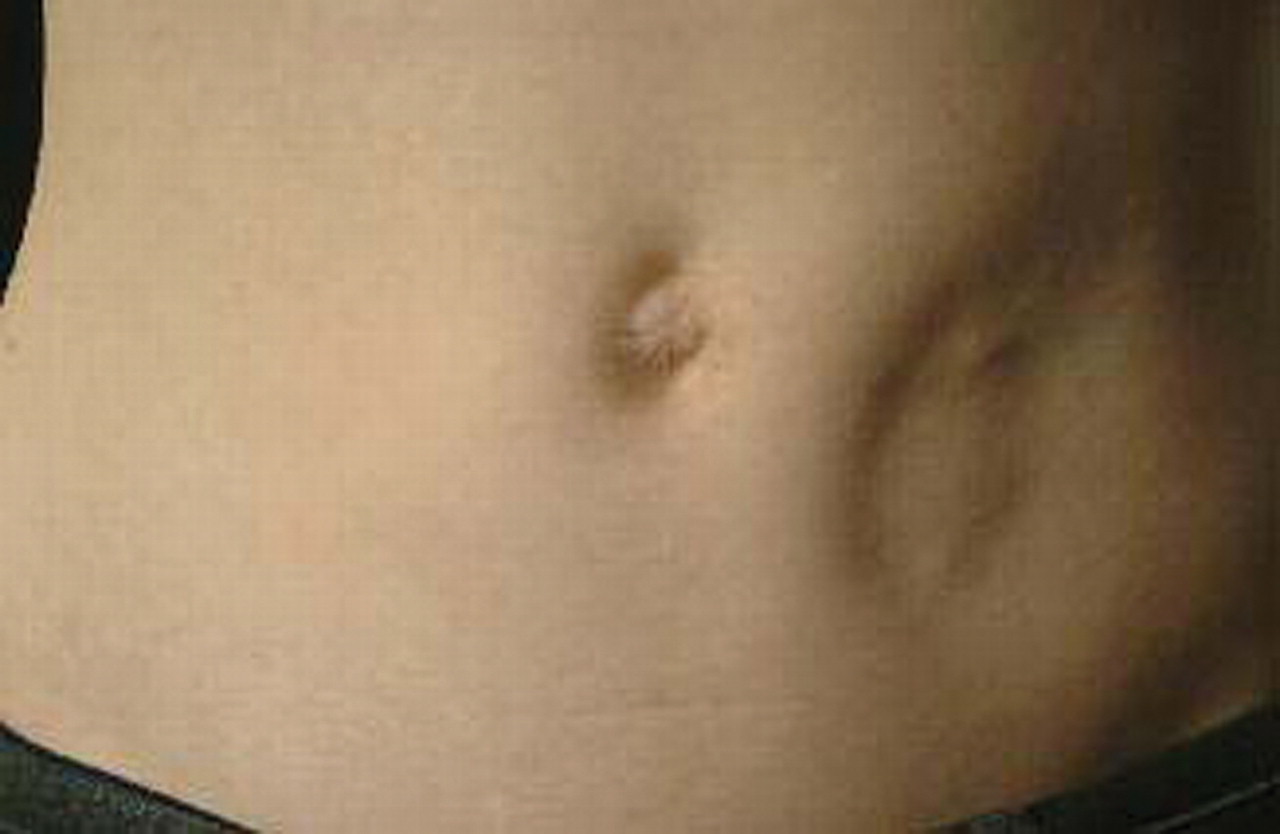
This adverse effect can occur if the injection site of insulin is not rotated
What is lipodystrophy?
Which insulins are rapid-acting? SATA
A. Regular (R)
B. Humalog
C. Novolog
D. NPH (N)
E. Apidra
Humalog,
Novolog, and
Apidra are considered rapid-acting insulins.
These insulins have a quick onset of action and are designed to mimic the body's natural insulin response after a meal. They are typically taken just before or immediately after meals to help control blood sugar levels. Regular (R) and NPH (N) insulins, on the other hand, have a slower onset and longer duration of action compared to rapid-acting insulins.
