Define inelastic collision
A type of collision where the objects either start together or end together
Define elastic collision
A type of collision where the objects start separate and end seperate
Define the term impulse
A change in momentum
300 points, what is the name of one of Mr.Plattel's pets?
Jelly, Bean or McCartney
Which layer is the most important to life in this soil horizon?
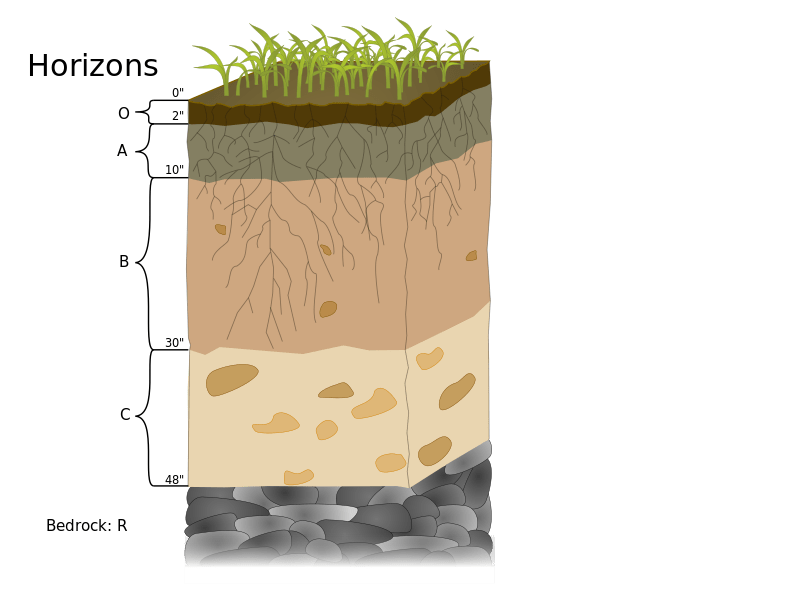
O (topsoil)
What happens to the total kinetic energy of the system after an inelastic collision
It decreases
What happens to the total kinetic energy of the system after an elastic collision
It remains unchanged
Two objects of equal masses are traveling in opposite directions at the same speed. Make a true statement about their momentums.
That they have equal momentums with different signs.
The process in which particles ( normally toxins), increase as the trophic level increases for a species
Biomagnification
Two objects have an inelastic collision. Object A is at rest and has a mass of 10 kg. Object B, which has a mass of 40 kg, collides with it while traveling at a speed of 3 m/s. What are the speeds of both objects?
m1*v1 +m2*v2=Vl(m1+m2)
m2*v2/(m1+m2) =Vl
40 kg * 3 m/s / 10kg +40 kg = V
0.24 m/s
A bowling ball traveling at a speed of 10 m/s hits a ping pong ball at rest. What will the speed of both objects be after the collision?
Bowling ball 10 m/s
Ping Pong ball 20 m/s
What is the change in momentum between t=0-3s?
45 kg* m/s
Which species is the primary consumer? 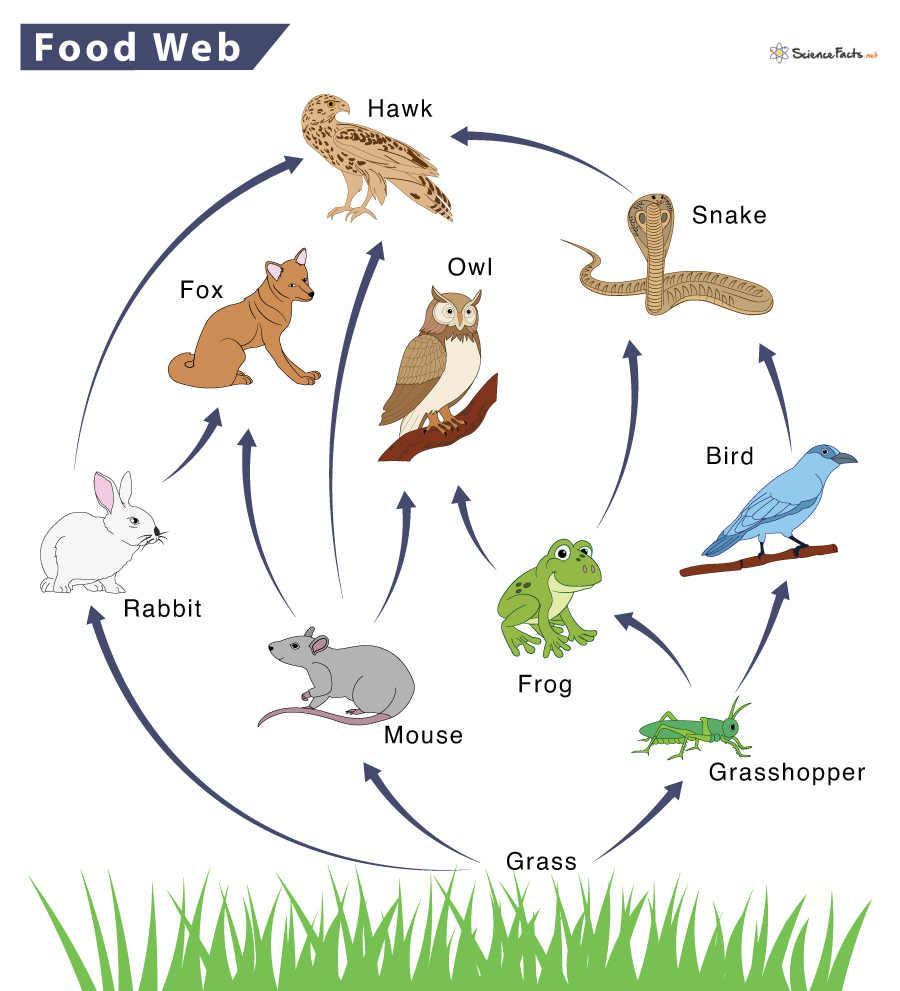
Mouse grasshopper or rabbit
A 5 kg cannon ball is loaded into a 300 kg cannon. When the cannon is fired, it recoils at -5 m/s. What is the cannon ball's velocity after the explosion?
Object 1 has twice the mass of object 2. If object 1 has half the speed of object 2 before the collision and object 2 has doubles it's initial speed after they collide what will the speed of object 1 be after this elastic collision?
