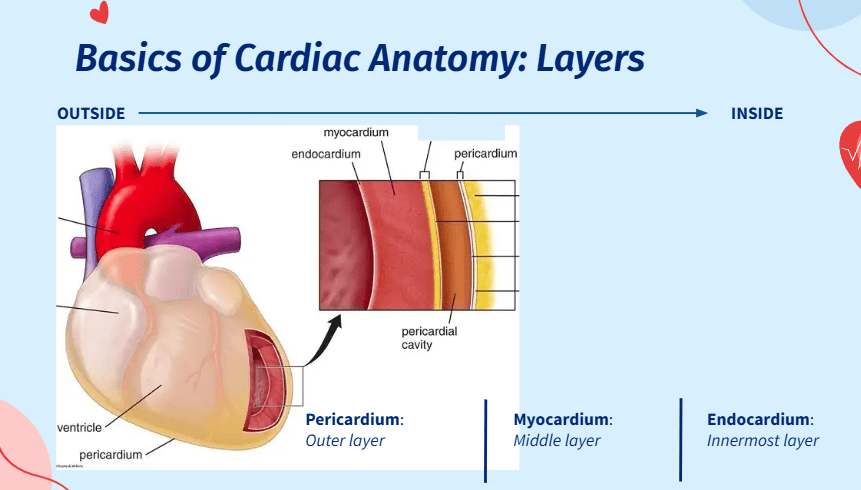
This is the tough outer layer covering the heart and major vessels.
What is the pericardium?
This plane slices the body into right and left (blue)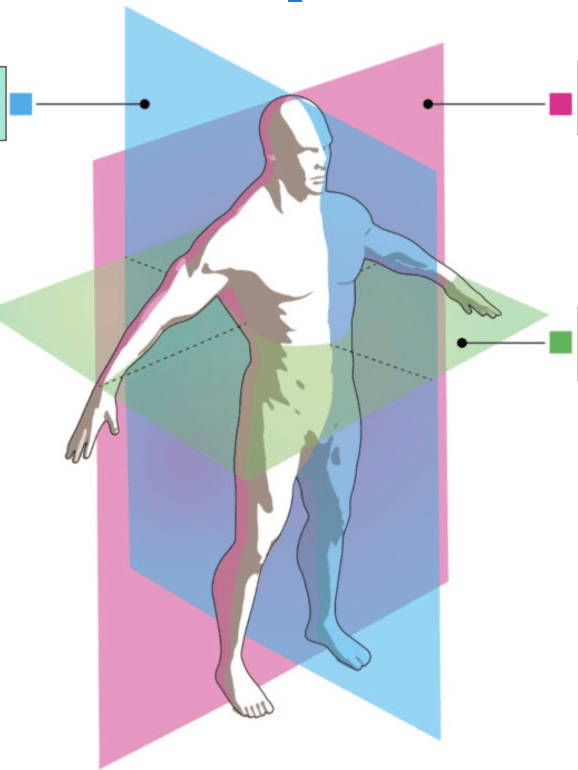
What is sagittal?
This helps increase conduction velocity along the nerve axons
Myelin sheath
This is the ratio of compressions:breaths given in standard adult CPR.
What is 30 compressions to 2 breaths?
This vessel carries oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of your body, including muscles, organs, etc.
What is the aorta?
This is the pacemaker of the heart.
What is the sinoatrial node?
Name this imaging plane
Consists of the brain and spinal cord
Central nervous system
This is the lab you would order if you want to look at a patient's white blood cell counts.
What is a CBC (complete blood count)?
This condition can cause headaches, nausea, vomiting, blurred vision
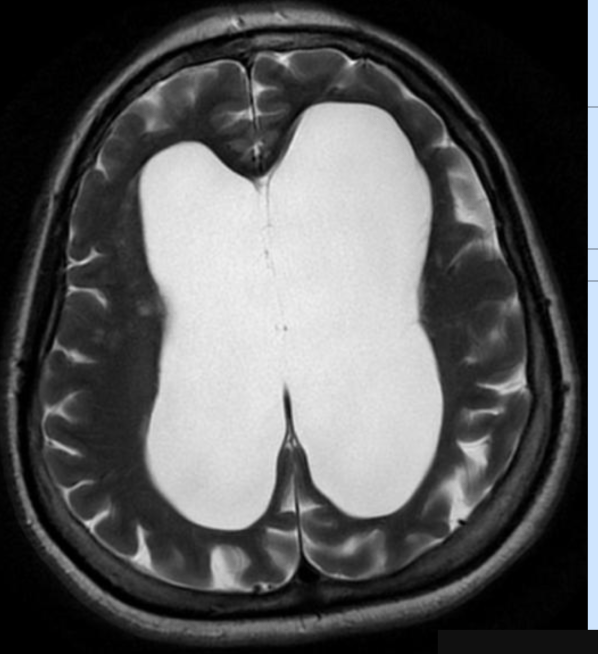
Hydrocephalus
These valves close during diastole.
What are the semilunar (aortic and pulmonic) valves?
