Which anatomical plane divides the body into inferior and superior halves?
Transverse Plane
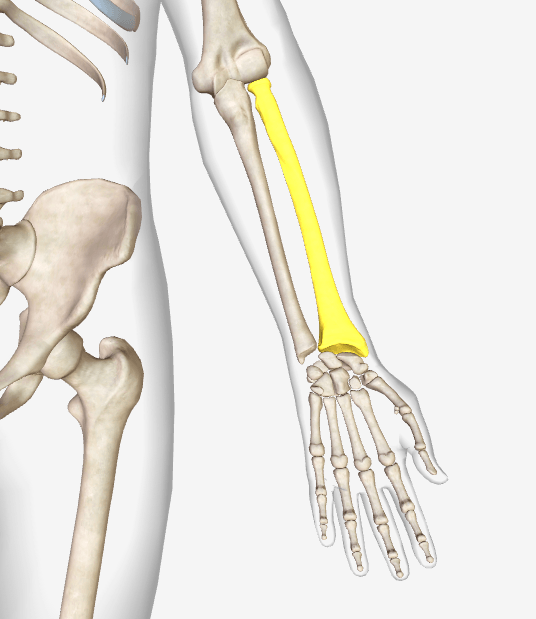
Identify this bone.
Radius
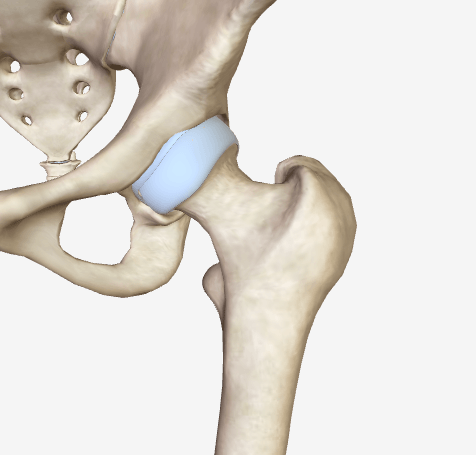
Name this type of synovial joint.
Ball-and-socket.
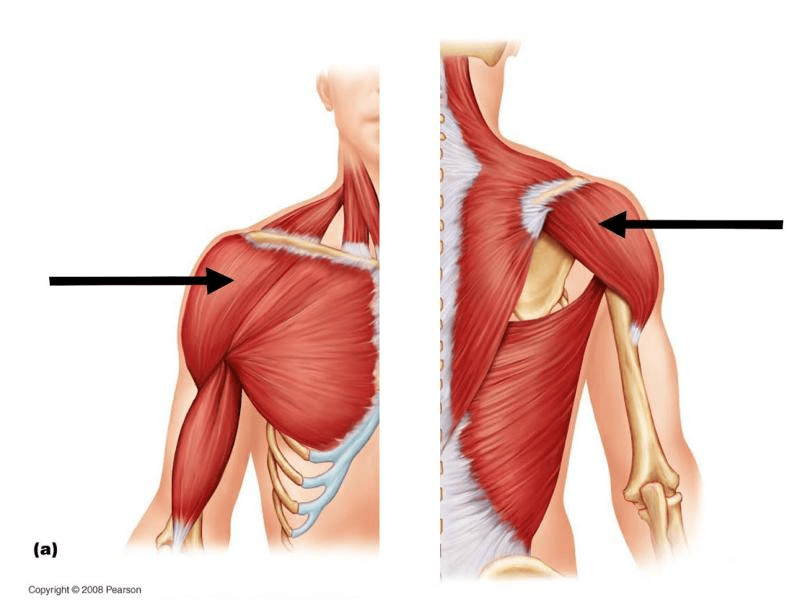
Identify the muscle.
Deltoid.
Name the connective tissue structure which attaches muscles to bones.
Tendon.
The scapula is _____________ to the clavicle.
The scapula is posterior to the clavicle.
Name the bones of the pectoral girdle.
Clavicle and scapula.
The sutures between the bones of the cranium form what type of joint?
Fibrous.
A bundle of muscle fibers is called a _______.
Fascicle.
In what structure or region of long bones is the majority of red bone marrow found?
Spongy bone and/or epiphyses.
What joint movement is shown here?
