What are the types of muscular tissue?
skeletal
smooth
cardiac
What is the name of this structure

Fascicle
attaches bone to bone
ligaments
Type of muscle that is found in the limbs
skeletal
This muscle typeis only found in the heart
cardiac
attaches muscle to bone
tendon
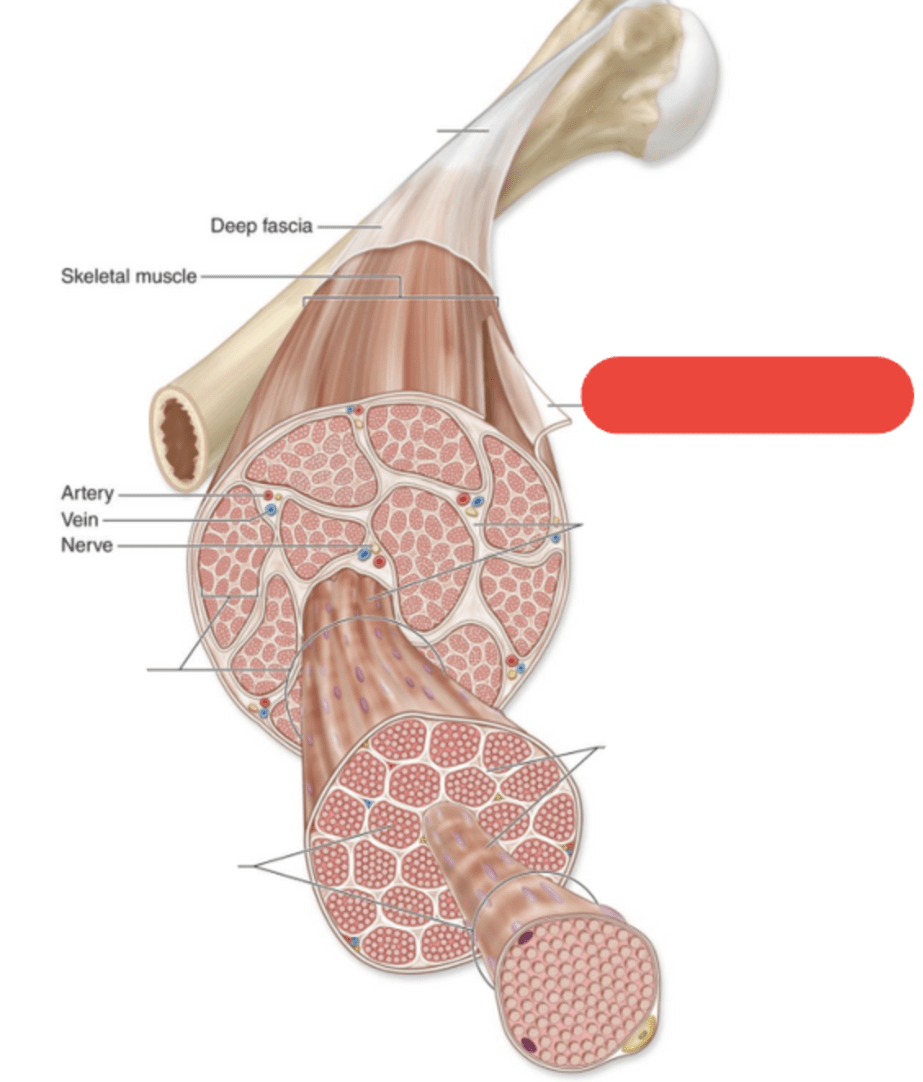
What is the name of this layer of connective tissue?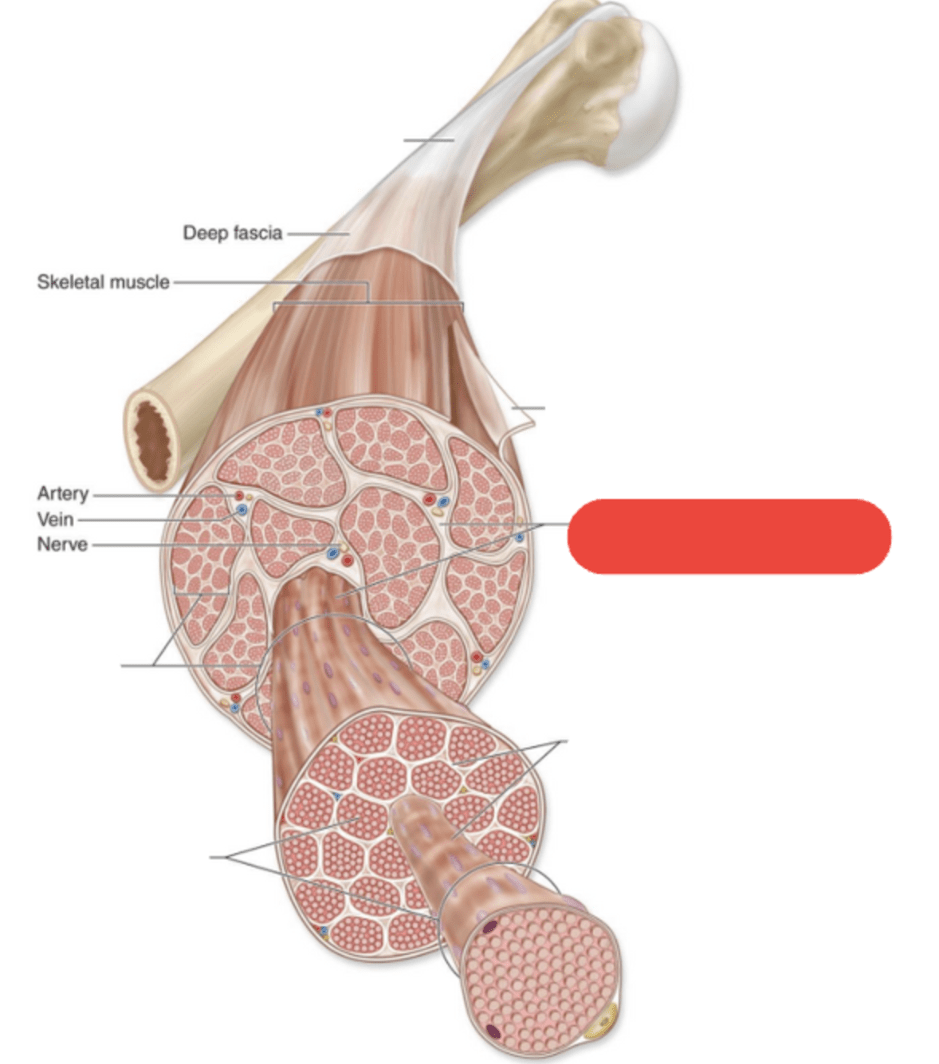
Perimysium
Individual muscles are separated by ________
Fascia
Muscle tissue type that is connected to the bones
skeletal
Muscle cells found within fibers are called ________
myocytes
Name the 2 types of muscle tissue that are striated
cardiac and skeletal
Myofibrils are made of myofilaments called ______ and _______
actin (thin) and myosin (thick)
Thin filaments in the muscle are made up of the protein _______
Actin
Name 3 functions of the Muscular System
Movement of the body (uses bones as anchors and levers)
Maintains Posture
