What is the primary role of physical therapists in screening patients?
Early detection of medical conditions and determining whether the issue falls within their scope of practice.
Provide an example of a Schedule II drug
Morphine, Codeine, Fentanyl
What is the polarity of a Cathode?
NEGATIVE
What imaging modality is commonly used to evaluate bone fractures?
X-ray
What type of imaging is shown in the photos below?
What is an X-ray?
Should describe an psychiatric condition (bipolar, depression, etc.
What is the difference between pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics?
Pharmacokinetics is what the body does to a drug (absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion); pharmacodynamics is what the drug does to the body.
What is the uninterrupted bidirectional flow of ions or electrons and must change direction at least
one time per second?
What type of imaging provides detailed views of soft tissues like ligaments and tendons?
MRI (best), CT scan another option
What viscera refers to the region indicated below?
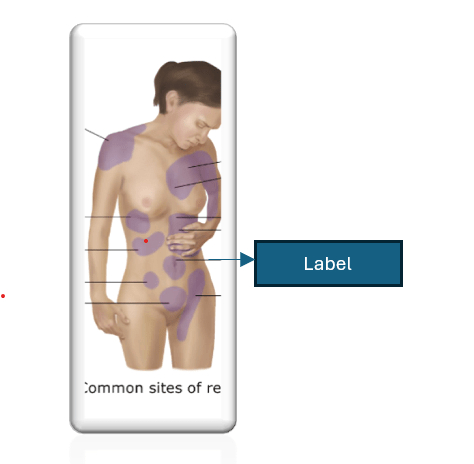
What is the small intestine or the appendix?
What is the significance of yellow flags in physical therapy, and what tools can help identify them?
Yellow flags indicate psychosocial risk factors that may hinder rehabilitation. Tools like OSPRO-YF, Örebro Musculoskeletal Pain Questionnaire, and Keele STarT Back Tool can help identify them.
What is the first-pass effect?
The metabolism of a drug by the liver or gut wall before it reaches systemic circulation, reducing bioavailability
What are some key radiographic features you would expect to see in someone with osteoarthritis?
joint space reduction, osteophytes, cartilage reduction
What type of imaging is shown in the photos below?
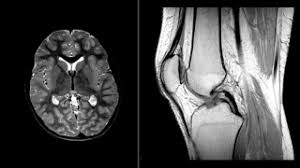
What is an MRI?
Name 4 constitutional signs that may indicate a need for further medical evaluation.
Fever
Diaphoresis
Sweats
Nausea
Vomiting
Diarrhea
Pallor
Dizziness/syncope
Fatigue/Weakness
Weight loss
What does the term "therapeutic index" refer to, and why is it important?
The ratio of a drug’s toxic dose to its effective dose; it indicates drug safety
Name 4 contraindications for TENS/IFC
Pacemaker or other active implants (local)
Pregnancy (local)
Carotid sinus (local)
Damaged skin (local)
Lack of normal skin sensation (local)
Impaired cognition
Thrombosis or thrombophlebitis
Hemorrhage (local)
Malignant tumors (local)
Eyes, internally, and on reproductive organs
What is the difference between T1 and T2 imaging in MRI scans?
T1 shows fat as bright and fluid as dark, while T2 shows fluid as bright and fat as dark.
What type of imaging is represented in the photo below?
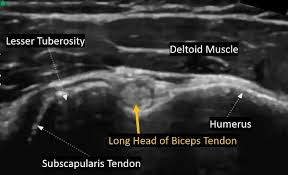
What is an ultrasound?
What follow-up steps should a PT take when identifying red flags in a patient?
Perform a thorough review of systems, document findings, and refer to a qualified healthcare provider.
Why might a patient experience side effects when switching from a brand-name drug to a generic drug?
Individual variability in response due to differences in inactive ingredients or bioavailability.
What is the gate control theory?
Selective stimulation of the large-diameter
afferent fibers (Aβ) can result in a gating, or
blocking, of noxious afferent input from
smaller-diameter unmyelinated
nociceptive C fibers and small myelinated
A-delta fibers (Aδ) at the level of the spinal
cord.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of CT scans compared to MRI? Name at least 3
Advantages: faster imaging, better for bone detail. Disadvantages: higher radiation exposure, less detail for soft tissues.
What viscera refers to the region indicated below?
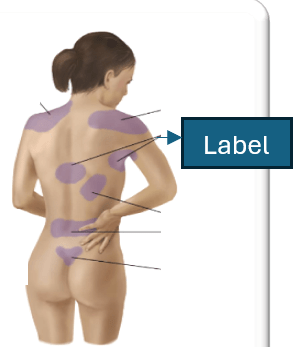
What is the duodenum?
(The original picture refers to a Penetrating duodenalulcer)