Antibody associated with neonatal lupus/congenital heart block?
What is Anti-Ro or Anti-La?
The blood test to ensure accurate Ca+2 levels
What is albumin?
The level of CK, via rhabdomyolysis, that warrants IVF to protect kidney function.
What is 5000 U/L?
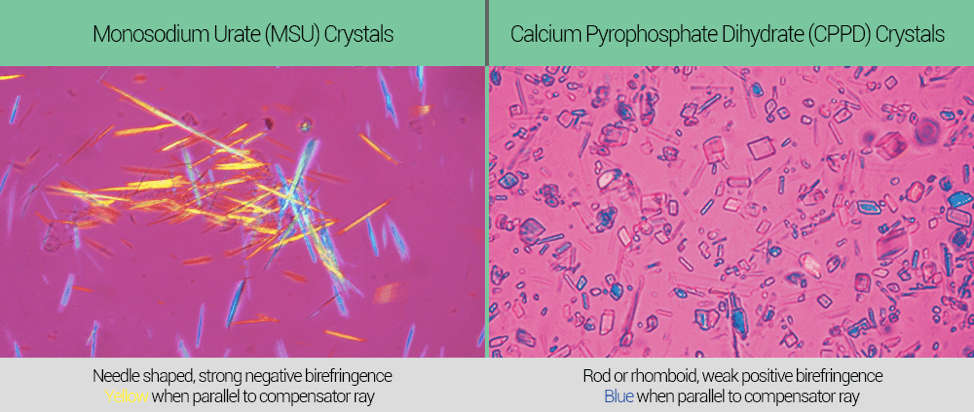
How do gout and pseudogout differ on microscopy (including shape of crystals)?
How do gout and pseudogout differ on microscopy?
Gout – Negative birefringent rods
Pseudogout – positive birefringent rhombus shaped crystals.
3 causes of elevated ALP outside of the liver/biliary system.
What is:
1.Bone
2.Intestinal Mucosa
3.Kidneys
4.Tumours
5.Pregnancy (Placenta)
List 3 atypical bacteria that cause CAP
What are:
Chlamydophila pneumoniae
Chlamydophila psittaci
Legionella pneumophila
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Coxiella burnetii
Francisella tularensis
Initial, rapid acting, medication (from fish) that may be administered for hyperCa+2 .
What is calcitonin?
4 units/kg every 12 hours
Tachyphylaxis occurs
Medication cause of transaminitis and CK elevation.
What are statins?
Acquired bone disease associated with hearing loss?
What is Paget’s Disease
•Osteoclast abnormality
–Accelerated bone turnover
•Features
–Asymptomatic
–Bone Pain
–Hearing Loss
•Labs: Elevated ALP
•Treatment: Bisphosphonates

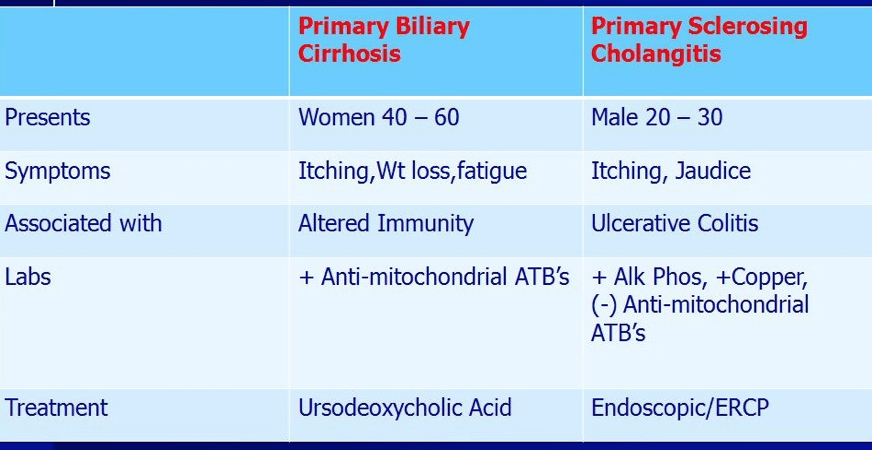
Two immune mediated causes of cholestatic liver injury
2 immune mediated causes of cholestatic liver injury.
