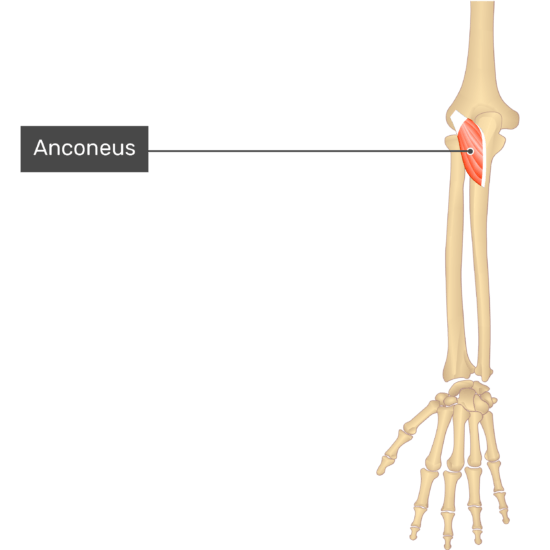
The triceps brachii and anconeus both extend the forearm at the elbow joint. What are there origins and insertions?
Triceps Brachii
- Origin: Lateral Head – Posterior surface of the humerus, superior to radial groove. Long Head - Infraglenoid tubercle of scapula. Medial Head – Posterior surface of the humerus, inferior to the radial groove.
- Insertion: Olecranon of ulna

Anconeus
- Origin: Posterior aspect of lateral epicondyle of the humerus
- Insertion: Olecranon and proximal end of body of the ulna
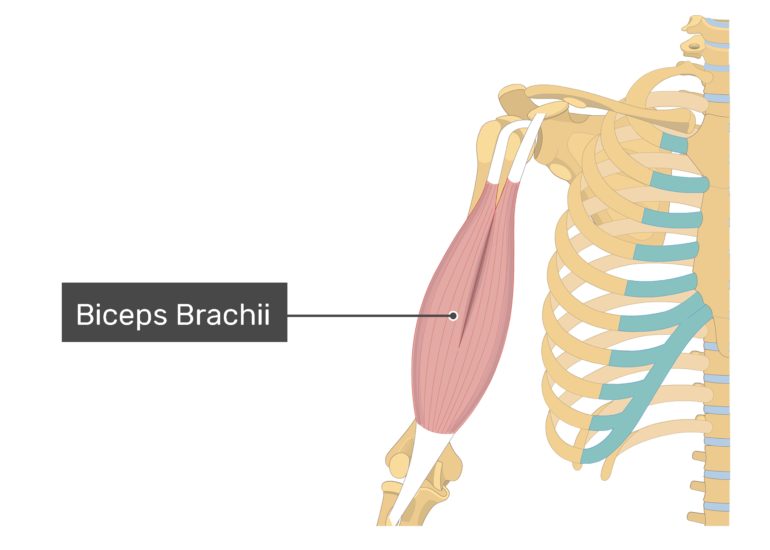
The biceps brachii has two heads. What are there origin and instertions.
Bonus (100): What is the insertion the brachioradialis? Origin? Action?
Biceps Brachii
- Origin: Long Head – supraglenoid tubercle of scapula. Short Head – Apex of coracoid process of scapula
- Insertion: Radial Tuberosity and Antebrachial Fascia
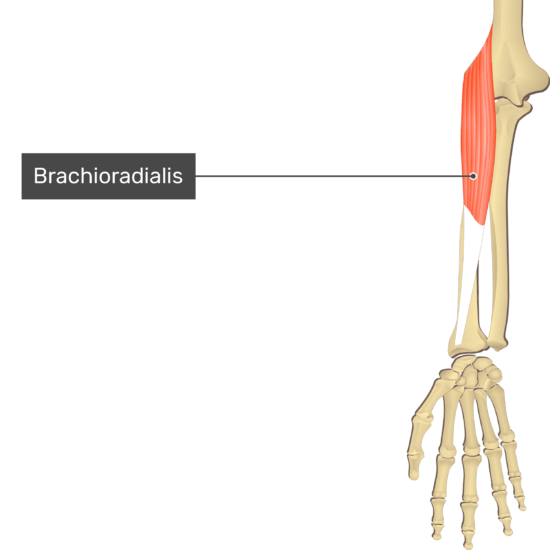
 Brachioradialis
Brachioradialis
- Origin: Superior two thirds of lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus
- Insertion: Lateral aspect of distal part of the radius
- Action: Flexes forearm at the elbow joint
This nerve lies in a groove posterior to the medial epicondyle, where it can be felt against the "funny bone." It supplies the following muscles.
- Flexor digitorum profundus (Medial part)
- Flexor carpi ulnaris.
Ulnar Nerve (C8-T1)


