What is the most common mechanism of injury for whiplash?
Motor vehicle accidents
What is a stride length?
The distance between two successive placements of the same foot
What is a plumb line?
Vertical line representing gravity drawn from the body's center of gravity equidistant from the medial malleoli.
What muscle group commonly contributes to tension headaches?
Suboccipitals and upper cervical extensors
What is torticollis?
Abnormal positioning of the head relative to the body
What does IASTM stand for?
Instrument Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization
Name a structure that becomes compressed with TOS.
brachial plexus, subclavian vein, subclavian artery
What is mastication?
chewing
What is the optimal headrest position and why?
Name one cause of a hip-hiking gait.
What is a Dowager's Hump?
What muscle's trigger point often causes pain around the eye and temple?
What self care is recommended for a patient with torticollis?
address postural imbalances, recommend OT or PT, diaphragmatic breathing
What is petechiae?
Red dots showing capillary damage
What are 2 (local or systemic) contraindications to working TOS.
Uncontrolled hypertension, atherosclerosis, muscle relaxers, anti-inflammatories, cervical rib
Name a trait or mechanism unique to the TMJ.
bilaterally functioning synovial joints with articular discs
Swallowing Test. Palpate and pincer grasp SCM, patient swallows. Pain swallowing indicates TrP in SCM.
Weakness of what muscles commonly leads to a Trendelenburg gait?
Describe the knee position.
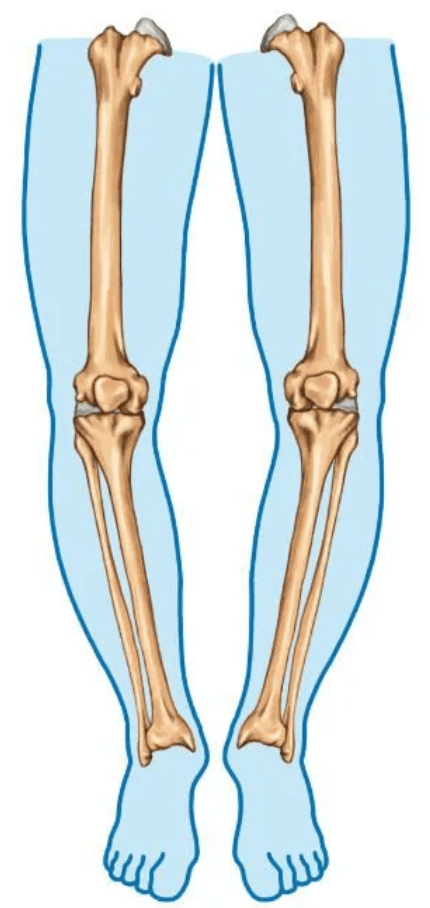
Genu varum.
Name two red flags for headaches requiring medical referral for treatment.
Sudden severe onset, neurological deficits, fever, confusion, visual changes
What is spasmodic torticollis?
Adult onset, intermittent, muscles twitch/jerk, improved with rest
Name 2 common errors?
non specific treatment goal, lack of anatomical knowledge, excessive emollient, overgripping
Where are the 3 locations the brachial plexus is easily compressed?
Between anterior/middle scalene, clavicle and first rib, and pec minor and coracoid process
What is the primary mover for depression of the mandible?
gravity, then hyoid muscles
Name three anterior neck muscles affected by whiplash.
Rectus capitis anterior, rectus capitis lateral, longus collis, longus capitis, platysma, supra and infrahyoids
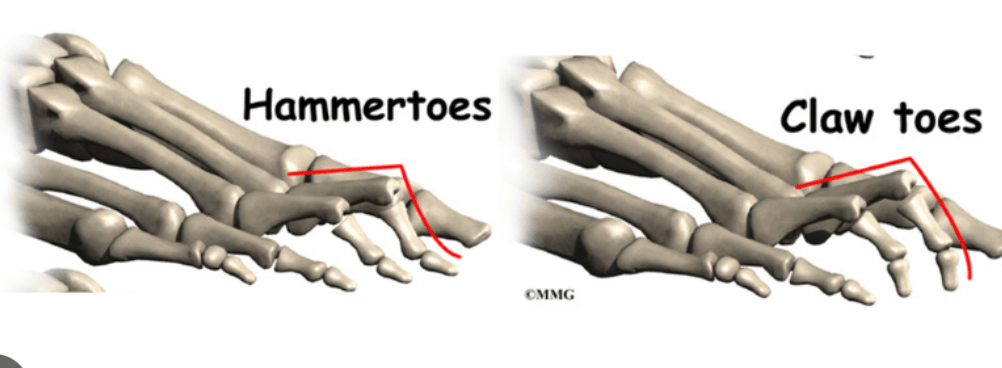
Name a visual indicator of foot overpronation.
What is the difference between a hammer toe and a claw toe?
What is the difference between a primary and secondary headache?
Primary: headache is condition (tension or migraine)
Secondary: result of underlying pathology (hypertension, trauma)
What is the difference between acute acquired and congenital torticollis?
Acute acquired: sudden onset, muscle shortened and spasmed
Congenital torticollis: present at birth
Name 2 absolute contraindications.
infection, thrombosis, fever, undiagnosed lump, uncontrolled hypertension, neurogenic condition
Name two causes for thoracic outlet syndrome, unrelated to posture or activities of daily living.
cervical rib, systemic immune or metabolic disorder (diabestes, hypothyroidism, rheumatoid arthritis), trauma, pregnancy
What self care would you recommend to a patient with TMJD?
pterygoid (using cork) and suboccipital stretch, intraoral self massage
Which large cervical ligament is commonly injured in whiplash?
Anterior Longitudinal Ligament
Describe a diplegic gait.
stiffness and difficulty coordinating movement in both legs (scissoring gait)
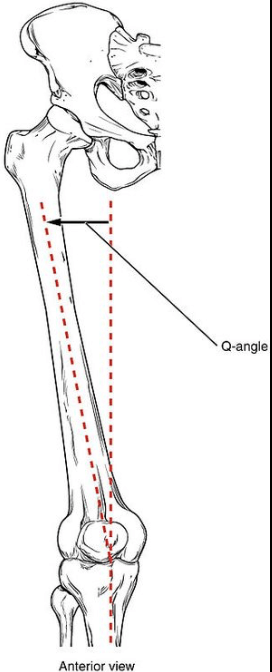
What is the Q angle?
describes the relationship between the pelvis, leg and foot.
What is a paroxysmal neurological disorder?
Conditions causing sudden brief attacks of involuntary movement or cerebellar disfunction
What are considerations of working on a baby with torticollis?
Parental consent, patient positioning, still developing cranial structures
What are the 5 metrics to determine proper dosing? (hint: TTIPS)
Time, Treatment angle, Instrument Shape, Pressure, stroke rate
Describe and explain the cervical distraction test.
Client seated or supine
Grasp occiput and frontal bone
Return head to neutral and slowly traction in superior direction hold at least 30 seconds
Positive sign- reduction in symptoms as nerve root compression or facet joint compression is relieved
Name the two tests for TMJD.
AROM (C or S shape), 3 knuckle test