What chromosome is the Alpha chain and the Zeta chain gene located on?
16
How does sodium citrate prevent coagulation?
Removes calcium which prevents coagulation cascade.
What is the primary function of a Cytotoxic T cell?
Main role is to destroy virally infected cells.
What is the definition of Anemia?
A decrease in the oxygen-carrying capacity of the body/blood.
Where are red blood cell inclusions normally removed?
Spleen
Vit B12, or Folate
What is 2,3 DPG and what is its function in regards to oxygen/hemoglobin?
2,3 DPG increases oxygen off-loading capabilities from its tense and relaxed state.
What is the name of the inherited form of Aplastic Anemia?
Fanconi's anemia
What color tube is a sodium citrate?
Light Blue
RBC's utilize (aerobic/anaerobic) metabolism as a primary source of energy.
Anaerobic
Red blood cells use this to produce energy.
Glucose
Which WBC arrives first at the site of inflammation
Neutrophils
What is lymph fluid?
Mostly clear fluid derived from blood comprised of WBC and bathes the tissues and drains through the lymphatic system into the bloodstream.
Is a MCHC of 34% considered abnormal?
No, the normal range of MCHC is 32-36%
What are the two Primary Lymphatic Tissues?
Thymus & Bone Marrow
The spleen is divided into two parts, what are they?
Red pulp
White pulp
Hgb C is caused by what substitution?
Leucine in the 6th position instead of glutamic acid
What 3 things will EPO do to RBC production?
-Increase RBC production
-Decrease RBC maturation time
-Promotes the early release of RBC from marrow
What is the formula for corrected reticulocyte count?
CRC =
Patient Retic % * Patient HCT / 45 (average Hct)
What is the storage form of iron?
Ferritin
What are the inclusion in a reticulocyte composed of?
RNA remnants
CD4 markers are found on which type of T cell?
Helper T-Cells
What is normal adult hemoglobin (Hgb A) composed of?
α2 β2
What is the last stage a RBC can undergo mitosis?
Polychromatic Normoblast
What is the normal M:E ratio for adults?
2:1
Which of the following would be most likely in a patient presenting with anemia and a reticulocyte count >2%
-Vit B12 deficiency
-Folate deficiency
-Acute blood loss
-Acute lymphocytic leukemia
Acute blood loss
Which chromosome is the beta chain gene of hemoglobin located on?
11
What color tube is EDTA?
Lavender
True or False
The O2 & CO2 exchange of RBCs requires energy input via ATP.
False
A sneaky nurse notices a clot in her lavender tube she drew. Instead of redrawing the tube like a good nurse, she just removes the clot and trashes it.
What CBC result in the lab will be most affected?
Platelet count will be decreased.
Following splenectomy, what 3 things will be increased in circulation?
Platelets
WBCs
Abnormal RBC
What is the normal % of Reticulocytes in a patient with Bone Marrow that IS COMPENSATING for anemia correctly.
> 2%
What protein carries Iron? (transport)
Transferrin
Define schistocytes
RBC fragments
What CBC parameter can be analyzed using a sodium citrate tube?
Platelet count to combat platelet satellitism from an EDTA tube
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase plays an important role in maintaining iron in the ferrous state by producing reduced _____ , which detoxifies H2O2
Glutathione
What stains are used below? What type of cells are shown in both pictures?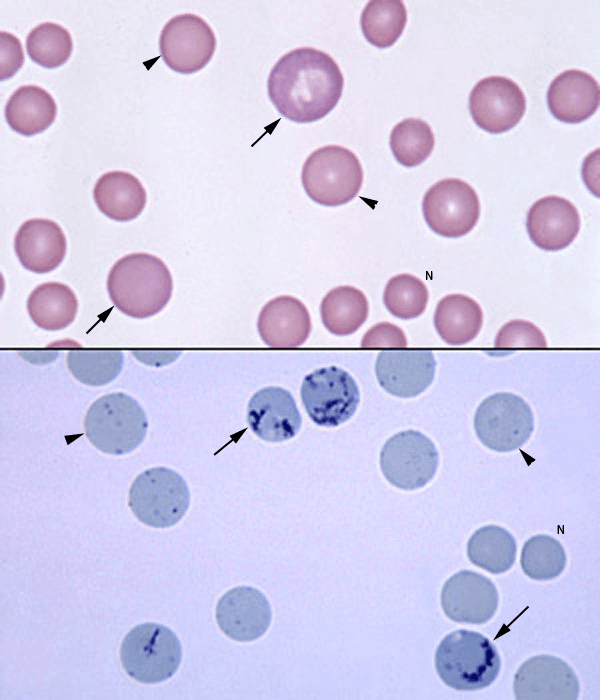
Top: Wright Stain
Bottom: New Methylene Blue stain
Both show reticulocytes and mature erythrocytes.