What statement or statements are INCORRECT regarding Diabetic Ketoacidosis?
A. DKA occurs mainly in Type 1 diabetics.
B. Ketones are present in the urine in DKA.
C. Cheyne-stokes breathing will always present in DKA.
D. Severe hypoglycemia is a hallmark sign in DKA.
E. Options C & D
The answer is E.
This is the type of insulin that CANNOT be mixed in the same syringe with other insulins.
What is long-acting insulin (e.g., glargine, detemir)?
This is the only type of insulin that can be administered intravenously
What is regular insulin (Humulin R® , Novolin R®)?

Which insulins are short-acting? SATA
A. Lantus
B. Lente (L)
C. Regular (R)
D. Humulin
E.Novolin
Regular (R) Humulin Novolin
Regular (R), Humulin, and Novolin are short-acting insulins.
Lantus and Lente (L) are long-acting insulins.
Short-acting insulins have a rapid onset of action and a shorter duration of action, typically lasting for about 2-4 hours. They are used to control blood sugar levels after meals or to correct high blood sugar levels. Long-acting insulins, on the other hand, have a slower onset of action and a longer duration of action, providing a steady release of insulin over a longer period of time to maintain basal insulin levels throughout the day.
A patient who has diabetes is nothing by mouth as prep for surgery. The patient states they feel like their blood sugar is low. You check the glucose and find it to be 52. The next nursing intervention would be to:
A. Administer Dextrose 50% IV per protocol
B. Continue to monitor the glucose
C. Give the patient 4 oz of fruit juice
D. None, this is a normal blood glucose reading
A.
The patient is NPO for surgery and can NOT eat but is experiencing hypoglycemia. Normally, you could give the patient 15 grams of a simple carbohydrate like 4 oz of fruit juice or soda, glucose tablets, gel etc. per hypoglycemia protocol However, the patient can NOT eat due to surgery prep. Therefore the nurse would need to administer Dextrose 50% IV per protocol to help increase the blood glucose and recheck the glucose level.
This is the only type of insulin that can be mixed with short acting insulin
What is intermediate-acting insulin (e.g., NPH)?
This class of medications can mask the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia
What are beta-blockers (e.g., metoprolol)?
Beta-blockers can mask the symptoms of hypoglycemia