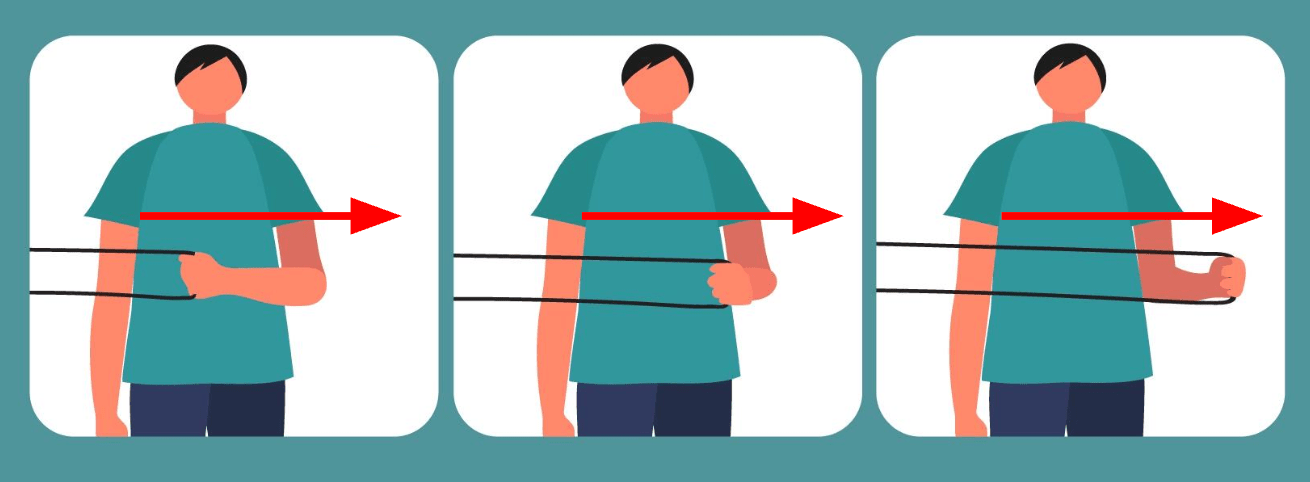
Shoulder lateral rotation (or external rotation)
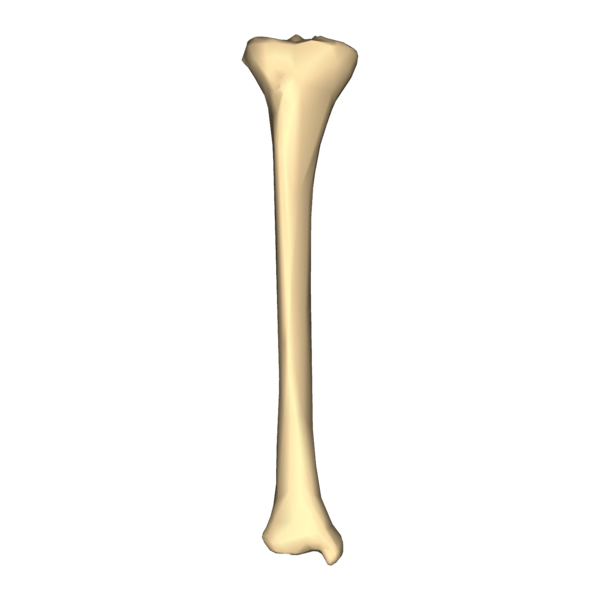
This is an anterior view of what lower extremity bone?
Tibia.
Describe the relationship between mobility and stability in joints.
Mobility and stability are inversely related. As mobility increases, stability decreases and vice versa.
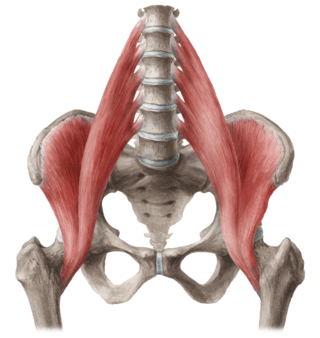
Identify this muscle group and state its action.
Iliopsoas. Responsible for hip flexion.
Analyze the exercise shown below. Include all of the following: Joint name, movement name, plane, axis, agonist, antagonist, and contraction type.