1.PBC
2.PSC
3.IgG4 Cholangiopathy.
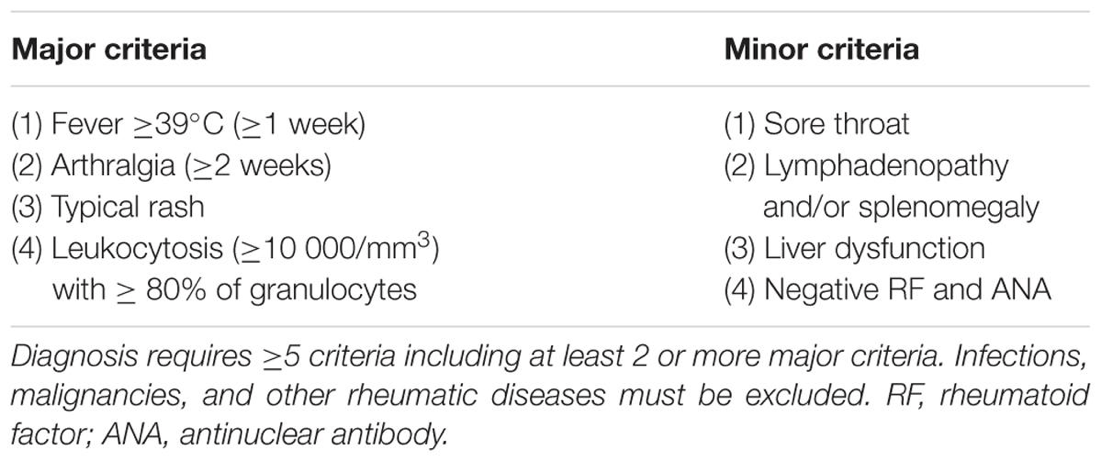
•Fever
•Lymphadenopathy
•Splenomegaly
•Ferritin 2000
•LDH/AST elevated
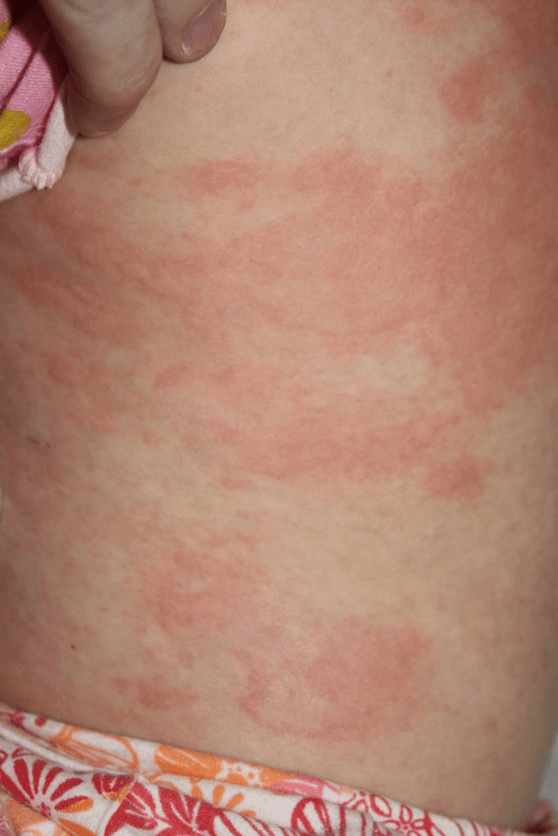
What is Adult onset Still’s disease?
The 3 mechanisms of malignancy related hypercalcemia.
What are:
1.Tumor secretion of PTHrP
2.Osteolytic metastases and
3.Tumor production of 1,25 (OH)2 Vitamin D?
Clinical Fx include autonomic instability, fever, delirium and rigidity.
What is Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome?
3 features highly suggestive of PMR
3 features highly suggestive of PMR – 3 of:
•Abnormal ESR (elevated)
•Age > 50
•Rapid response to steroids at moderate doses (10-20 mg daily)
•Proximal muscle pain and stiffness lasting >30 min in AM.
