What type of organism consists of a single cell that performs all life processes, such as reproduction, nutrition, and waste removal?
Unicellular
What is the main difference between autotrophs and heterotrophs in how they obtain nutrients?
Autotrophs make their own food; heterotrophs consume others
What is the gas required for photosynthesis?
Carbon dioxide
In animals, this red pigment in blood binds oxygen for transport to tissues.
Haemoglobin
What is the function of phloem tissue?
Transport sugars
Multicellular organisms have cells that are _____ for specific functions
specialised
Name two structures in a leaf important for gas exchange.
Stomata, spongy mesophyll
Which part of the digestive system absorbs most nutrients?
Small intestine
These two main vessels in a plant’s vascular system move water/minerals and sugars, respectively.
Xylem and phloem.
Name the theory that explains upward water movement in plants.
Cohesion–tension theory
Correct order of biological organisation in multicellular organisms
Cell→Tissue→Organ→System
How are alveoli adapted for gas exchange? (Give two features)
Large surface area, thin walls
Name two products of photosynthesis.
Glucose, oxygen
In an open circulatory system, the transport medium is not confined to vessels but flows into these body spaces.
body cavities or haemocoels
Which blood vessels exchange gases in mammals?
Capillaries
The process in which unspecialised cells develop into specialised cells with distinct functions and eg nerve/muscle cells
Differentiation
What process transports glucose from leaves to the rest of the plant?
Translocation (via phloem)
What are the two main types of digestion in mammals?
Physical, chemical
As blood moves from the lungs to the body, its carbon dioxide content changes in this way.
decreases
What is the waste product of anaerobic respiration in animals?
Lactic acid
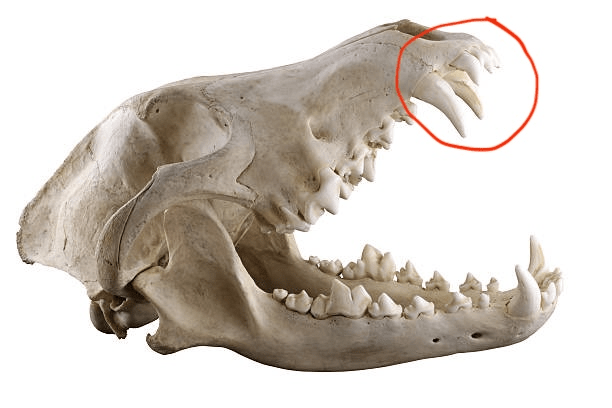
Describe what role the circled area has in digesting food.
Bonus points if you can tell what animal this skull belongs to (+250)
killing and holding prey tearing meat making it easier to digest.
What theory explains the upward movement of water in plants?
Transpiration–cohesion–tension theory
Compare the nutrient requirements of autotrophs and heterotrophs.
Autotrophs: CO₂, H₂O, minerals, light
Heterotrophs: organic molecules, O₂
In plants, the composition of the phloem sap changes depending on this process that moves sugars from sources to sinks.
translocation
What structures open and close stomata?
Guard cells