Who is your favorite Saja boy?
Only acceptable answer: Jinu
best treatment for lumbar disc herniation
conservative care
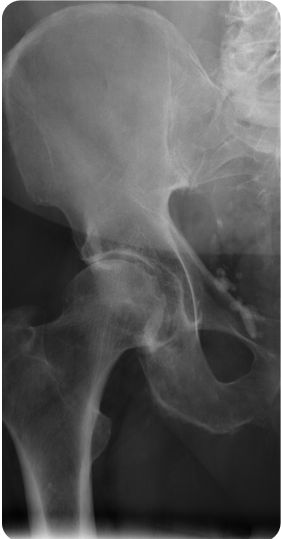
A 69-year-old woman presents to her PCP w/ increasing right hip pain and stiffness x the past 6 months, worsened upon walking and in the evenings. PMH is notable for HTN. ROS is neg for fevers, back pain, sensory loss, or weakness. VSS. PE is notable for slight pain and mildly decreased internal rotation of the right hip when flexed. There is no associated lower extremity weakness or sensory loss. A hip radiograph is performed as pictured above. What is the most likely diagnosis for this patient’s hip pain?
osteoarthritis
Which of the following is an important element of nonpharmacologic treatment of osteoarthritis in the hips or knees
You're on the sidelines of a high school soccer game. A 17 year old soccer player attempts a stepover pull. He falls after rapidly changing direction on one foot. What physical exam maneuver would best evaluate for the most probably injury
Lachman (anterior drawer)
what is one of the most common causes of cervical radiculopathy
cervical spondylosis (degenerative changes), disc herniation
A 65-year-old man presents to your clinic with a chief complaint of worsening low back pain over the past 2 weeks. He reports no specific trauma or injury, numbness in the buttocks or perineum, or loss of bowel or bladder function. The pain is localized to his left lower back, and he reports that it radiates down his posterior thigh to about the level of the knee. Physical examination reveals some muscle tension around the L3 region on the left and a positive supine straight leg raise test. What is the most appropriate treatment option for this patient?
A 25-year-old man is in the recovery room after a closed reduction of a right displaced tibial fracture. He reports the sudden onset of intense pain in his right leg. He describes the pain as a burning sensation and also reports a decreased sensation on the anterior aspect of his foot. Blood pressure is 99/65 mm Hg. You examine the leg and note a pallor and a tense feeling of the tissues. Surgery is consulted, and they obtain pressures of the leg, including an anterior compartment pressure of 36 mm Hg. What is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
fasciotomy!
A 58-year-old man presents to the clinic with bilateral hand and wrist pain that has been progressively worsening for 6 months. He says the pain is accompanied by morning stiffness that now lasts up to 45 minutes, which slows him down when getting up for work. On PE, you note the proximal joints of both hands are swollen and tender. What is the most likely diagnosis?
RA
Falls in older patients presents a severe health hazard. Fortunately, clinicians can prevent falls by assessing patients for fall risk. Which of the following instructions are best supported by the CDC’s stopping older adults’ accidents, deaths, and injuries toolkit for evaluation of fall risk?
Stand up from a seat and walk 10 feet forward and return back in ≤ 12 seconds ( the timed up and go (TUG) test)
most common cause of acute shoulder pain?
supraspinatus or rotator cuff tendonitis
What is a common cause of back pain in young athletes that worsens with lumbar extension?
spondylosis
 A 17-year-old girl presents after a witnessed generalized tonic-clonic seizure. She reports pain in her right shoulder and difficulty moving her right arm. You order a shoulder radiograph. After obtaining the image above, you are told the patient could not tolerate the positioning required for all three views of the shoulder. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A 17-year-old girl presents after a witnessed generalized tonic-clonic seizure. She reports pain in her right shoulder and difficulty moving her right arm. You order a shoulder radiograph. After obtaining the image above, you are told the patient could not tolerate the positioning required for all three views of the shoulder. What is the most likely diagnosis?
 posterior shoulder dislocation
posterior shoulder dislocation
A 44-year-old man presents to his PCP for continuous knee, hip, and shoulder stiffness and pain in his hands, arms, legs, and neck over the past year. He also has felt fatigued and has had difficulty concentrating almost every day at his sales job. He has intermittent headaches. He has tried acetaminophen and ibuprofen, but they have not improved his symptoms. He reports no mood changes but feels helpless about his symptoms and pessimistic about his pain improving. On PE, he has tenderness to palpation in all muscle groups. All joints have a full ROM without crepitus or swelling. Lab studies include CBC, LFTs, ESR, CK, and TSH. All are WNL. What is the most appropriate initial treatment, in addition to education about his condition?