What are three manifestations of this disorder?
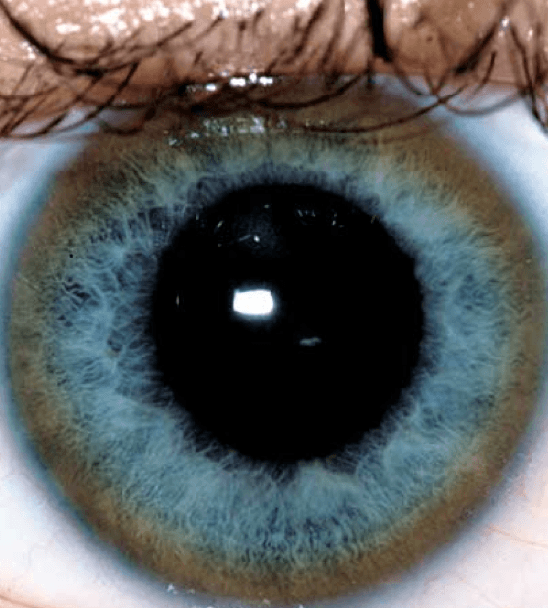
Wilson’s Disease
What are:
1.Neurologic Changes
•Asterixis, Parkinsonian, Dementia, Dsyarthria
2.Psychiatric
3.Hemolysis
4.Kayser Fleischer Rings
5.Fanconi Syndrome
6.Cardiomyopathy
7.Hypoparathyroidism
This kidney condition causes acidosis with hyperkalemia
What is Type 4 Renal Tubular Acidosis
(will accept Hyporeninemic Hypoaldosteronism)
Common Causes:
1.Diabetes
2.Heparin, Calcineurin Inhibitors, NSAIDS
3.Potassium Sparing Diuretics
4.Interstitial Nephritis
5.Adrenal Insufficiency
GI organ complication of hypercalcemia
What is pancreatitis?
4 Clinical Signs of Dermatomyositis.
What are:
1.Heliotrope Rash
2.Mechanics hands
3.Shawl sign
4.Gottron’s papules
5.Calcinosis Cutis
6.Nail Fold Telangiectasia
7.Periungal Erythema
8.Poikiloderma
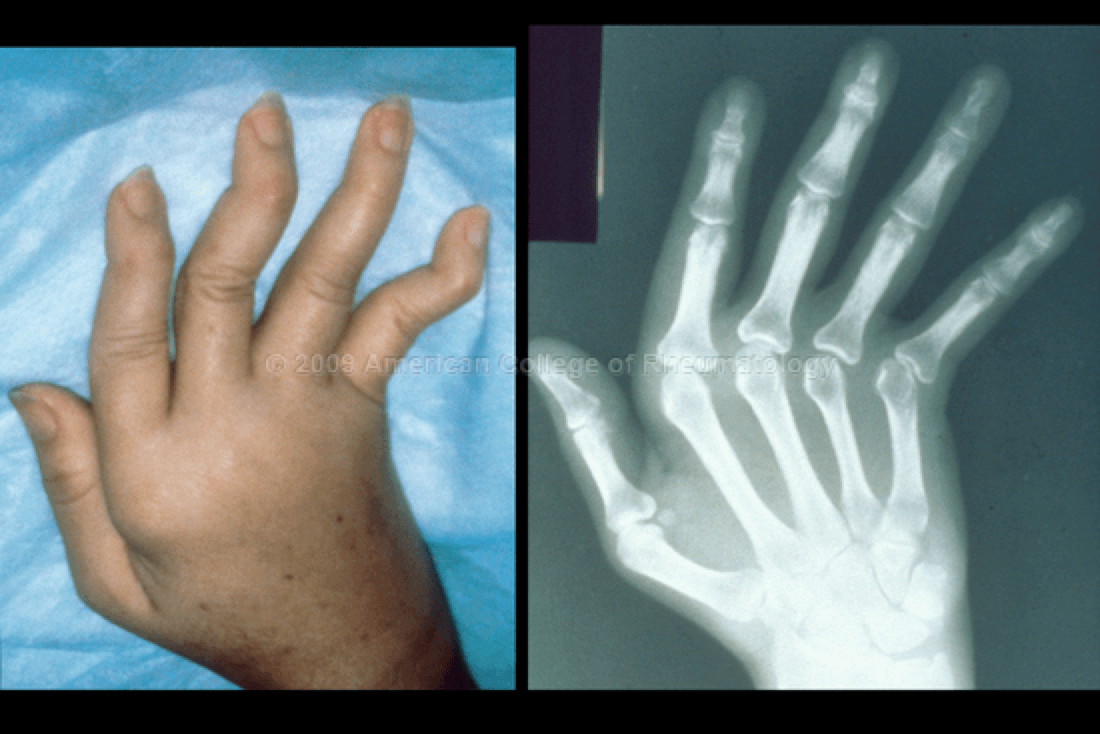
What is Jaccoud Arthropathy?
