Name this type of fracture.
What is a comminuted fracture.
The most common etiology of a fracture.
What is trauma.
The nurse observes this device upon assessment.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/IMG_3955-569d63f13df78cafda9d44a7-fc085801f3c943afa23c5c747cbf198a.jpeg)
What is external fixation.
Ketorolac (toradol) is commonly prescribed following orthopedic surgery and belongs to this medication class.
What is NSAIDs.
What is Rest, Ice, Compress, and Elevate.
This direct complication of a bone fracture results in infection of the bone, marrow, and surrounding tissue.
What is osteomyelitis.
A patient asks why they are receiving an antibiotic after their TKA procedure. The nurse identifies this indication as the reason.
What is prophylactic antibiotic use. Antibiotics are given immediately prior, during, and after most arthroplasty procedures to help protect against infection.
Nonsurgical realignment of a fracture.
What is a closed reduction.
This condition occurs when there is an increased pressure within enclosed osteofascial space, reducing capillary perfusion below the level necessary for tissue viability.
What is compartment syndrome.
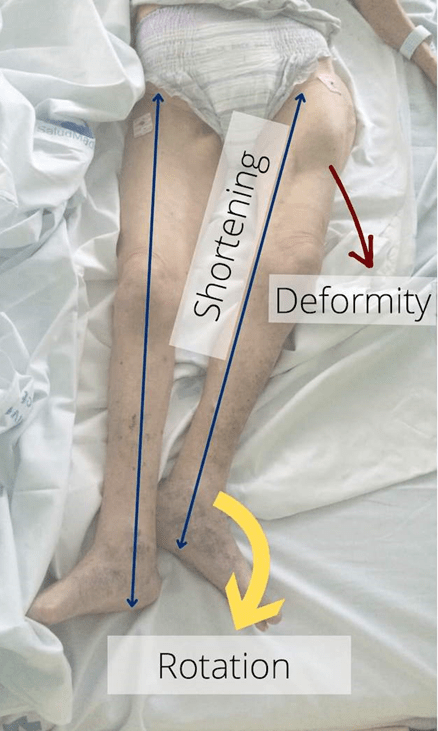
On assessment of a patient following a GLF, the nurse suspects this condition after assessing the patient.
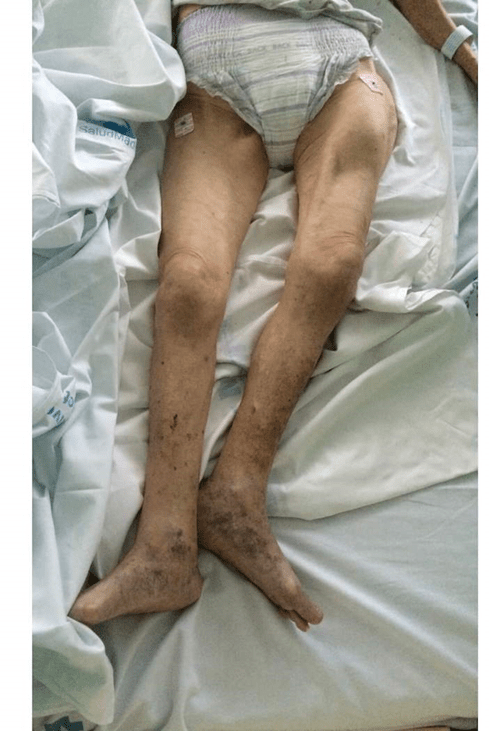
What is a hip fracture. Note the presence of external rotation, limb shortening, and obvious deformity.
This medication class includes carisoprodol (Soma), metaxalone (Skelaxin), and methocarbamol (Robaxin).
What is muscle relaxants.
Three interventions to prevent VTE.
What are administration of anticoagulant or antiplatelet medication, use of devices such as SCDs or ted hose, and encouraging mobility (early ambulation and ROM).
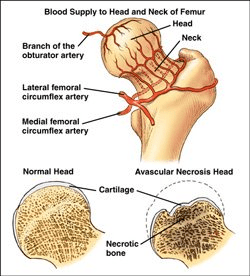
Dislocation of the hip joint is considered a medical emergency due to the possibility of this direct complication.
What is avascular necrosis.
Three topics to include in a teaching plan for a patient with a new cast.
What are:
- keeping it dry
- do not put anything into the cast
- do not pull out padding
- elevate extremity above the heart for 48H
- monitor pain and neurovascular function
- maintain proximal and distal ROM
- use a hair dryer on cool to manage itching
An injury to a muscle or tendon.