Generates Body Heat
Plays a role in other body systems
- Respiration, Digestion, Urination
What is this layer of connective tissue named?
Epimysium
Thick filaments in the muscle are made up of the protein ________
Myosin
Name each type of muscle tissue and the type of control we have over them
Skeletal = voluntary
Cardiac = involuntary
Smooth = involunatry
Layer of connective tissue that separates and surrounds fascicles (bundles of muscle fibers)
Perimysium
This tissue is mainly found in the walls of hollow organs
smooth muscle
What is the name of this structure: the smallest unit of contraction in a muscle
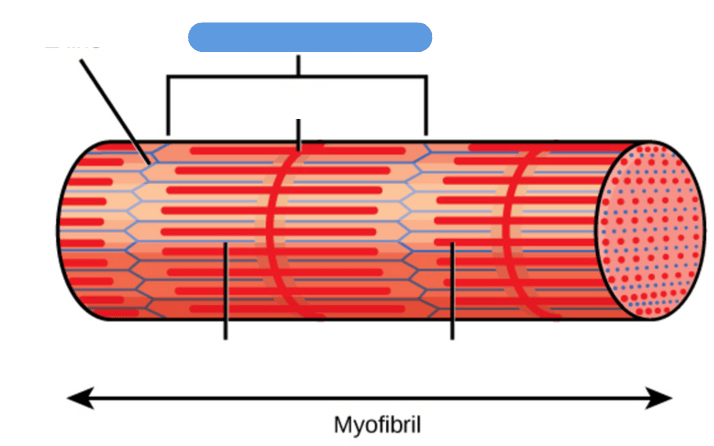
Sarcomere
Layer of connective tissue that surrounds each individual muscle fiber
Endomysium
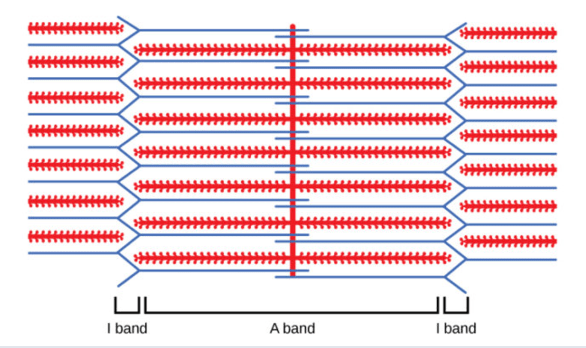
Dark bands in the muscle are known as the _________ and are made up of the protein ________
A band
Myosin (thick filament)
Is this sarcomere contracted or relaxed?