Four causes of ALT & AST elevation > 1000.
What are:
1. Shock Liver
2. Toxin (Tylenol)
3. Acute Viral Hepatitis (HAV, HBV)
4. Autoimmune
5. Budd Chiari Syndrome
6. Wilson’s Disease
7.Transient Stone
Most common causative agent of HIV cholangiopathy?
What is Cryptosporidium parvum?
HIV Cholangiopathy
•Biliary obstruction from infection associated strictures
•Cryptosporidium, CMV, Microsporidium, Cyclospora
•RUQ Pain + Diarrhea +/- Fever
•Diagnosis: ERCP
•Treatment: Endoscopic

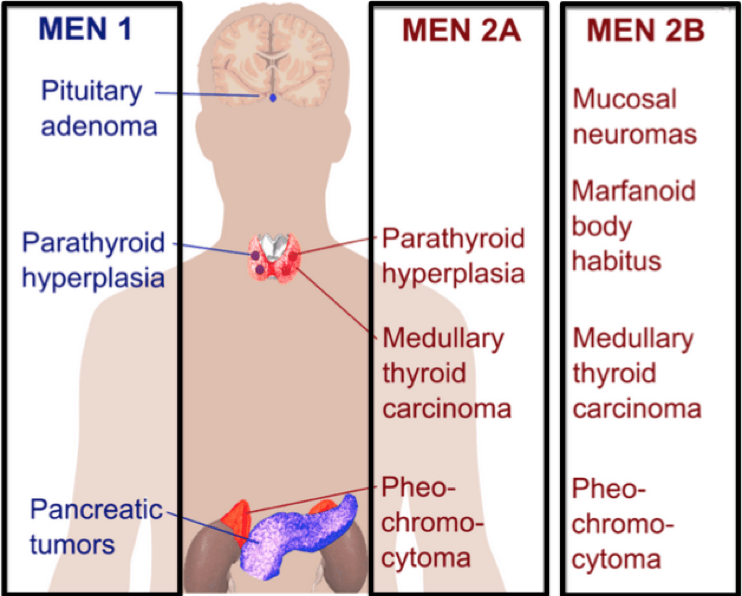
The 2 other organs involved in MEN1 (other than the parathyroid gland).
What is the pancreas & pituitary?
Name five laboratory abnormalities associated with rhabdomyolysis other than elevated Creatine Kinase?
What are:
1.Hyperkalemia
2.Hyperphosphatemia
3.Hypocalcemia
4.Hyperuricemia
5.Myoglobinuria
6.AKI
7.DIC
8.Metabolic Acidosis
9.Hypoalbuminemia
This microorganism causes migratory polyarthralgias of large joints.
Later in the disease course patients develop diarrhea, abdominal pain and may progress to a severe wasting syndrome.
What is Whipple’s Disease caused by Tropheryma whipplei?
Four cardinal manifestations:
•Arthralgias
•Diarrhea
•Abdominal pain
•Weight loss
Diagnosis: PAS-positive macrophages (biopsy)
Treatment: 1 year of antibiotics (TMP-SMX)
This medication has shown benefit in transplant-free survival in patients with ACUTE liver failure, regardless of cause.
What is N-Acetylcysteine?