What is the primary pathway utilized by RBCs to produce 90 to 95% of glucose?
Embden-Meyerhof Pathway (EMP)
Define HCT
Hematocrit: Packed cell volume: Typically 45%
What cells are spiculated with numerous, short, evenly spaced blunt surface projections.
Crescent shaped RBCs that have pointy projections are typically seen in what disease?
Sickle Cell anemia
What is the main function of a neutrophil?
Phagocytosis typically of bacteria
What is Aplastic anemia?
Aplastic anemia = bone marrow hypocellularity resulting in peripheral blood hypocellularity
What hormone is high in cases of Anemia of Chronic disease which prevents iron uptake in the gut and iron release by macrophages?
Hepcidin
What stain can be used to visualize iron in bone marrow
Prussian Blue
What three indices are used to classify anemia types?
MCV
MCH
MCHC
Define Polychromasia
Immature red cells that are slightly larger and blue tinged compared to other red cells
Characteristic color of Carboxyhemoglobin
Bright Cherry Red
What type of cell is characteristic of Infectious Mononucleosis?
Atypical or Reactive Lymphs
What stain are reticulocytes visible with?
New Methylene Blue
Carboxyhemoglobin results in a (left/right) shift on the oxygen dissociation curve.
Left (binds Hgb 200X more strongly)
Chediak-Higashi Syndrome is associated with what?
Giant granules in all granulated cells. Patient also has albinism and photophobia
Define Extramedullary Hematopoiesis
Creating new cells outside of the bone marrow
What is the name for the cells indicated by the arrow? 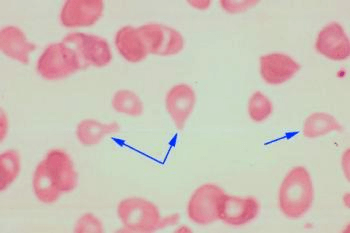
Dacrocytes / Teardrop cells
Describe a Right Shift on the Oxygen Dissociation curve.
A right shift on the oxygen dissociation curve results in hemoglobin having a decreased O2 affinity, resulting in increased diffusion of O2.
Define a shift to the left in regards to a WBC differential
Bone marrow is responding to the increased WBC count by sending out younger cells- seen as banded neutrophils in the peripheral smear
In what organ would I find 1/3 of the bodies platelets?
Spleen
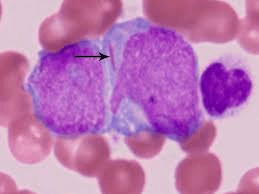
What inclusion is the arrow pointing to?
Auer Rod
PK (pyruvate kinase) deficiency spot test is opposite of the G6PD (glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase) deficiency spot test. If the patient has a PK deficiency the spot test will (Fluoresce/ Not fluoresce)
Fluoresce.
What organs can perform Extramedullary Hematopoiesis
Liver and spleen
The Methemoglobin Reductase Pathway serves what function?
Maintains iron in the Ferrous (2+) form via NADH produced from glycolysis
Where is EPO produced and what does it do?
Hormone produced by the kidneys and steps up RBC production
Define eosinophilia and what condition relates to it?
Increased amount of eosinophils and usually seen with allergies or certain parasitic infections
Identify this cell. What disease is it associated with?