This muscle is the primary flexor of the elbow joint. It attaches from the anterior aspect of the distal half of the humerus and inserts onto the coronoid process and tuberosity of the ulna.
Brachialis

The Extensor Digiti Minimi, Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis, Extensor Digitorum (Communis) and Extensor Carpi Ulnaris share a common tendon. What is it, where does it attach and what pathology is associated with it?
Does the extensor carpi radialis longus also share this tendon?
Common Extensor Tendon, Lateral Epicondyle and Lateral Epicondylitis

Extensor Carpi radialis longus originates on the lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus
The pronator quadratus attaches to the distal 1/4th of the _____ and the ______. It _______ the forearm at the radioulnar joints.
Pronator Quadratus
- Origin: Anterior Aspect of distal 1/4th of ulna
- Insertion: Anterior aspect of distal one quarter of radius
- Action: Pronates forearm at radioulnar joints
- Nerve Supply: Anterior antebrachial interosseus nerve (C7-C8)
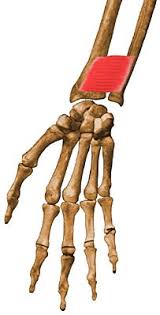
Damage to this nerve results in radial nerve palsy. It supplies most of the muscles of the dorsal surface of the forearm.
A. Anterior Interosseous Nerve
B. Posterior Interosseous Nerve
C. Musculocutaneous Nerve
The answer is A. Posterior Interosseous Nerve (Origin: Radial Nerve)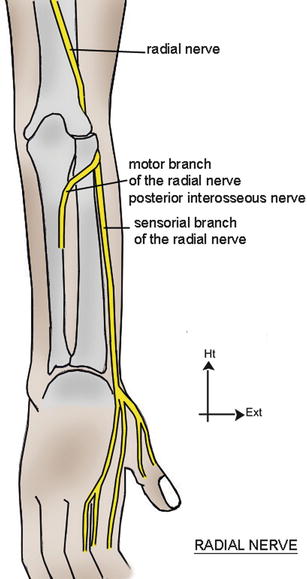


Side Note: Anterior Interosseous Nerve is a continuation of the median nerve.
The ______ _______ longus resides on the posterior aspect of the forearm. It originates from the posterior aspects of proximal half of ulna and middle 1/3rd of radius and interosseus membrane of forearm. It inserts on the lateral aspect of base of the 1st metacarpal bone.
Abductor Pollicis Longus
- Origin: Posterior aspects of proximal half of ulna and middle 1/3rd of radius and interosseus membrane of forearm
- Insertion: Lateral aspect of base of the 1st metacarpal bone
- Action: Abducts and extends the thumb at 1st carpometacarpal joint

Muscle 1
- Origin: Lateral Epicondyle of the humerus and supinator crest and supinator fossa of the ulna
- Insertion: Anterior, lateral and posterior aspects of proximal third of the radius
Muscle 2
- Origin: Medial supracondylar ridge of the humerus via the common flexor tendon and medial aspect of the coronoid process of the ulna
- Insertion: Middle one third of anterolateral aspect of the radius
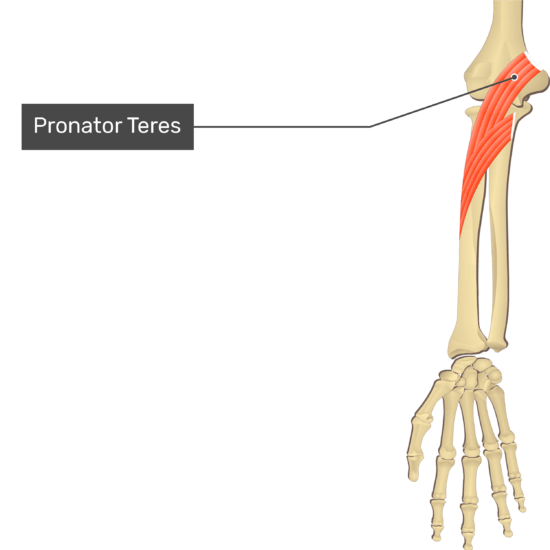
Muscle 1 = Supinator Muscle

