These 2 drug classes are used for all patients with PAD
What are Antiplatelets and statins?
This procedure Improves survival in multivessel CAD with LV dysfunction (it also improves survival in multivessel CAD and diabetes)
What is a CABG?
This is the Initial diagnostic test for syncope when arrhythmia is suspected
What is a resting ECG?
You should avoid this drug class while taking nitrate therapy
What are Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors?
Asymptomatic murmurs require a TTE evaluation if they have one of the following qualities
Grade ≥3/6, late systolic or holosystolic, diastolic, or continuous
This is the Recommended heart valve type for patients older than 65 years (mechanical vs bioprosthetic)
What is a Bioprosthetic heart valve?
This condition is characterized by Upper extremity hypertension, radial-femoral pulse delay, and infraclavicular systolic murmur
What is an Aortic coarctation?
This is the ankle-brachial index (ABI) value diagnostic of PAD
What is ≤0.90?
This P2Y12 inhibitor has dyspnea as side effect
What is Ticagrelor?
These Drugs inhibit SVT induction and block AV conduction
What are β-Blockers and nondihydropyridine calcium channel blockers?
These medications are used in the Treatment of acute pericarditis
What are NSAIDs and colchicine?
This condition is characterized by a Late-peaking systolic murmur, diminished S2, delayed and diminished carotid upstroke
What is Severe aortic stenosis?
This is the recommended aortic valve type for patients younger than 50 years (mechanical vs bioprostetic)
What is a Mechanical heart valve?
Name an Indication for intervention in aortic coarctation
Systolic pressure gradient ≥20 mm Hg or evidence of collateral flow
This drug is used to improve symptoms of PAD despite antiplatelet and statin therapy
What is Cilostazol?
When a young woman during the peripartum period presents with ACS, this is the most likely diagnosis
What is a Spontaneous coronary artery dissection?
Name 3 drugs commonly associated with QT prolongation
antibiotics (e.g., macrolides like erythromycin, and fluoroquinolones), antipsychotics (e.g., haloperidol, quetiapine), antidepressants (e.g., citalopram, escitalopram), and other medications such as methadone and ondansetron
disopyramide, procainamide, quinidine, dofetilide, ibutilide, and sotalol
These are the Specific β-blockers associated with reduced mortality in patients with HFrEF
What are Bisoprolol, metoprolol succinate, and carvedilol?
This condition is characterized by Bounding peripheral pulses, diastolic decrescendo murmur along the sternal border
What is Aortic regurgitation?
This is the recommended Treatment of symptomatic chronic severe mitral regurgitation in a nonsurgical candidates
What is Transcatheter mitral valve replacement (TMVR)?
This is the systolic blood pressure target for acute aortic dissection
What is ≤120 mm Hg within 1 hour?
This is the diagnostic test for PAD if the ankle-brachial index (ABI) is >1.4
What is the Toe-brachial index?
These are the 3 Contraindications to early β-blocker therapy after STEMI
Cardiogenic shock, hypotension, conduction disturbance
This is a type of supra ventricular tachycardia with short PR interval and slurred QRS upstroke
Atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia (AVRT)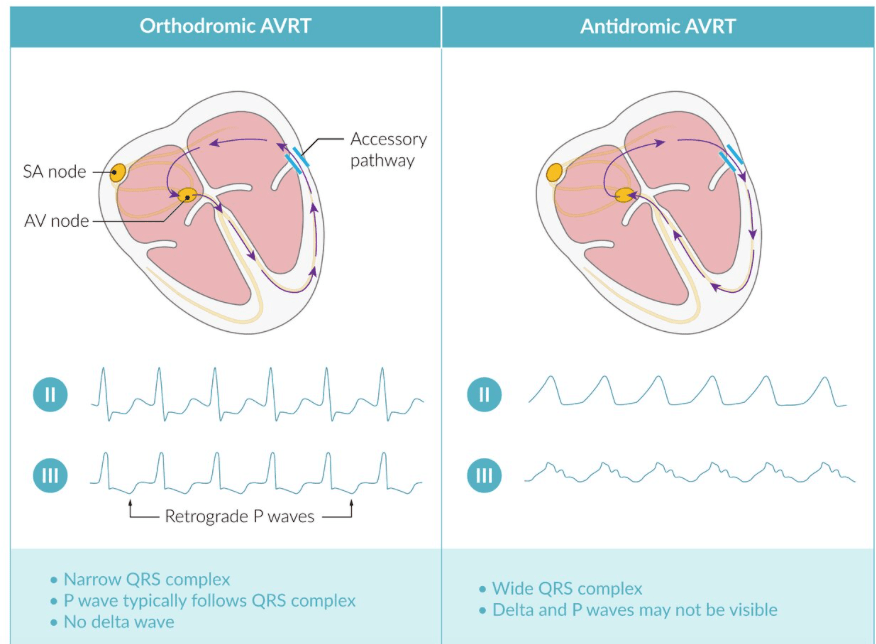
This is the prefered Drug class to use for therapy for inherited long QT syndrome
What are β-Blockers?
This condition is characterized by a continuous murmur heard beneath the left clavicle
What is a Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)?
This is how often you should get a TTE after a valve bioprothesis
You should get a TTE at 5 years, then annually starting at 10 years after valve replacement
This type of (acute) aortic dissection requires surgical repair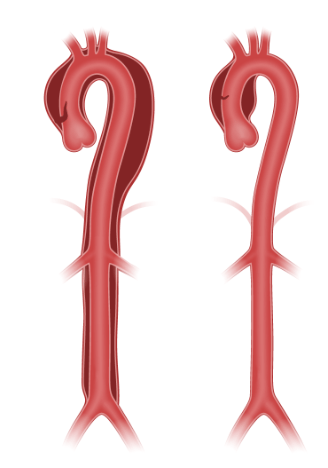
What is Acute type A aortic dissection ?
Name The "6 P's" of acute limb ischemia
Paresthesia, pain, pallor, pulselessness, poikilothermia (coolness), paralysis
This Syndrome is characterized by angina, abnormal stress test results, but normal coronary arteries on angiograms
What is Cardiac syndrome X (microvascular angina)?
This inherited disorder is characterized by ST-segment coving in leads V1-V3, VF, and cardiac arrest
What is Brugada syndrome?
This class of chemotherapy(used in both solid and hematologic malignancies) causes and Irreversible dilated cardiomyopathy
Anthracyclines (including doxorubicin, epirubicin, and idarubicin)
This condition is characterized by a Holosystolic murmur along left sternal border that increases with inspiration
What is Tricuspid regurgitation?
Name the TEE criteria for severe aortic stenosis
Valve area ≤1.0 cm2, peak velocity >4 m/s, mean gradient >40 mm Hg
Name the 3 indications for abdominal aortic aneurysm repair
Symptoms
size ≥5.5 cm
expansion >0.5 cm/year