Draw the plasma membrane correctly labeling the hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions.

Enzymes speed up exergonic reactions by lowering _____ __ ________.
Energy of Activation.
Do plants perform cellular respiration?
Why do plants perform perform cellular respiration?
Yes. They need energy too!
The basic chemical equation for photosynthesis.
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O
What is inhibition?
Mechanisms that block or reduce the transmission of signals between cells or within a cell, preventing or altering cellular responses.
Does exergonic reaction release or require energy? Does an endergonic reaction release or require energy?
Exergonic Reaction - net releases of energy
Endergonic Reaction - net requirement of energy
The basic chemical formula for cellular respiration.
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP
Which comes first?
PS II or PSI
PS II
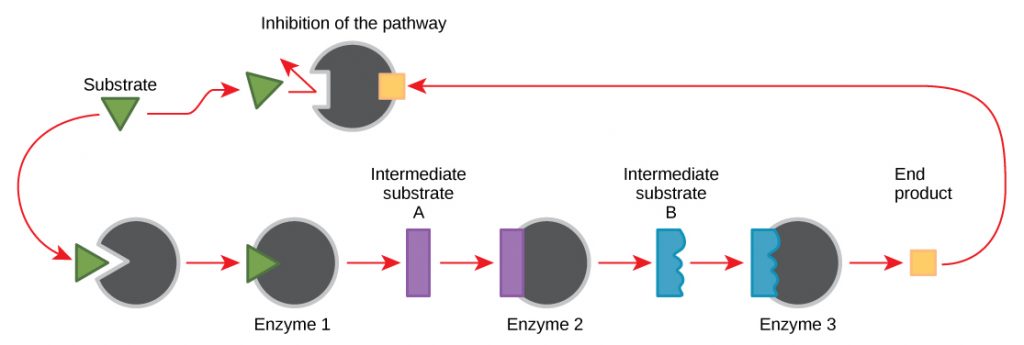
What is feedback inhibition?
A cellular control mechanism, in which the activity of an enzyme is inhibited by the end product of a biochemical pathway.
In 3 words or less for each; what happens to a blood cell in each type of solution:
Hypotonic, Isotonic, Hypertonic
Hypotonic - swells (hemolysis)
Isotonic - nothing (healthy)
Hypertonic - shrink (crenation)
Describe the difference between catabolic and anabolic pathways.
Catabolic reactions break down complex molecules into simpler ones, releasing energy, while anabolic reactions build complex molecules from simpler ones, requiring energy.
A crucial coenzyme and electron carrier involved in cellular respiration, carrying high-energy electrons to the electron transport chain, where their energy is used to generate ATP
NADH