Muscle 2 = Pronator Teres
These two muscles serve to flex digits 1-5 and do not cross the elbow joint. They both attacth to the interrosseus membrane.
Muscle 1: The flexor _______ _______ arises from the distal 2/3rds of anterior surface of the radius and inserts into tha palmar aspect of the base of the thumb.
Muscle 2: The ______ ______ profundus arises from the anterior surface of the radius and inserts into palmar aspects of bases of the distal phalange’s of the lateral 4 digits. It lies deep to flexor digitorum superficialis.
Flexor Pollicis Longus
- Origin: Anterior surface of the radius, adjacent interosseous membrane of the forearm
- Insertion: Palmar aspect of the base of the distal phalanx of the thumb
- Action: Flexes thumb

Flexor Digitorum profundus
- Origin: Medial aspect of the coronoid process of the ulna, superior 3/4ths of anterior and medial surfaces of the body of the ulna
- Insertion: Palmar aspects of bases of the distal phalange’s of the lateral 4 digits
- Action: Flexes the lateral 4 digit

What nerve supplies the biceps brachii and brachialis? Which nerve is the brachialis also innervated by?
A. Anterior Interrosseus from the Median ENrve
B. Posterior Interrosseus from the Radial Nerve
C. Musculocutaneus (C5-C6)
D. Radial Nerve (C7)
C. Musculocutaneus (C5-C6) and D. Radial Nerve (C7)

Name all 5 muscles that attach to the common flexor tendon.
Pronator Teres, Flexor Carpi Radialis, Palmaris Longus, Flexor Digitorum Superficialis, Flexor Carpi Ulnaris

These msucles do not cross the elbow. They all have an adjacent attachment to the interrosseus membrane.
Extensor Pollicis Brevis arises from the posterior surface of distal half of radius. What is its insertion? Action?
Extensor Pollicis Longus arises from the posterior surface of middle one third of ulna. What is its insertion? Action?
Extensor indicis arises from the posterior surface of distal 1/3rd of ulna. What is its insertion? Action?
Extensor Pollicis Brevis
- Origin: Posterior surface of distal half of radius/adjacent interosseous membrane of forearm
- Insertion: Dorsal aspect of base of proximal phalanx of thumb
- Action: Extends Thumb
- Nerve Supply: Posterior antebrachial interosseous nerve (C7-C8)
Extensor Pollicis Longus
- Origin: Posterior surface of middle one third of ulna and interosseous membrane
- Insertion: Dorsal aspect of base of distal phalanx of thumb
- Action: Extends thumb
- Nerve Supply: Posterior antebrachial interosseus nerve (C7-C8)

Extensor Indicis
- Origin: Posterior surface of distal 1/3rd of ulna and interosseous membrane
- Insertion: Extensor expansion of index finger
- Action: Extends index finger
- Nerve Supply: Posterior antebrachial interosseus nerve (C7-C8)
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13064/8LeykiQd7Yp25OWWSlXwIQ_sT7FwpdY8.png)
These muscles are supplied by which nerve?
____ Nerve
- Triceps Brachii
- Anconeus
Superficial Branch of _____Nerve
- Brachialis
- Brachioradialis
- Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus
Deep Branch and or _______ Interosseous Nerve (C7-C8)
- Supinator
- Abductor pollicis longus
- Extensor digitorum
- Extensor carpi radialis brevis
- Extensor digiti minimi
- Extensor pollicis brevis
- Extensor pollicis longus
- Extensor indicis
- Extensor carpi ulnaris
- Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis
Radial Nerve (C5-C8)
- Enters the forearm between the brachioradialis and brachialis and, at or inferior to the level of the lateral epicondyle
- Divides into superficial and deep branches.
- Deep branch continues to become the posterior interosseus nerve

The Extensor digiti minimi inserts onto the Extensor expansion of the _____ digit, Extensor carpi radialis brevis inserts onto dorsal aspect of the base of the _____ metacarpal, Extensor digitorum inserts onto the dorsal aspects of the bases of both the ______ and ______ phalanges of the medial 4 digits and the Extensor carpi ulnaris inserts onto the medial aspect of the base of the ______ metacarpal bone.
Extensor carpi radialis longus inserts onto the dorsal aspect of the base of the ______metacarpal bone.
Extensor Digiti Minimi
- Origin: Lateral epicondyle via common extensor tendon
- Insertion: Extensor expansion of the 5th digit
- Action: Extends the 5th digit