What is a strain.
This condition is identified when a patient with metastatic prostate cancer presents with a non-traumatic fracture of his femur.
What is a pathologic fracture.
This condition is diagnosed when MRI results show a complete ACL tear.
What is a third degree sprain. (ACL is a ligament, and a complete tear is classified as third degree).
A patient arrives to the floor after TKA surgery and the nurse assesses their pain level. The patient states their pain is at a 0/10. The nurse briefly reviews the PACU record, noting that the patient received no analgesics post-operatively. The nurse suspects the patient received what intervention prior to surgery that is responsible for their lack of pain?
What is a nerve block. (may be femoral, although other nerves can be utilized - obturator, sciatic, lumbar plexus).
Emergent fasciotomy is indicated for this condition.
What is compartment syndrome.
The nurse expects to see an elevated creatine protein kinase in this indirect complication of bone fracture.
What is rhabdomyolysis.
Correct use of a cane.
What is holding the cane in the arm opposite of the affected leg.
The correct medical term for a partial joint replacement.
What is hemiarthroplasty.
A patient has decided to have an elective THA. The nurse knows of at least two indications for this procedure.
What are OA, RA, avascular necrosis, or congenital deformities. More emergent THA may also be performed for certain fractures or severe and/or recurrent dislocation.
An audible or palpable grating or crunching sensation upon movement of a fractured extremity.
What is crepitation.
The nurse anticipates what common medication order for a patient with confirmed rhabdomyolysis.
What is aggressive IV hydration. (Example, NS @ 150ml/h).
The most common surgical procedure to realign a fractured bone.
What is ORIF (open reduction internal fixation).
What is prosthesis dislocation.
During an educational session, the nurse includes two important movements a patient should NOT do following total hip replacement.
What are DON'T: flex hip >90 degrees, adduct hip, internally rotate hip, or cross legs at knee/ankle.
The condition seen in picture B. 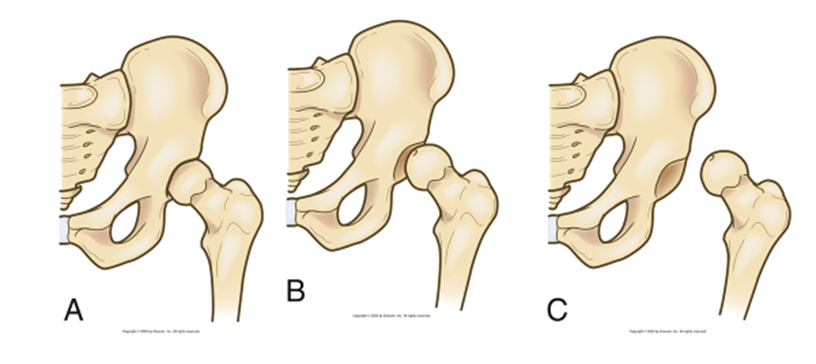
What is subluxation of the hip, meaning a partial or incomplete displacement of the joint surface. (picture A is a normal hip joint, picture C is a dislocated hip joint).
Stages of bone healing include: _________, Granulation Tissue, __________, Ossification, Consolidation, and ___________.
What is (in order) Hematoma, Callus Formation, and Remodeling.
The 5 P's of Neurovascular Assessment.
What are pain, paresthesia (numbness/tingling), paralysis, pulses, and pallor.
This common post-operative symptom is being managed by pregabalin (Lyrica).
What is neuropathic pain.
This force must be applied for effective traction.
What is countertraction. (can be patient's body weight or actual weights on pulleys).
A patient 36H post-op from a hip pinning suddenly reports dyspnea, chest pain, and has become restless. The nurse is concerned about this indirect complication when they assess the patient's chest:

What is FES (fat embolism syndrome). The picture demonstrates a petechial rash, which may occur on the patient's neck, chest, axilla, head or conjunctiva.
The nurse observes the following order and anticipates educating the patient on two important topics.
Dilaudid 1mg/ml
Basal rate: 0.1 mg/h
Bolus: 0.1 mg
Lockout Interval: 10 min
4H Max: 4 mg
This is an order for a dilaudid PCA. Education topics could include (1) only the patient should push the PCA button, (2) the PCA will deliver a constant amount of dilaudid (basal rate) with the option of additional dilaudid (bolus dose) each time the patient pushes the button, (3) there is a lockout feature to reduce the risk of overdose, (4) the patient should have continuous pulse oximetry to monitor O2 levels, and (5) dilaudid is an opioid with several potential side effects including respiratory depression, hypotension, AMS, and constipation.