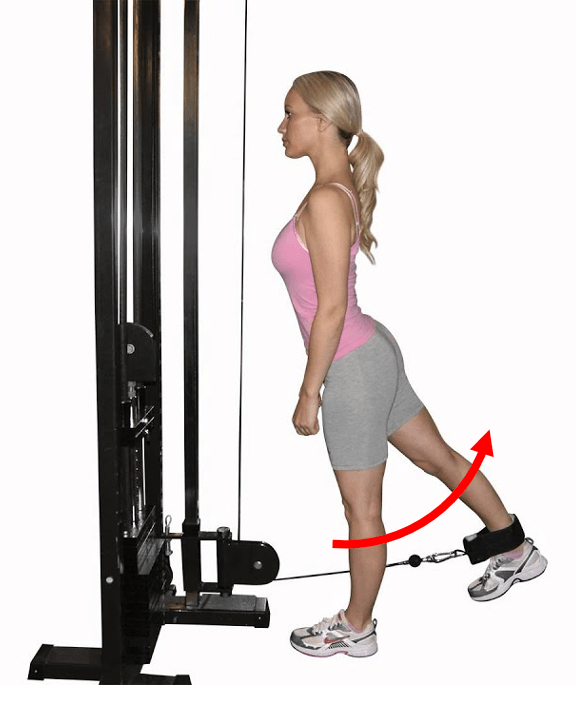

Joint: Hip
Movement: Extension
Plane: Sagittal
Axis: Frontal
Agonist: Gluteals
Antagonist: Iliopsoas
Contraction Type: Concentric
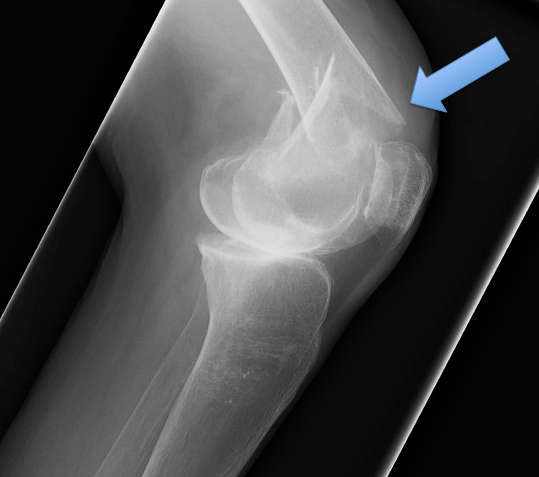
Describe the specific anatomical location of this fracture.
Distal end of the left femur.
What are the two primary biochemical components which make up the extracellular matrix of bone tissue?
[Hint: What did you learn from the chicken bones in our bone lab?]
Calcium phosphate minerals and collagen proteins.
What specific type of joint exists at your first knuckle (aka metacarpo-phalangeal joint)?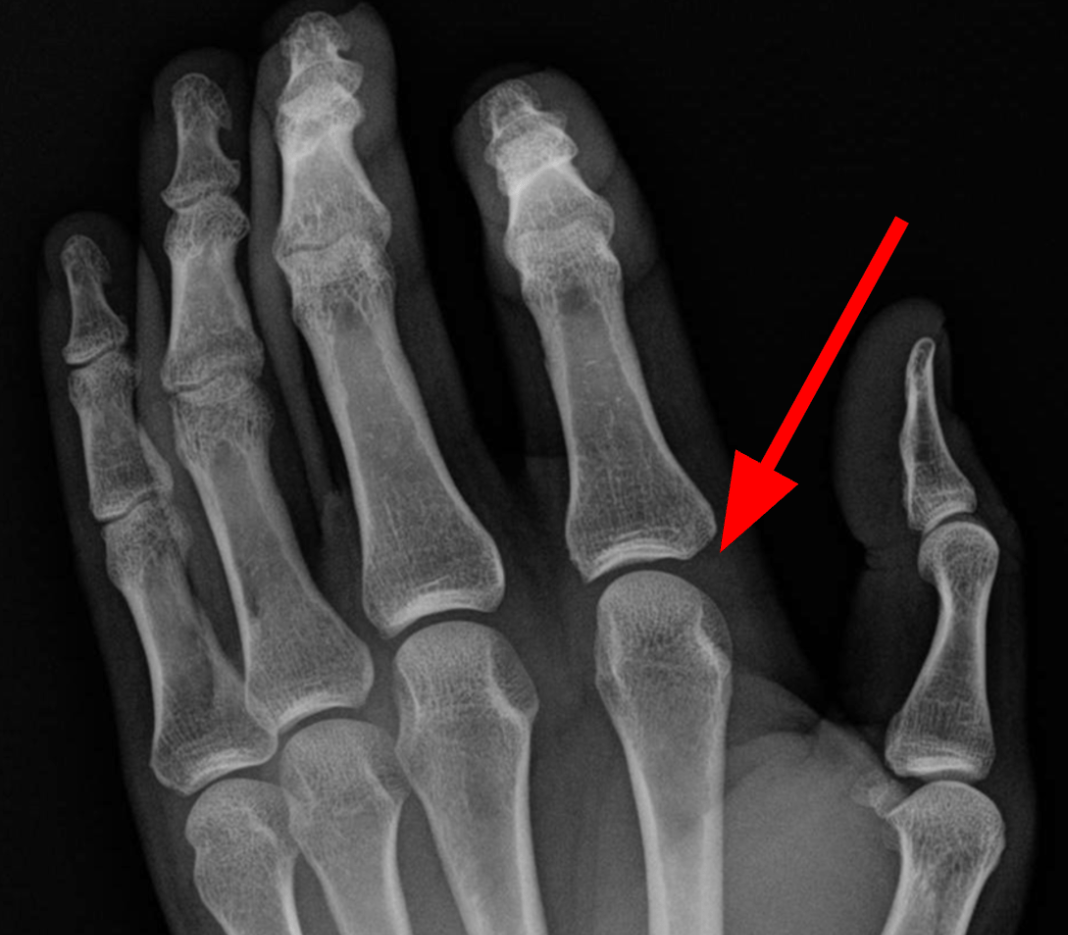
Synovial condyloid joint
Match each Olympian with their gastrocnemius fiber type composition.