Treatment is focused on patient education and quality-of-life improvements, such as exercise. Psychological therapies are recommended for patients without initial improvement, a concurrent mood disorder, or maladaptive coping strategies. These include cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), pharmacological therapy for pain or sleep (e.g., amitriptyline, duloxetine), and rehabilitation programs. CBT has been specifically shown to help improve catastrophizing behavior, which presents as helplessness, pessimism, rumination about pain-related symptoms, and magnification of pain. Pharmacological treatment with NSAIDs, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI) are not generally recommended.
what does varus and valgus stress test evaluate for?
MCL, LCL
most common cause of acute neck pain?
cervical strain
A 32-year-old woman presents to the clinic with 3 weeks of low back pain. It began after she lifted her toddler out of her crib, and it has never happened to her before. For the past week, she has been resting and taking one tablet of over-the-counter ibuprofen twice a day without relief. Her past medical history includes gestational diabetes and well-controlled hypothyroidism. Her only medication is levothyroxine. She has no recent trauma or bowel or bladder dysfunction. Vital signs are within normal limits. On physical examination, there is tenderness to palpation with evidence of spasm along the right lumbar paraspinal musculature and restricted range of motion of the lumbar spine due to pain. The remainder of the exam is normal. What is the most appropriate imaging test at this time
nothing
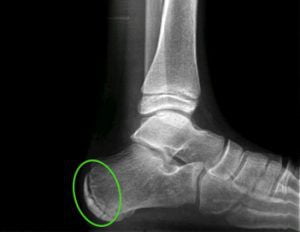
A 9-year-old boy presents to the clinic with a two-week history of bilateral heel pain. He plays soccer and basketball but denies injury to his feet. Physical examination reveals tenderness to direct palpation over the calcaneal apophysis bilaterally. No overlying erythema or warmth is noted. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?

A 39-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician for 3 months of morning stiffness in her hands, wrists, and feet. The stiffness improves with activity and ibuprofen but has been gradually worsening over time. On PE, there is tenderness and swelling of the second through fifth metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints of both hands and wrists. There is also tenderness and swelling of the third through fifth metatarsophalangeal joints bilaterally. Lab findings reveal the presence of RF and anti-ccp Abs. The patient is started on MTX. How should disease activity be routinely monitored over time?
Disease activity should be assessed on a routine basis over time, and the American College of Rheumatology recommends monitoring several disease activity measures. Some examples of these measures are the 28-joint Disease Activity Score, which counts the tenderness and swelling at 28 specific joints and trends either the erythrocyte sedimentation rate or the C-reactive protein, and the Clinical Disease Activity Index, which also counts tenderness and swelling at 28 specific joints and includes both patient and clinician global assessment of disease activity. Disease activity measures have been shown to accurately reflect disease activity and its severity, have remission criteria, and are feasible to perform in clinical settings.
name one PE maneuver used to evaluate for rotator cuff impingement
Neer, Hawkins
what is the spurling maneuver specific for?
cervical root compression
forward flexion of spine improves symptoms in this condition
spinal stenosis
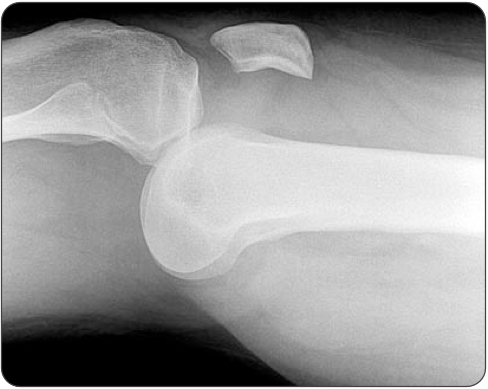 A 31-year-old man was the restrained passenger involved in a head-on motor vehicle collision, and he presents with an extremity injury. An X-ray is obtained and shown above. Which of the following is considered a hard sign of vascular injury in this patient?
A 31-year-old man was the restrained passenger involved in a head-on motor vehicle collision, and he presents with an extremity injury. An X-ray is obtained and shown above. Which of the following is considered a hard sign of vascular injury in this patient?
acceptable answers: absence of a pulse, pulsatile bleeding, rapidly expanding hematoma, an audible bruit, or a palpable thrill
list 3 extraarticular manifestations of RA
skin (nodules), pulm (fibrosis), cardiac (pericarditis , eyes, ACD, vasculitis
what does the lift off test evaluate?
inability to bring hand off their back indicates internal rotation defect, which could indicate subscapularis defect