Contracted
Compare it to the sarcomere below that is relaxed.

Name of this structure: holds myosin filaments in place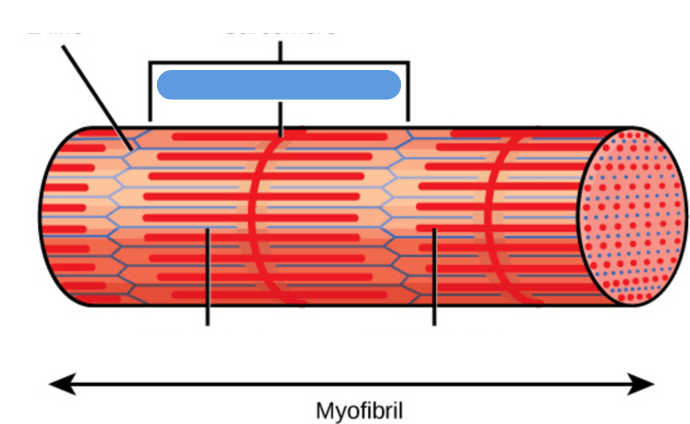
M-Line
Middle of the sarcomere; holds myosin filaments in place.
Outermost layer of connective tissue that surrounds entire muscle
Epimysium
Type of muscle tissue that is not striated
smooth
Muscle fibers are made up of ___________
myofibrils
What is the name of this struture: Ends of the sarcomere; connects actin filaments.

Z-line
The __________ is the smallest unit of contraction in a muscle fiber
Sarcomere
Energy molecule that allows myosin to release from actin and reset during a muscle contraction