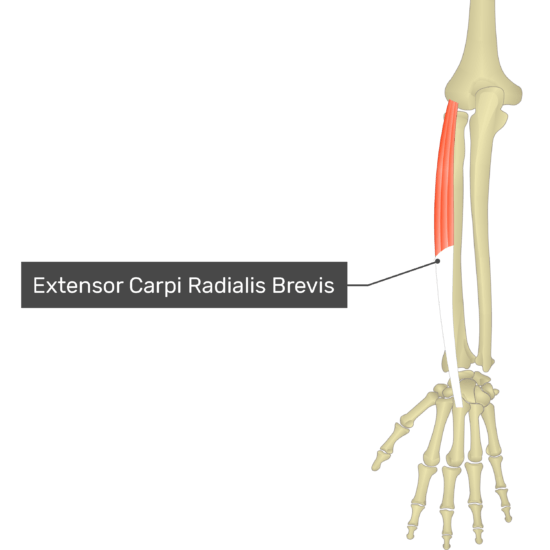
Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis
- Origin: Lateral epicondyle via the common extensor tendon
- Insertion: Dorsal aspect of the base of the third metacarpal
- Action: Extends hand at the radiocarpal joint (wrist) joint and abducts hand at the radiocarpal and midcarpal joints
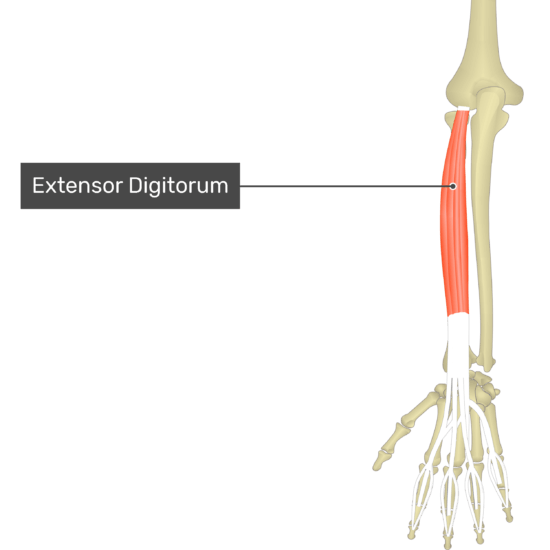
Extensor Digitorum
- Origin: Lateral epicondyle via the common extensor tendon
- Insertion: Dorsal aspects of the bases of both the middle and distal phalanges of the medial 4 digits
- Action: Extends the lateral 4 digits
E
Extensor Carpi Ulnaris
- Origin: Lateral epicondyle via common extensor tendon and the posterior border of the ulna
- Insertion: Medial aspect of the base of the 5th metacarpal bone
- Action: Extends and adducts hand at radiocarpal (wrist) joint

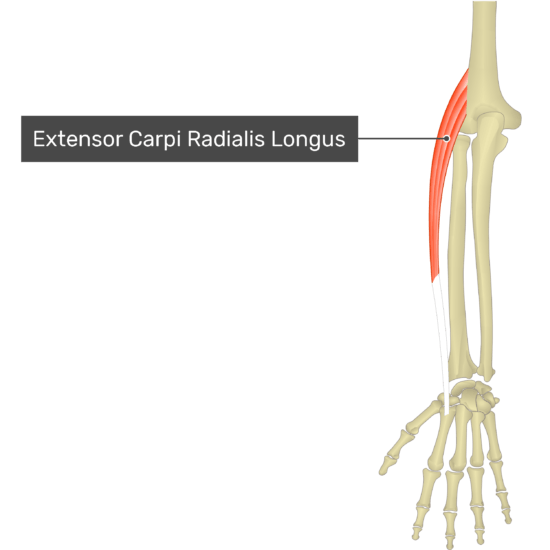
Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus
- Origin: Lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus
- Insertion: Dorsal aspect of the base of the second metacarpal bone
- Action: Extends hand at the radiocarpal (wrist) joint and abducts hand at radiocarpal and midcarpal joints