This lung is highlighted (R or L)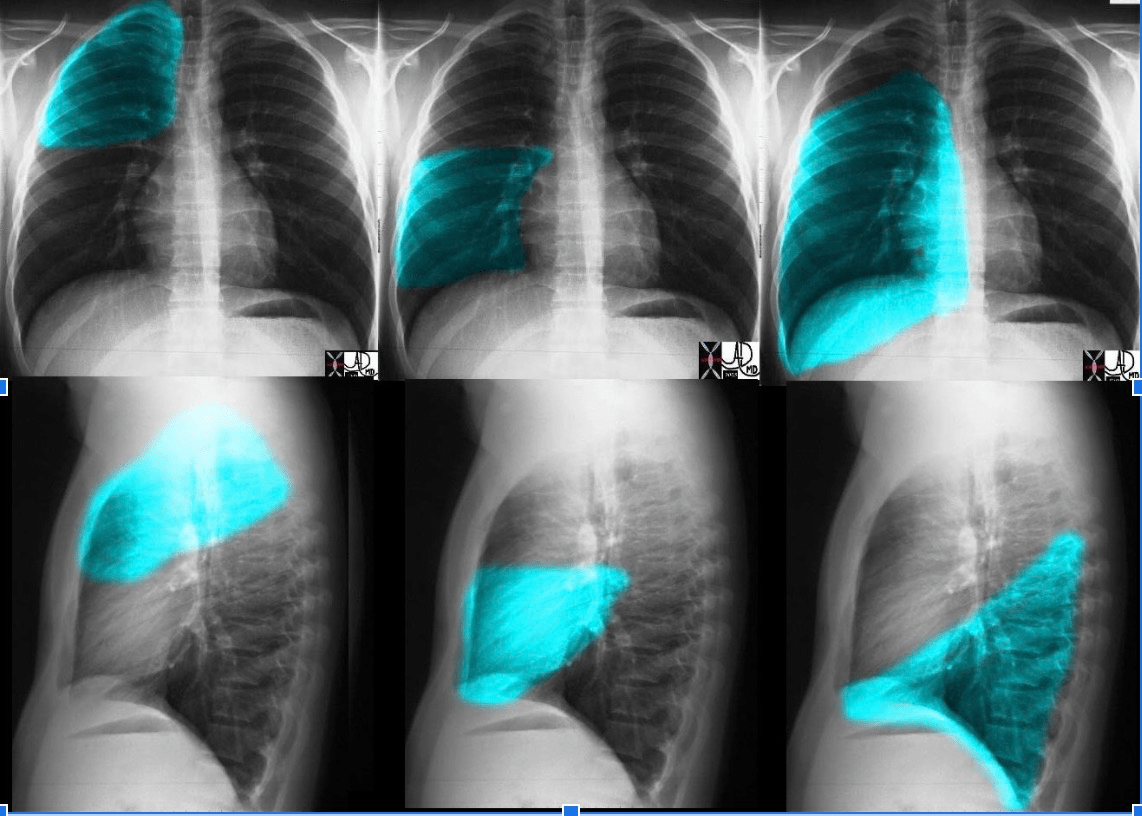
Right
This lobe of the brain controls vision
Occipital lobe
This is the correct rate of chest compressions per minute during CPR.
What is 100-120 BPM?
The complex that denotes ventricular depolarization on an EKG
What is the QRS complex?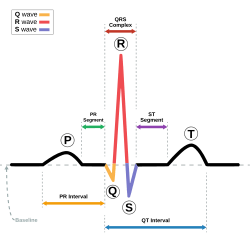
This value represents the amount of peripheral resistance the heart overcomes during systole.
What is afterload?
Name this condition
Tension pneumothorax
This part of the brain controls coordination and balance
Cerebellum
This is the valve you hear when auscultating at site B.
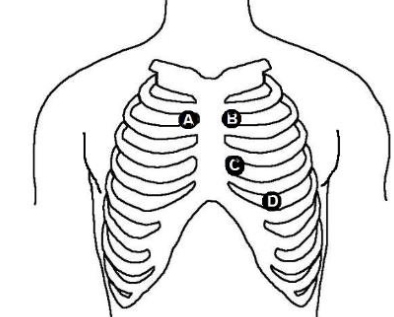
What is the pulmonic valve?
This is the structure that lines the lungs
What is the visceral pleura?
The HR, in BPM, of this EKG?
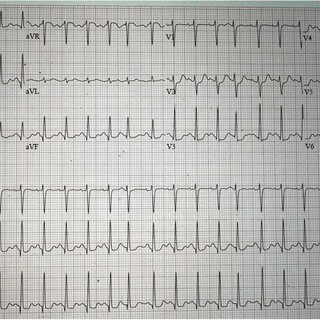
What is 150 BPM?
What pathology is shown? Be specific.
What is *Acute* subdural hemorrhage?
This cranial nerve controls facial sensation
Trigeminal nerve (CN V)
What is the treatment for an acute asthma attack?
What is albuterol (short-acting beta-agonist)?
What type of lung diseases have an increased residual volume?
What is obstructive lung disease?