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate)
What is this structure called? 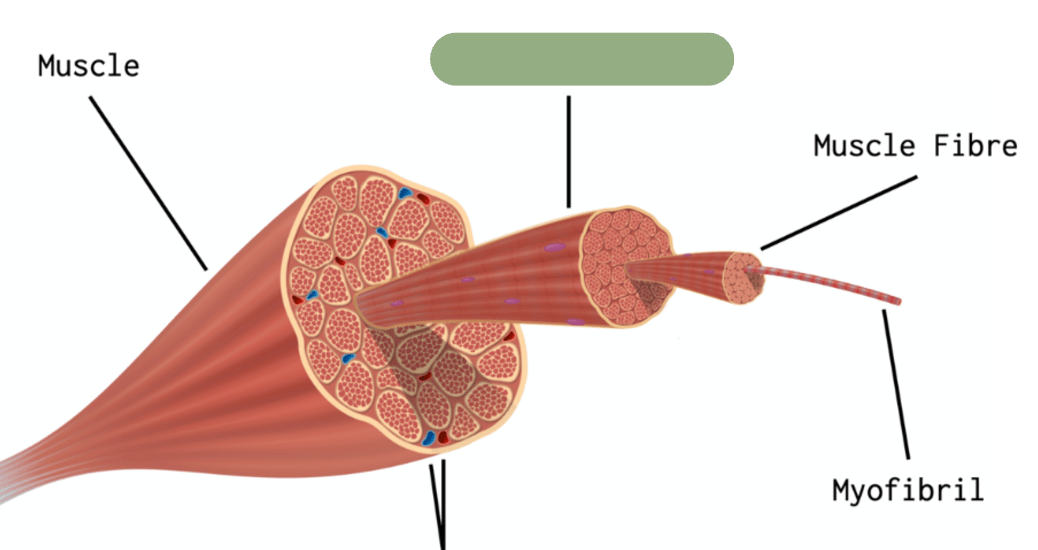
Fascicle
What is the name of this structure? 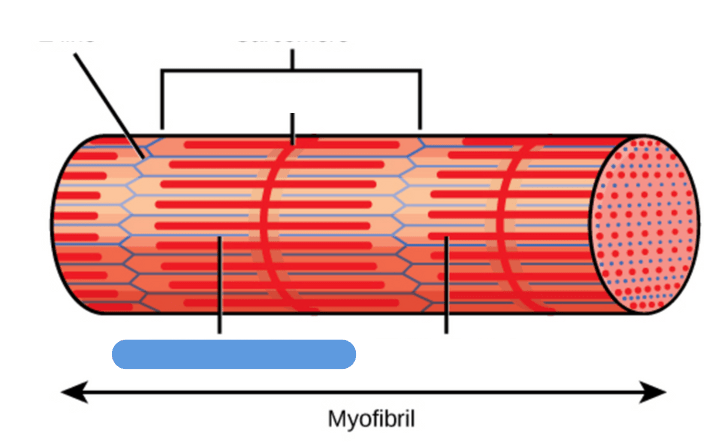
Actin (thin) filament
Explains how muscles contract by the sliding of actin (thin filaments) past myosin (thick filaments) within the sarcomere, shortening the muscle fiber and generating force.
Sliding Filament Theory
What is the name of this connective tissue?

Endomysium
What is the name of this structure?
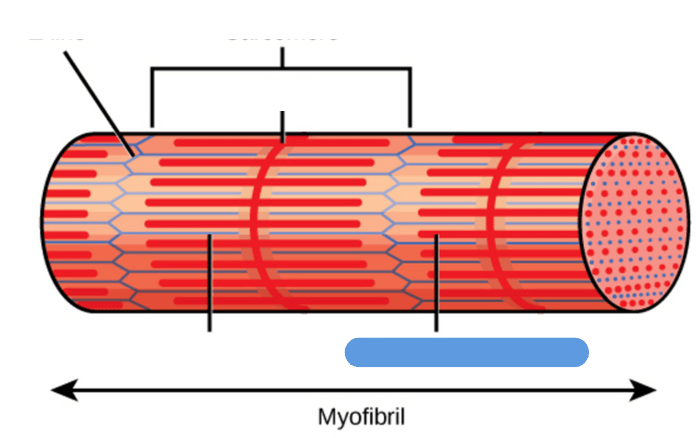
Myosin (thick) filament
What is the name of this structure? 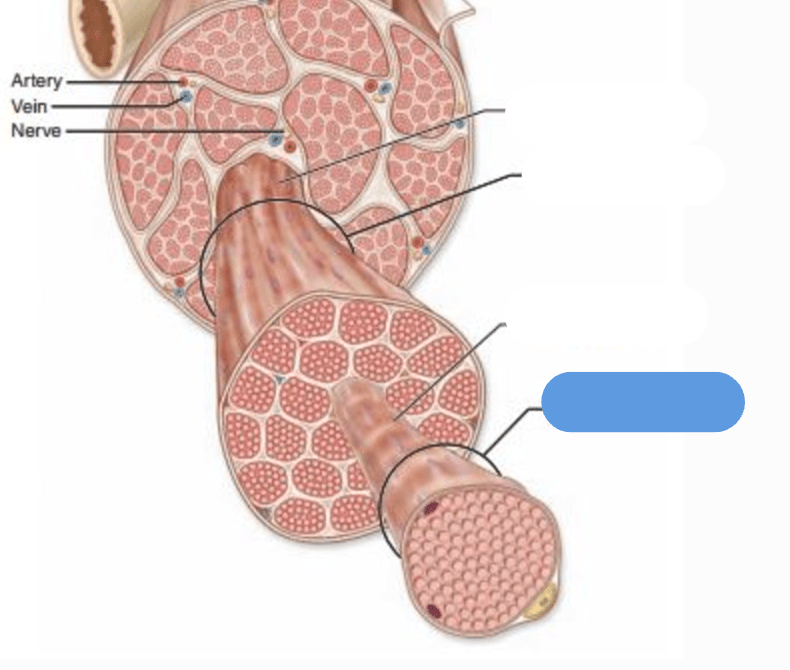
Muscle Fiber