The _____ ______ ____inserts into the palmar aspects of the bases of the 2nd and 3rd metacrpals.
The flexor carpi ulnaris inserts to the ______, hook of _____ and proximal aspect of 5th metacarpal.
The _____ _____ inserts into the palmar aponeurosis and flexor retinaculum of the hand.
The _____ _______ superficialis inserts into the palmar aspects of the bodies of the middle phalanges of medial 4 digits.
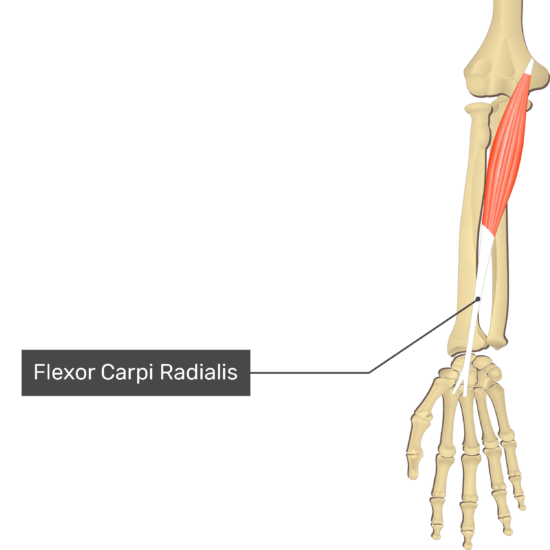
Flexor Carpi Radialis
- Origin: Medial epicondyle of the humerus via common flexor tendon
- Insertion: Palmar aspects of bases of the second and third metacarpal bones
- Action: Flexes hand at radiocarpal (wrist) joint and abducts hand at radiocarpal and midcarpal joints
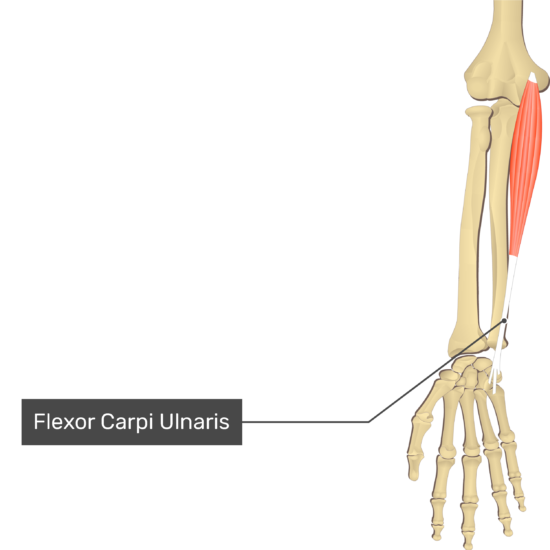
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
- Origin: Medial epicondyle via common flexor tendon, proximal 2/3rds of the body of the ulna and olecranon
- Insertion: Pisiform, hook of hamate, and proximal aspect of the base of the 5thmetacarpal bone
- Action: Flees and abducts the hand at the radiocarpal (wrist) joint
Palmaris Longus
- Origin: Medial epicondyle via common flexor tendon
- Insertion: Palmar aponeurosis and flexor retinaculum of the hand
- Action: Flexes hand at the radiocarpal (wrist) joint and stabilizes the palmar aponeurosis.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13109/WVIUiW3dOxD0Lt6c6Paw8w_U7ZZMWG3P9_M._palmaris_longus_1.png)
Flexor Digitorum Superficialis
- Origin: Medial epicondyle of the humerus via the common flexor tendon, sublime tubercle of ulna, proximal half of anterior border of humerus
- Insertion: Palmar aspects of the bodies of the middle phalanges of medial 4 digits
- Action: Flexes the medial 4 digits of the hand

Which nerve supplies these structures:
_____ Nerve
- Pronator teres
- Palmaris Longus
- Palmaris longus
- Flexor digitorum superficialis
_____ Interosseous Nerve
- Flexor pollicis longus
- Flexor digitorum profundus (Lateral Part)
- Pronator quadratus
Median Nerve (C6-T1)
- The median nerve usually enters the forearm between the two heads of the pronator teres. It descends in the middle of the forearm to the midpoint between the styloid processes.
- The anterior interosseous nerve arises from the median nerve in the cubital fossa which also descends down the middle of the forearm
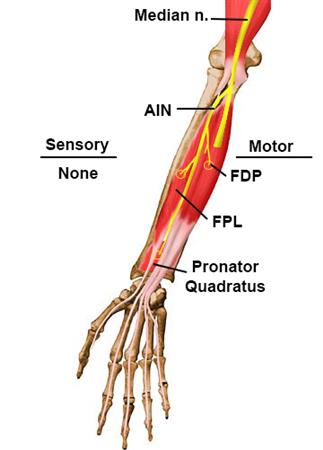
Injury to the median nerve may result in weakness of the two long flexors and a characteristic pinch attitude on attempted flexion of the distal phalanges of the thumb and index ("anterior interosseous nerve syndrome").