1V1-V2=-(V1l-V2l)
1/2 V - V= -(X - 2V)
-1/2V=-X+2V
-2.5V=-x
X=2.5V
A ski lift has 4 chairs on it and is moving the chairs at a speed of 4 m/s. Chair 1 and 2 are both moving north and both have a total mass of 300 kg each. Chair 3 and 4 are moving south and have a total mass of 100 each. What is the total momentum of the system?
pnet=p1+p2+p3+p4
pnet= 2(4*300)+2(-4*100)
pnet=1600 kg*m/s
Two objects with identical masses, m1 and m2, have an elastic collision. The initial velocity of m1 is -9.0 m/s and of m2 is -3.0 m/s. After the collision, what will be the velocity of m1?
They trade velocities
m1= -3 m/s
At what latitude would you expect the biodiversity to be the greatest?
The equator. 0 degrees lat.
An object is sitting at rest and exploded into two parts. Part 1 has 60% of the mass while part 2 has 40% of the mass. How different will their velocities be?
V(m1+m2)=m1*v1l +m2*v2l
-(m1*v1l) =m2*v2l
m1/m2=v2/v1
So if the left is 0.6/0.4 their velocities will be v2=60% v1=40% of the total velocity.
In example if object is 1 is moving at a speed of 4 m/s object 2 HAS to be moving at a speed of 6 m/s.
A tennis ball is thrown at a wall at a speed of 40 m/s. The tennis ball bounces off of the wall and hits another wall. What will it's speed be after it hits the second wall?
A 1200 kg car slows from 40.0 m/s to 5.0 m/s in 2.0 s. What force was applied by the brakes to slow the car?
-21000 N
A 35 kg child moving at 5 m/s jumps onto a 40 kg sled that is initially at rest on a horizontal ice surface.
Determine the total momentum of the child-sled system after the child jumps onto the sled AND Determine the total energy of the child-sled system after the child jumps onto the sled.
175 kgm/s
200 J
Would you expect the biodiversity to be greater for a mountain or a flat land? (assume the same area)
Mountain