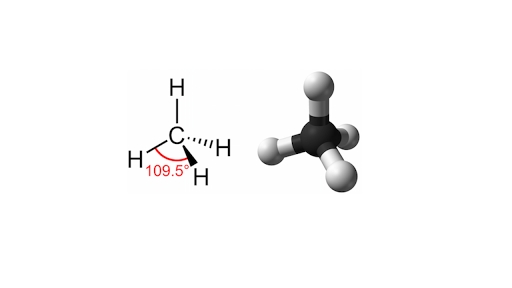
Why is carbon unique to life?
It's ability to make 4 bonds and create large amounts of molecules.
What is polarity?
What is the pull of electrons from one atom to another in a covalent bond causing the atoms to become slightly charged.
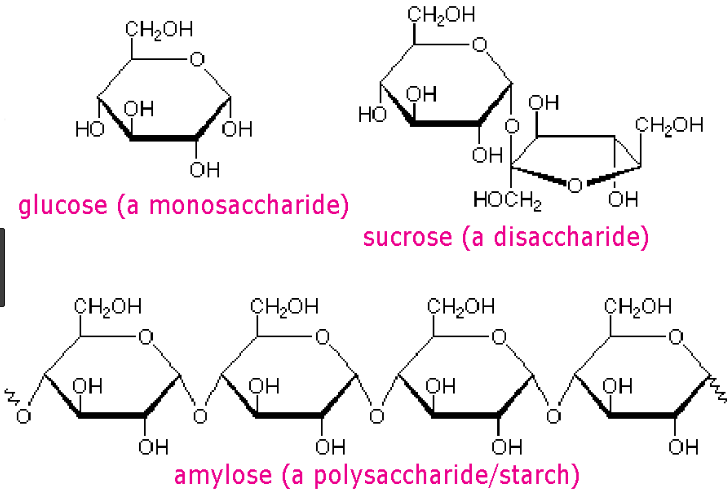
Difference between monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
What is polysaccharides (3+ monosacchrides) and disaccharides (2 monosaccharides) being made up of monosaccharides (a single saccharide).
Draw the structure of a saturated fatty acid.
What is CH2-(CH2)n- COOH

All the proteins produced in a cell.
What is a proteome?
What is a hydrogen bond?
What is the attraction of one partially positive hydrogen atom to the partially negative oxygen atom of another water molecule.
Draw a diagram of alpha-glucose.
What is C6H12O6 (with OH on C1 is down and C2 is down)

Calculate the BMI of a person who is 90kg and 180cm. Is this person underweight, normal, overweight, or obese.
What is 27.7 and overweight.

The function of Rubisco.
An enzyme that fixes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere during photosynthesis.
The artificial synthesis of urea from inorganic substances demonstrated....
The fact that both life and non-life are made from the same materials AND that the "vital factor" did not exist, at least not in the sense of 1800s scientists believed.
how does dipolarity and hydrogen bonding explain cohesion?
The attraction of the dipolar molecule to other dipolar molecules through hydrogen bonding. The hydrogen bonding then causes the substance to be cohesive, sticking more to itself than to other substances.
Name 2 examples of a monosaccharide, disaccharide, and polysaccharides each.
What is Monosaccharides: glucose, fructose, ribose, galactose Disaccharide: sucrose, lactose, maltose Polysaccharide: starch, glycogen, cellulose
Why are lipids more suitable for energy storage than carbohydrates?
What is containing more bonds and therefore more kcal per gram (9 vs 4) -- ie. the amount of energy released per gram is doubled. There is no water associated with the droplets in the cell so they are 6x more efficient at storing energy. It is ideal for long term but not for short term as it can not be broken down quickly.
Draw the basic structure of an amino acid, label the functional groups
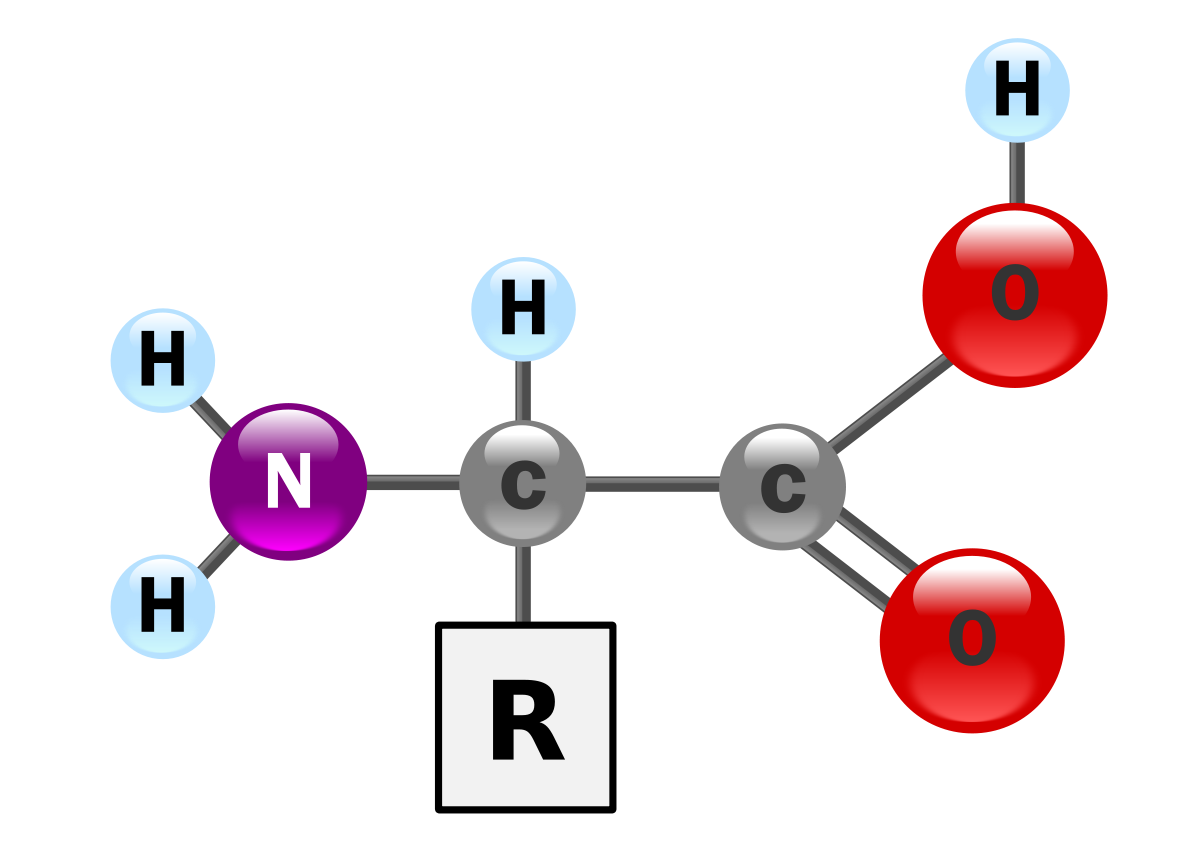 Amine group (NH2)
Amine group (NH2)
Carboxyl group (COOH)
Give two examples of anabolism and two examples of catabolism in your body.
Anabolism: protein synthesis, DNA synthesis, Photosynthesis, synthesis of complex sugars (starch/ glycogen).
Catabolism: digestion of food, cell respiration, digestion of complex carbons into monosaccharides.
How and why is cholesterol moved through the blood?
It is moved through lipoproteins due to their hydrophobic nature cholesterol can not move through the blood (hydrophilic), therefore it is packaged into special vesicles called lipoproteins were it is transported.

