what is osteomyelitis
Severe infection of bone, bone marrow, and surrounding soft tissue
clinical manifestations of acute osteomyelitis
•Infection of < 1 month in duration
•Local manifestations
•Pain that worsens with activity; is unrelieved by rest
•Swelling, tenderness, warmth
•Restricted movement
what is chronic osteomyelitis
•Infection lasting > 1 month or has failed to respond to initial antibiotic treatment
•Continuous and persistent or process of exacerbations and remissions
subjective data
•Past health history
•Bone trauma, open fracture, open or puncture wounds, other infections
•Medications
•Use of analgesics or antibiotics
•Surgery or other treatments
Bone surgery
•IV drug and alcohol abuse, malaise
•Anorexia, weight loss, chills
•Weakness, paralysis, muscle spasms
•Local tenderness, increase in pain
Irritability, withdrawal, dependency, anger
health promotion of osteomyelitis
•Control other current infections
•Persons at risk
•Are immunocompromised
•Have diabetes, orthopedic prosthetic devices, vascular insufficiencies
•Encourage to call HCP about local signs
what is the most common organisms to cause osteomyelitis?
Most common microorganism is Staphylococcus aureus, but can be caused by variety of organisms
systemic manifestions
•Fever
•Night sweats
•Chills
•Restlessness
•Nausea
•Malaise
•Drainage (late)
clinical manifestations of chronic osteomyelitis
•Systemic manifestations reduced
•Local signs of infection more common
•Pain, swelling, warmth
•Granulation tissue turns to scar tissue → avascular → ideal site for microorganism growth → cannot be penetrated by antibiotics
objective data
•Restlessness, high spiking temperature, night sweats
•Diaphoresis, erythema, warmth, edema
•Restricted movement, wound drainage, spontaneous fractures
•↑ WBC, + cultures, ↑ ESR, presence of sequestrum and (dead bone)
acute care of osteomyelitis
•Immobilization and careful handling of affected limb
•Assess and treat pain
•Dressing care - sterile technique
Proper positioning/support of extremity
indirect entry (hematogenous) of osteomyelitis
•Young boys
•Blunt trauma
•GU and respiratory infections
•Vascular insufficiency disorders
interprofessional care of acute osteomyelitis
•Aggressive, prolonged IV antibiotic therapy (Gentamicin)
•Cultures or bone biopsy
•Surgical debridement and decompression
•IV antibiotics via CVAD
•May be started in hospital, continued at home/ skilled nursing facility
•IV antibiotics 4-6 weeks or longer
•Variety of antibiotics, depending on microorganism
what are long term and mostly rare complications of osteomyelitis
•Septicemia
•Septic arthritis
•Pathologic fractures
•Amyloidosis (abnormal protein builds up in tissues and organs leading to organ failure)
nursing diagnoses
•Acute pain
•Ineffective health management
•Impaired physical mobility
acute care/ medications
•Patient teaching adverse and toxic reactions to antibiotic therapy (Gentamicin, Cipro, Levaquin)
•Ototoxicity, impaired renal function, neurotoxicity
•Hives, severe or watery diarrhea, bloody stools, throat and mouth sores
•Tendon rupture
Monitor peak and trough levels
•Lengthy antibiotic therapy can cause an overgrowth of Clostridium difficile
•Patient and family are often frightened and discouraged
•Continued psychologic and emotional support
direct entry of osteomyelitis
•Via open wound
Foreign body presence
dx studies of osteomyelitis
•Bone or soft tissue biopsy
•Blood and/or wound cultures
•WBC count
•Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
•C reactive protein
•X-rays/ MRI/ CT scans
•Bone scans
planning for osteomyelitis
•Have satisfactory pain and fever management
•Do not experience any complications associated with osteomyelitis
•Adhere to treatment plan
Maintain a positive outlook on outcome of disease
nursing implementation
•Ambulatory Care
•Patient/caregiver teaching regarding antibiotic administration and management of CVAD
•Wound care/dressing changes
Physical and psychological support
pathophysiology of osteomyelitis
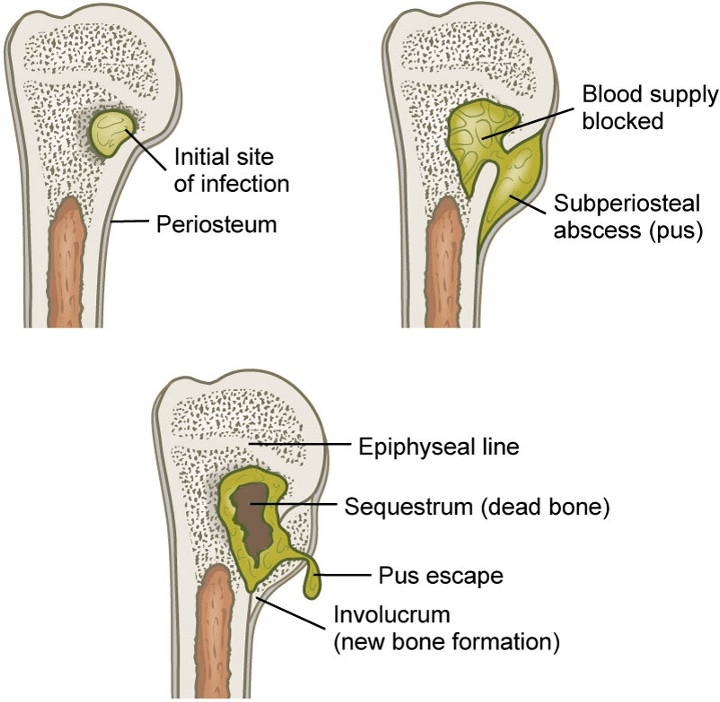 •Microorganisms grow → increase pressure in bone → ischemia and vascular compromise
•Microorganisms grow → increase pressure in bone → ischemia and vascular compromise
•Infection spreads through bone → cortex devascularization and necrosis
interprofessional care of chronic osteomyelitis
•Surgical removal
•Extended use of antibiotics
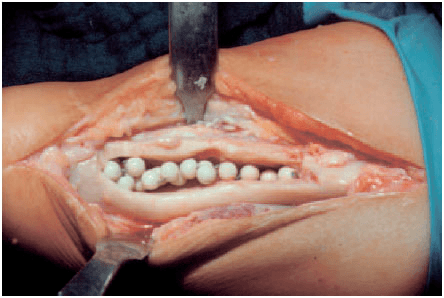 Acrylic bead chains containing antibiotics
Acrylic bead chains containing antibiotics
Intermittent or constant antibiotic irrigation of bone
•Casts or braces
•Negative-pressure wound therapy
•Hyperbaric oxygen therapy
•Removal of prosthetic devices
•Muscle flaps, skin grafts, bone grafts
•Amputation
evaluation of osteomyelitis
•The patient will
•Have satisfactory pain management
•Follow treatment regimen
•Verbalize confidence in ability to implement treatment plan
•Demonstrate increase in mobility/ range of motion