Which insulins are intermediate-acting? SATA
A. Lente (L)
B. NPH (N)
C. Regular (R)
D. Humulin
E. Novolog
Lente (L) and
NPH (N) are both intermediate-acting insulins.
Intermediate-acting insulins have a slower onset of action and a longer duration compared to rapid-acting insulins like Regular (R), Humulin, and Novolog. Lente (L) and NPH (N) are commonly used to provide basal insulin coverage throughout the day and help control blood sugar levels between meals and overnight.
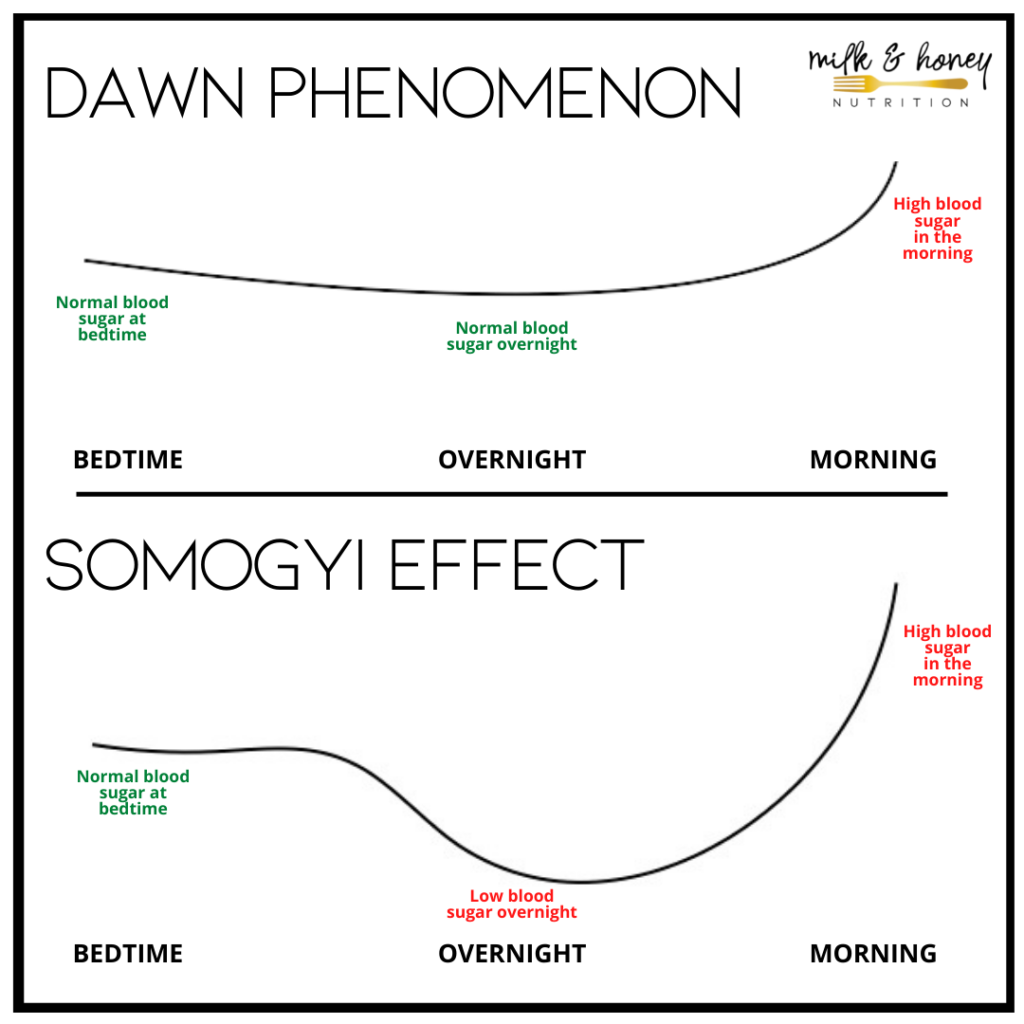
The nurse is caring for a client who has normal glucose levels at bedtime, hypoglycemia at 2am and hyperglycemia in the morning. What is this client likely experiencing?
A. Dawn phenomenon
B. Somogyi effect
C. An insulin spike
D. Excessive corticosteroids
B, Somogyi effect
The Somogyi effect is when blood sugar drops too low in the morning causing rebound hyperglycemia in the morning. The hypoglycemia at 2am is highly indicative. The Dawn phenomenon is similar but would not have the hypoglycemia at 2am.
The timing of insulin injections is essential for efficient insulin administration. As a nurse, you need to
Know the ___, ___, and __ of all insulin administered.
ONSET
PEAK
DURATION
This is an early morning hyperglycemia due to a rebound effect from late-night hypoglycemia
Somogyi phenomenon
It happens when low blood sugar triggers a rebound effect, leading to high blood sugar
Treatment options include:
- adjusting the timing of insulin administration.
- lowering the dose of insulin before bed.
- changing the type of insulin.
- eating a snack with the evening insulin dosage.
- taking into account lifestyle factors, such as stress and exercise.
Which insulins are long-acting?
A. Regular (R)
B. Ultralente (U)
C. Novolin
D. Lantus
E. Levemir
The long-acting insulins are Ultralente (U), Lantus, and Levemir. Regular (R) and Novolin are not long-acting insulins.
The nurse is caring for a patient whose blood glucose level is 55mg/dL. What is the likely nursing response?
A. Administer a glucagon injection
B. Give a small meal
C. Administer 10-15 grams of a carbohydrate
D. Give a small snack of high protein food
C Administer 10-15 grams of a carbohydrate
The client has low hypoglycemia. This is generally treated with a small snack.
Which of the following statements is incorrect about diabetic ketoacidosis?
