A varying parameter that represents information.
A _______ is a varying voltage that represents sound.
What is Signal?
The periodic variations in air pressure radiating from an object vibrating between 20 and 20,000 Hertz (Hz).
What are Sound Waves?
The unit of measurement of audio level.
What is Decibel (dB)?
A recording that contains noise, distortion, or leakage (bleed).
What is a Dirty Recording?
All frequencies are being reproduced at equal levels.
A device that records sound without affecting the tonal balance of the instrument is said to have a _____________________, or a speaker system that accurately reproduces sounds without changing the tonal balance of the source.
What is a Flat Frequency Response?
Refers to two channels of audio represented as Left and Right (LR).
Can be played over two or more speakers.
What is Stereo?
The degree of progression in the cycle of a wave, where one complete cycle is 360 degrees.
What is Phase?
The rise and fall of volume of one note.
Attack: The beginning of the note. The first portion of the note’s ________ in which a note rises from silence to its maximum volume.
Decay: The portion of envelope of a note in which the ________ goes from maximum to some midrange level.
Sustain: The portion of _________ of a note in which the level is constant.
Release: The final portion of an ________ in which the note falls from its sustain level back to silence.
What is Envelope?
An object that is created to absorb low frequencies.
Place these objects in the corner of recording rooms to reduce the amount of bass reproduced in the room.
What is a Bass Trap?
Referring to the positive or negative direction of electrical, acoustical, or magnetic force. Two identical signals in opposite polarity are 180 degrees out of phase with each other at all frequencies. Two microphones placed in opposite directions will record in opposite phases, so the polarity must be switched on one microphone to achieve desirable results.
What is Polarity?
An ______ signal contains no digital processing.
What is Analog?
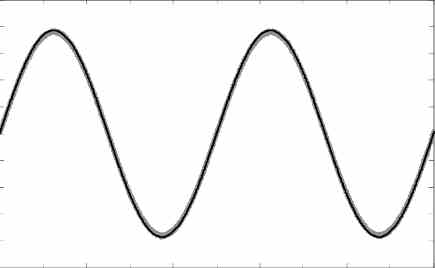
What is a Sine Wave?
Natural ___________in a room is a series of multiple sound reflections that make the original sound persist and gradually die away or decay.
What is Reverb (Reverberation)?
A stationary waveform created by multiple reflections between opposite room surfaces.
At certain points along the ________, the direct and reflected waves cancel and at other points they add together. These waves typically occur below 300 Hz (upper bass range) making bass sounds either louder or weaker. The most present frequencies are called Room Modes.
What is a Standing Wave?
The level difference in decibels between the signal level and the noise floor.
60 dB is good
70 dB is Fair
80 dB or greater is excellent
What is Signal-to-Noise Ratio (S/N or SNR)?
To combine two or more different signals into a common signal.
What is Mix?
DAILY DOUBLE!!!
The lowest frequency in a complex wave.
What is Fundamental Frequency?
The spreading out of sound waves when they strike a convex or convoluted surface or when they go through a small opening.
What is Diffusion?
The occurrence of excessive low frequencies in a room that create an unnatural sound. These frequencies can make the room sound “boxy” or “muddy”.
What is Coloration?
__________ is caused by recording at too high a level, using improper mixer settings, components failing, or vacuum tubes distorting.
This creates a change in the waveform, causing raspy or gritty sound quality, causing new frequencies to occur that were not present in the input signal.
What is Distortion?
The person in the recording or mixdown session who operates the recording equipment, mikes the instruments, and documents the session. This person maintains the sound quality and provides sound treatments that the producer or musicians request.
What is a Recording Engineer?
Tone quality. The subjective impression of spectrum and envelope. The quality of sounds that allows us to differentiate it from other sounds. For example, if you hear a trumpet, a piano, and a drum, each has a different timbre or tone quality that identifies it as a particular instrument.
What is Timbre?
The psychoacoustical phenomenon in which the subjective frequency response of the ear changes with the program level. Because of this effect, a program played at a lower volume than the original level subjectively loses low-and-high frequency response.
What is Fletcher and Munson?
An area of low pressure in a standing wave. In these areas, the bass frequencies will sound quieter or non-existent.
What is an Antinode?
The process of achieving the highest signal-to-noise ratio when input monitoring.
You want the strongest signal without distortion in your recording chain to achieve a clean recording.
What is Gain Staging?