A section of a DNA strand has a base sequence of TATGCGTGA. What is the complementary base sequence?
What is:
ATACGCACT
What is a mutation?
What is a permanent change in the DNA sequence of a cell.
What is transcription? Where does transcription take place?
What is:
Transcription occurs in the nucleus. DNA is used as a template and is copied into mRNA. mRNA then moves to the cytoplasm for the next stage of protein synthesis.
All organisms share the same 4 DNA nucleotide/bases. What are they?
What is:
Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine and Guanine.
What is biotechnology?
What is:
Biotechnology is the use of biological systems, living organisms, or parts of them to develop new products and technologies, with applications in healthcare, agriculture and industry.
What is being illustrated in the image?
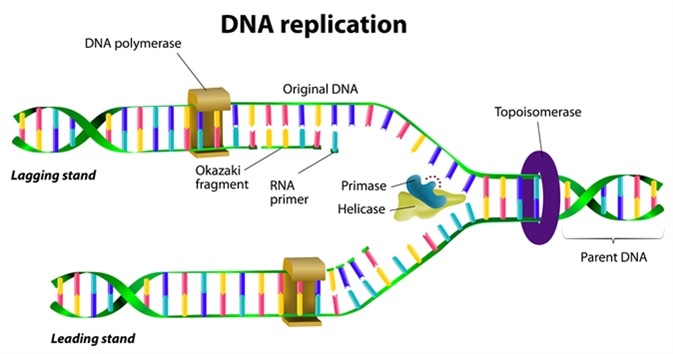
What is DNA replication.
What can cause mutations?
What is
Errors during DNA replication or from external factors like radiation or chemicals.
What process is illustrated in this image? 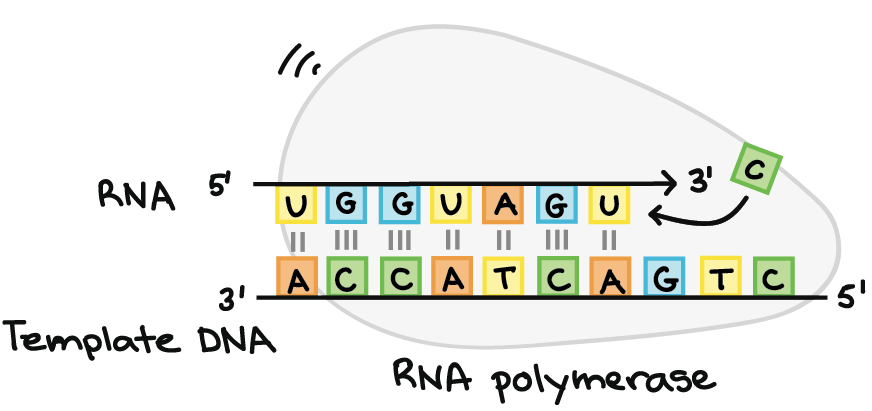
What is transcription.
Explain DNA Base pairing.
What is:
Adenine always pairs with Thymine
Cytosine always pairs with Guanine
What are GMOS
What are genetically modified organisms by humans, using genetic manipulation techniques.
What are the steps of DNA replication?
What is:
1st step: DNA unwinds by the enzyme helicase.
2nd step: Enzyme DNA polymerase adds new complementary strands to the separated DNA template.
3rd: New DNA strands using original DNA strand as a template.
Discuss the effect of mutations to the expression of a trait.
Changes in the DNA sequence, mutations, can be harmful, beneficial, or neutral.
Neutral means that some mutations will not cause a change in the protein produced.
Explain translation in protein synthesis.
What is when molecules of tRNA deliver amino acids, one at a time, to the ribosome, in the order specified by the triplet codons in the mRNA.
Peptide bonds join amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain (protein).
What does it mean when the genetic code is called redundant?
What is:
Most amino acids are encoded by more than one codon.
How is selective breeding similar to GMO?
What is humans control breeding and manipulate controls.
How are DNA and RNA similar and different.
What is:
They are both nucleic acids made of nucleotides.
They differ in sugar, structure and bases.
RNA is single stranded, has ribose as a sugar and no thymine base. It has base Uracil.
DNA is double stranded, has deoxyribose as a sugar and no Uracil as a base, but has thymine base.
What can introduce a new physical trait (phenotype) into a population?
What is a mutation.
What process is illustrated in the image?

What is translation.
Is a genetic code that is redundant a benefit? Explain your answer.
What is,
Yes, being redundant (having more than one code that specifies the same amino acid) a benefit.
Redundancy protects against mutation that might alter the final amino acid sequence.
What are some ethical issues related to genetic testing?
What is:
Discrimination by revealing health risks.
Describe the end product of DNA replication.
What is:
The end product of DNA replication is two identical DNA molecules, each consisting of one original (parental) strand and one newly synthesized (daughter) strand.
If a mutation changed the sequence of the code to a stop codon, what would happen?
What is:
The expression of the original codon would be changed and not expressed.
If a stop codon, such as UAA, UAG or UGA, occurs protein synthesis would stop prematurely.
In protein synthesis, what causes translation to stop?
What is:
Translation stops when the ribosome encounters a stop codon (UAA,UAG,UGA) on the mRNA
Discuss the genetic code and evolutionary relationships.
What is:
Scientist compare the sequences of bases between different species. This allows scientists to infer evolutionary relationships between species.
What is genomics?
What is:
It is the study of an organism's entire genome, which includes all of its genes and the interactions between them, as well as how they are affected by the environment.
It is a broader field of genetics.