A. Extreme Hyperglycemia that presents with blood glucose >600 mg/dL
B. Ketones are present in the urine
C. Metabolic acidosis is present with Kussmaul breathing
D. Potassium levels should be at least 3.3 or higher during treatment of DKA with insulin therapy
ANSWR: A
Extreme Hyperglycemia that presents with blood glucose >600 mg/dL is present only in Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Syndrome
What are the most common sign and symptoms of hypoglycemia?
Keep in mind the nmonic "HIWASH"
Headache
Irritability or anxiety.
Weakness or Fatigue.
Anxious
Shakiness & Sweating
Hungry
What is the correct way to mix NPR insulin with Regular insulin?
A. Air to NPH, air to Regular, draw up Regular, draw up NPH.
B. Air to Regular, air to NPH, draw up NPH, draw up Regular.
C. Air to Regular, air to NPH, draw up Regular, draw up NPH.
D. Air to NPH, air to Regular, draw up NPH, draw up Regular.
A
The correct way to mix NPR (Neutral Protamine Hagedorn) insulin with Regular insulin is to first inject air into the NPH insulin vial, then inject air into the Regular insulin vial. Next, draw up the desired amount of Regular insulin into the syringe and then draw up the desired amount of NPH insulin. This sequence ensures that the Regular insulin is drawn into the syringe first, followed by the NPH insulin.
A diabetic patient has the following presentation: unresponsiveness to voice or touch, tachycardia, diaphoresis, and pallor. Which of the following actions by the healthcare provider is the priority?
A. Send blood to the laboratory for analysis
B. Administer oxygen per nasal cannula
C. Administer the prescribed insulin
D. Administer 50% dextrose IV per protocol
D
Administer 50% dextrose IV per protocol
The nurse is teaching the client about insulin glargine. Which client statement indicates that the client has a correct understanding of the medication?
A. "This medication can be added to my insulin pump."
B. "I plan to take this medication 30 minutes before each meal."
C" I will administer this medication once each night before bed."
D. "I'll monitor my blood glucose levels at least every other day."
C. "I will administer this medication once each night before bed."
Insulin glargine is a modified human insulin with a prolonged duration of action (at least 24 hours). The medication is indicated for once-daily subcutaneous administration to treat adults and children with type 1 diabetes mellitus and adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. According to package labeling, the daily injection should be made at bedtime. Regular insulin is the only insulin that can be added to an insulin pump. Regardless of the type of insulin the client uses, the blood glucose should be monitored at least daily if not more often.
A client diagnosed with diabetes mellitus receives 8 units of regular insulin subcutaneously at 7:30 am. The nurse should be most alert to signs of hypoglycemia at what time during the day?
A. 9:30 am to 11:30 am
B. 11:30 am to 1:30 pm
C. 1:30 pm to 3:30 pm
D. 3:30 pm to 5:30 pm
A. 9:30 am to 11:30 am
Regular insulin is a short-acting insulin.
Its onset of action occurs in a half hour and peaks in 2 to 4 hours.
Its duration of action is 4 to 6 hours.
A hypoglycemic reaction will most likely occur at peak time, which in this situation is between 9:30 am and 11:30 am.
The blood glucose of a patient who is newly diagnosed with type 1 diabetes mellitus has a blood glucose level of 340 mg/dL. Which type of insulin prescribed for the patient is appropriate to administer at this time?
A. NPH + regular (70/30)
B. Glargine
D Regular
The nurse has taught a patient admitted with diabetes, cellulitis, and osteomyelitis about the principles of foot care. The nurse evaluates whether the patient understands the principles of foot care if the patient makes what statement?
a. "I should only walk barefoot in nice, dry weather."
b. "I should look at the condition of my feet every day."
c. "I am lucky my shoes fit so nice and tight because they give me firm support."
d. "When I am allowed to get out of bed, I should check the shower water with my toes."
b. "I should look at the condition of my feet every day."
Patients with diabetes mellitus need to inspect their feet daily for broken areas that are at risk for infection and delayed wound healing. Properly fitted (not tight) shoes should be worn at all times. Water temperature should be tested with the hands first.