Where is the proton-motive force generated during photosynthesis?
Thylakoid lumen
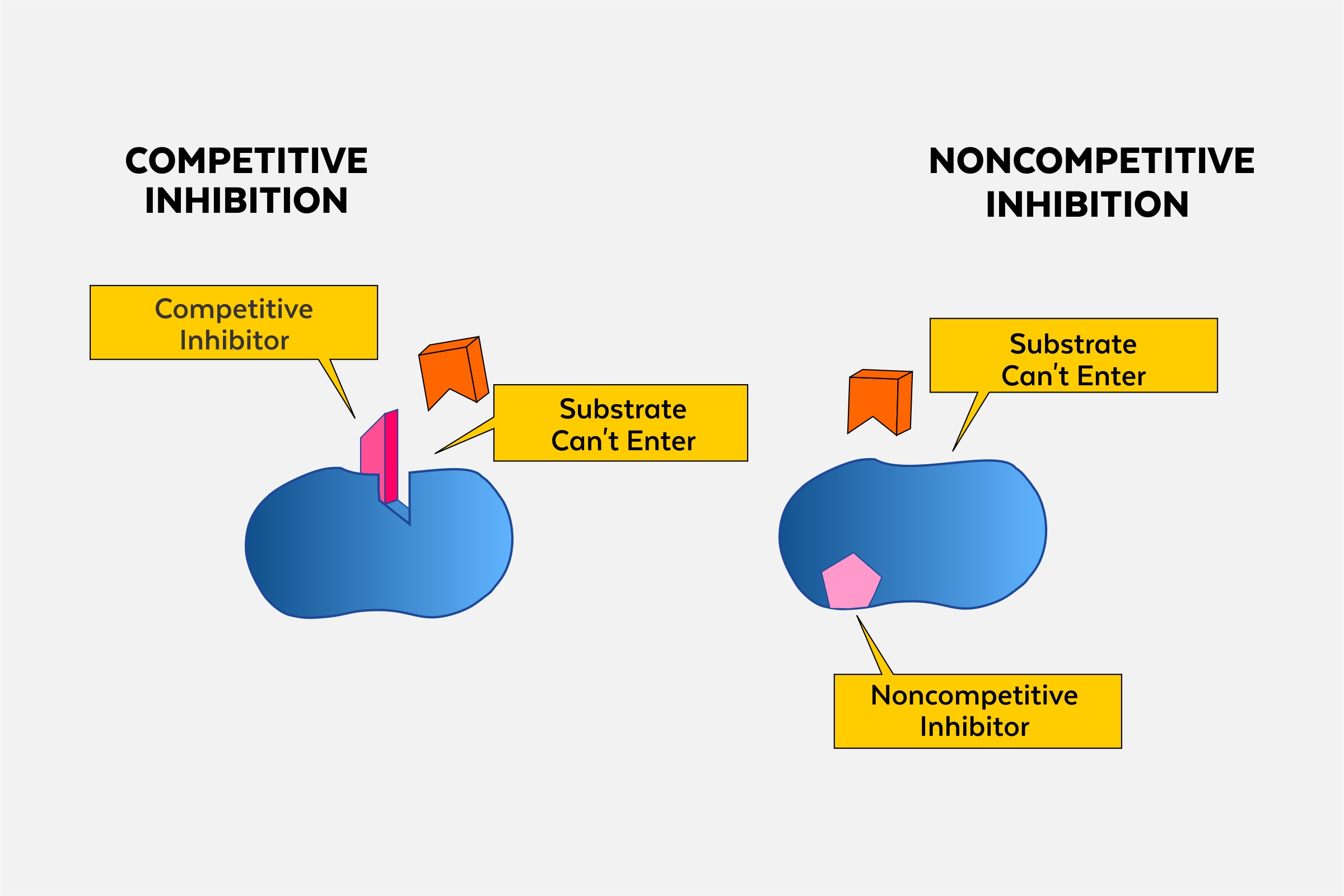
Competitive inhibition vs Non-competitive inhibition
Competitive inhibitors compete with the substrate for the active site, while noncompetitive inhibitors bind to a different site (allosteric site).
The purpose of each type of plasma membrane characteristics:
Cholesterol -
Phospholipid -
Integral Proteins -
Glycoproteins, glycolipids -
Phospholipids - forming the barrier
Proteins - facilitate the transport of molecules across the cell membrane
Cholesterol - high temperatures: stabilize the cell membrane by increasing its melting point; while at low temperatures: prevents them from interfering with each other
Glycoproteins, glycolipids - cell-cell recognition, adhesion, and signaling
Oxidize NADH to regenerate NAD+ without the presence of oxygen.
A crucial energy-carrying molecule and nucleotide similar to ATP, but with guanine instead of adenine, playing vital roles in protein synthesis and signal transduction.
GTP
What part of photosynthesis' process releases oxygen?
Splitting of water molecules.
Draw a diagram of non competitive inhibition.
What are 2 factors dictate the selective permeability of the plasma membrane?
- presence of transport proteins
- if the molecule large or small
- if the molecule polar or nonpolar
Protein synthesis is an example of a / an ______ pathway.
Why?
anabolic pathway
Synthesis!
What accepts electrons at the end of the electron transport chain?
Oxygen!
Using the 3 terms below correctly order the sequence for electron flow in photosynthesis.
- H2O
- NADH
- Calvin Cycle
H₂O → NADPH → Calvin cycle
How does protein kinase act in signal transduction?
Protein kinase adds a phosphate group to activate/inactivate proteins.