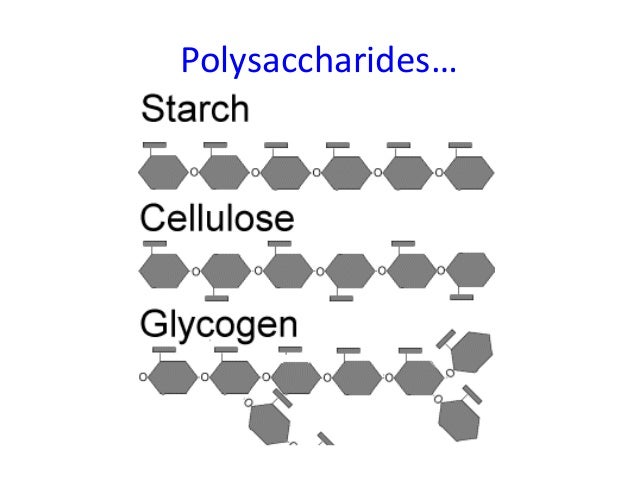
Describe the structural differences between glycogen and cellulose.
What is glycogen made up of alpha glucose, and alpha linkages. These include 1,4 and 1,6 bonds causing branched chains. Cellulose contains beta glucose molecules with beta linkages this causes the glucose molecules to flip every other monosaccharide and the chain to lay flat. It contains only 1,4 linkages.
Explain the similarities and differences between cis-monounsaturated fatty acid and a trans-polyunsaturated fatty acid.
What is the placement of the hydrogens on the double bonds in both the unsaturated fatty acids. Poly means many double bonds that have the Hydrogen atoms on opposite sides. Mono means one double bond with (cis), hydrogens on the same side of the double bond.
Name 5 functions of proteins within the body.
Any of the following are functions: enzymes (catalysis), muscle contraction, cytoskeleton, utensil strengthening, blood clotting, transport of nutrients and gases, cell adhesion, membrane transport, hormones, receptors, packing of DNA, Immunity...
Draw one example of a hydrolysis reaction using carbohydrates or proteins.


Explain the importance of water having a high heat capacity.
High heat capacity is the ability of water to maintain a stable temperature despite changes. The hydrogen bonds of water absorb large amounts of energy, but it requires a lot of energy to break, so the change in the temperature takes a long time to raise and lower.
Describe the structural similarities and differences between between amylopectin starch and glycogen.
What is similarities: both contain 1,4 & 1,6 alpha linkages with alpha glucose. Glycogen contains more 1,6 linkages than amylopectin.
Describe the health risks of lipids.
There is a positive correlation between trans fat and coronary heart disease, as well as some correlation to saturated fat, although this does not always fit. Polyunsaturated fat has links to have positive impacts in reducing the risk of coronary artery disease.
Draw a condensation reaction forming a peptide bond.
What is the removal of an OH (carboxyl group) and the H of an amine group to make water and bonding through the carbon and Nitrogen of the two different molecules to make a peptide bond.