Type of processing where external sensory input leads to cognition
Bottom Up
This blindness is characterized by missing parts in our visual field, like a cyclist when someone is driving. They don't see the bike because they are focused on cars.
inattentional blidness
Not using reason as a basis for behavior.
The decision has no mathematical basis.
Gambler's fallacy
Law of:
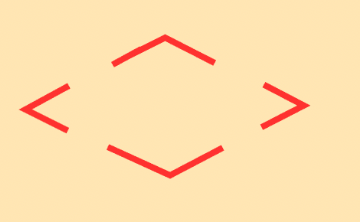
closure
g=
general intelligence
The most occurring piece of data in a set
mode
Type of processing where prior expectations and experiences prime thoughts
Top-down
This type of blindness is when we fail to see changes in the environment or image
change blindness
This is the tendency for the brain to value new information that supports existing ideas, sometimes called belief bias.
We see what we want to see
Confirmation Bias
Law of:

Figure & Ground
This is an image of what type of distribution:
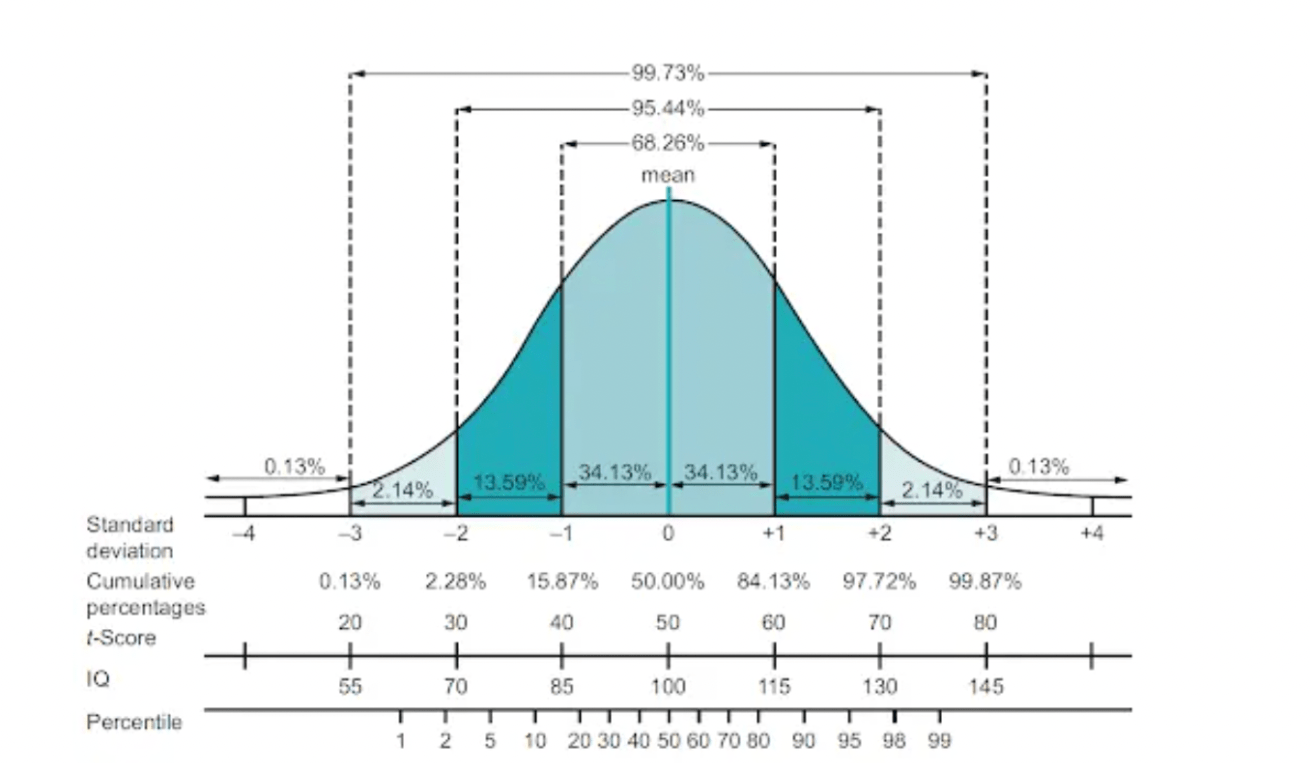
Symetrical or normal. Binet's IQ test uses this standard bell curve.
The center number in a data set that has been organized from lowest to highest
median
Reading uses which two types of processing?
Top & Bottom
binocular cue when our eyes look inward as an object nears our face
convergence
This is the tendency to interpret past events as more predictable than they actually were.
Hindsight bias
Law of:
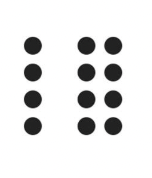
Proximity
This type of thinking considers all possible solutions, but is not great for subjective topics. It is time-consuming.
algorithim
What does a negative 3 Z-score represent?
three standard deviations below the mean
Perception is influenced by... names at least three
culture, context, schema
Monocular cue: Closer objects are clearer, and further objects are fuzzier
reletive clarity
Oh I already put so much in, I might as well see it through
Sunk cost fallacy
The Law of:
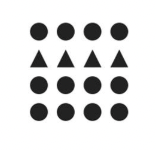
Similiarity
Short-cut thinking and decision-making that uses schemas
heuristics
The full list of data from lowest to highest
range
Perception style that is more common in Eastern cultures and looks at an object/ scene as a whole
Holistic
Monocular cue: Closer objects are larger, and further objects are smaller
relative size
is a cognitive bias where an individual's subjective confidence in their own abilities, knowledge, or judgment is greater than their objective accuracy or performance. This can lead people to take excessive risks, ignore contrary evidence, and make poor decisions across various aspects of life, from investing to personal relationships.
Overconfidence bias
Which psychologist is famous for implementing concepts based of the sum being more than the parts?
Gestalt
thinking about thinking
metacognition
This statistic is most easily skewed by outliers
mean