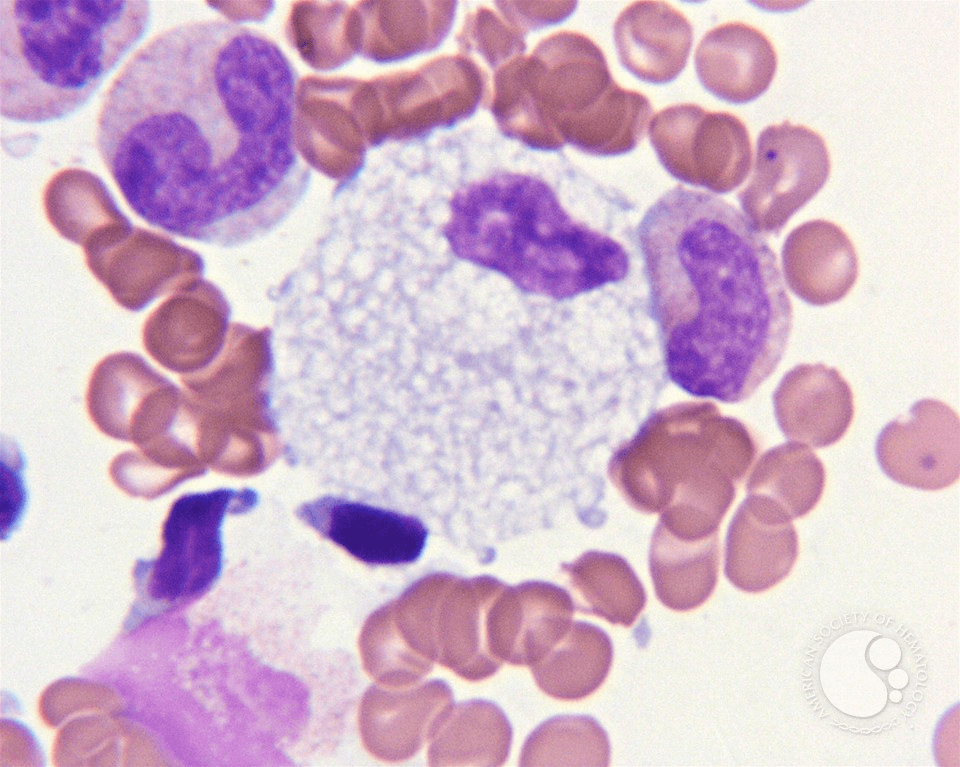
Foam cell (macrophage)
Niemann-Pick disease
What cell is indicated by the arrows and what disease are they seen with?
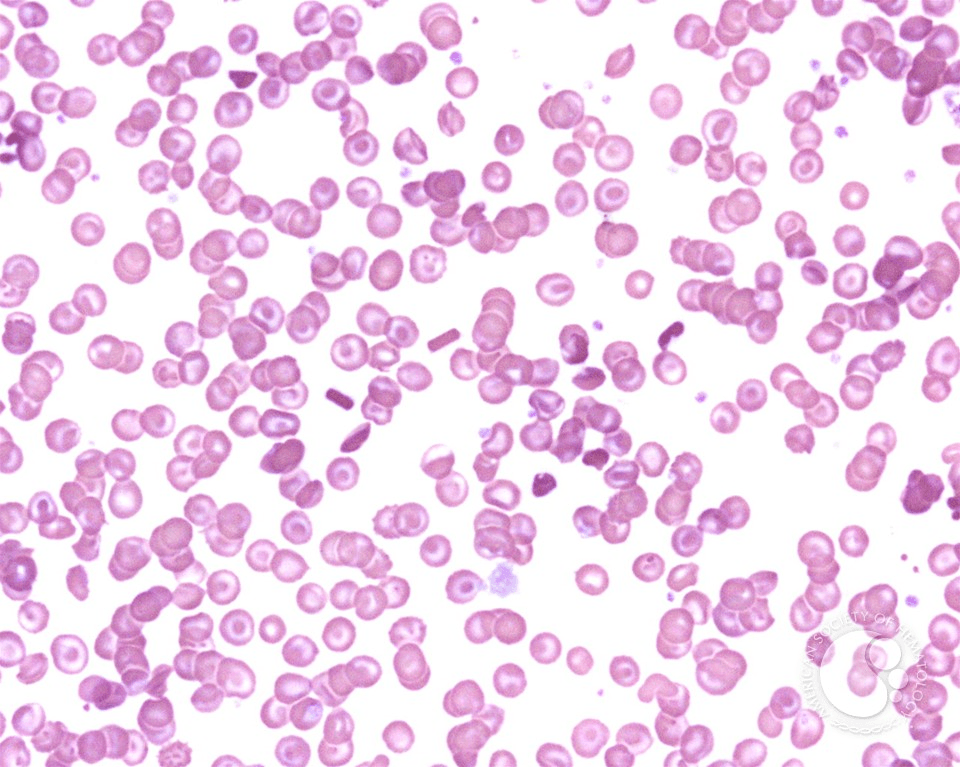
Bars of gold and Hgb C
Describe the shape of a normal RBC and what is the central zone called?
Biconcave disk with a central zone of pallor (whitening)
How long do RBC normally circulate? [what are their lifespans]
120 Days
Define hemolysis
Red cell breakdown
What are the causes of microcytic RBC? (5 TAILS)
Iron deficiency
Thalassemia
Sideroblastic Anemia
Lead Tox
Anemia of Chronic Disease
What is the typical range for monocytes?
5-10%