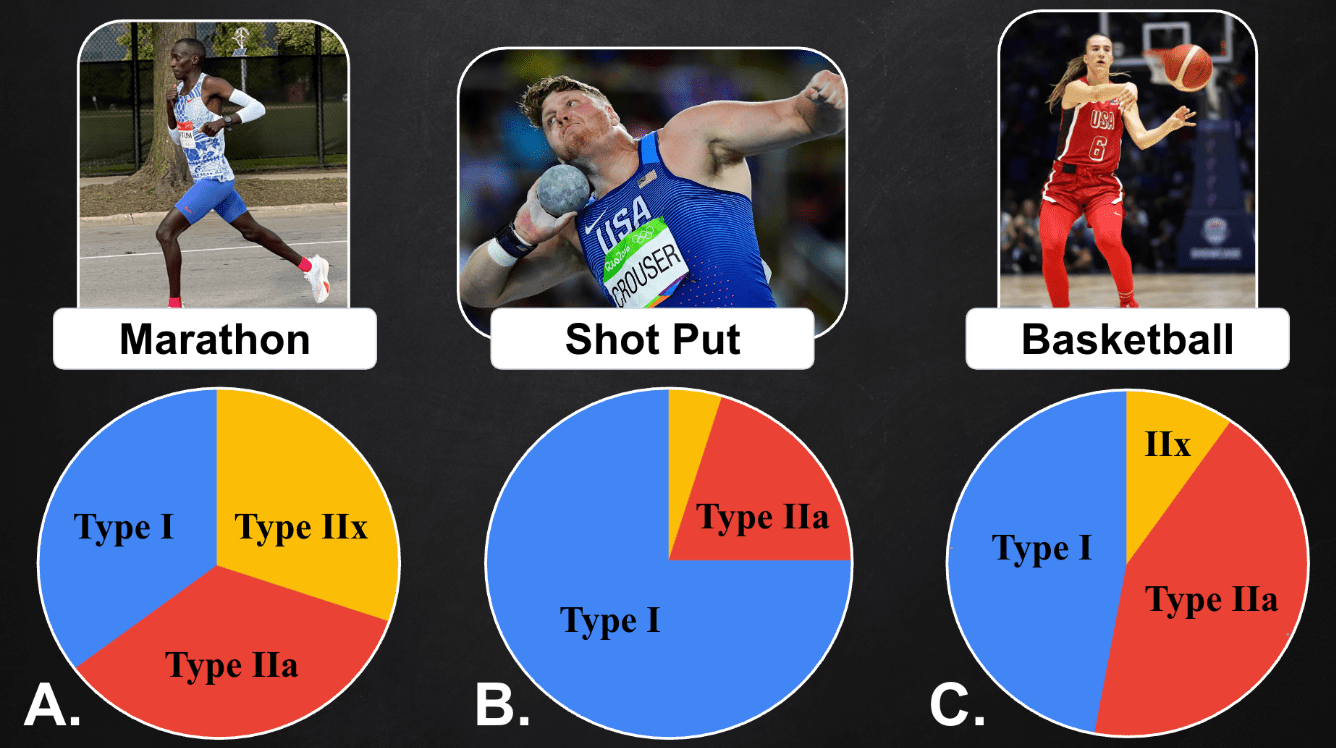
Marathon = B
Shot Put = A
Basketball = C
What was Coach Hanna's high school mascot?


List and analyze the joint movements that can occur at the wrist. Include the movement name, plane, and axis for each movement.
Movement Names: Flexion and Extension
Plane: Sagittal
Axis: Frontal
Movement Names: Abduction and Adduction
Plane: Frontal
Axis: Sagittal
Bonus: Circumduction
Name four of the major functions of the skeletal system.
Protection, support and maintenance of posture, attachment points for muscles (supporting movement), production of blood cells, storage and release of minerals, and storage of energy.
Describe what makes synovial joints unique compared to the other general joint types.
Synovial joints have a fluid-filled capsule between articulating bones.
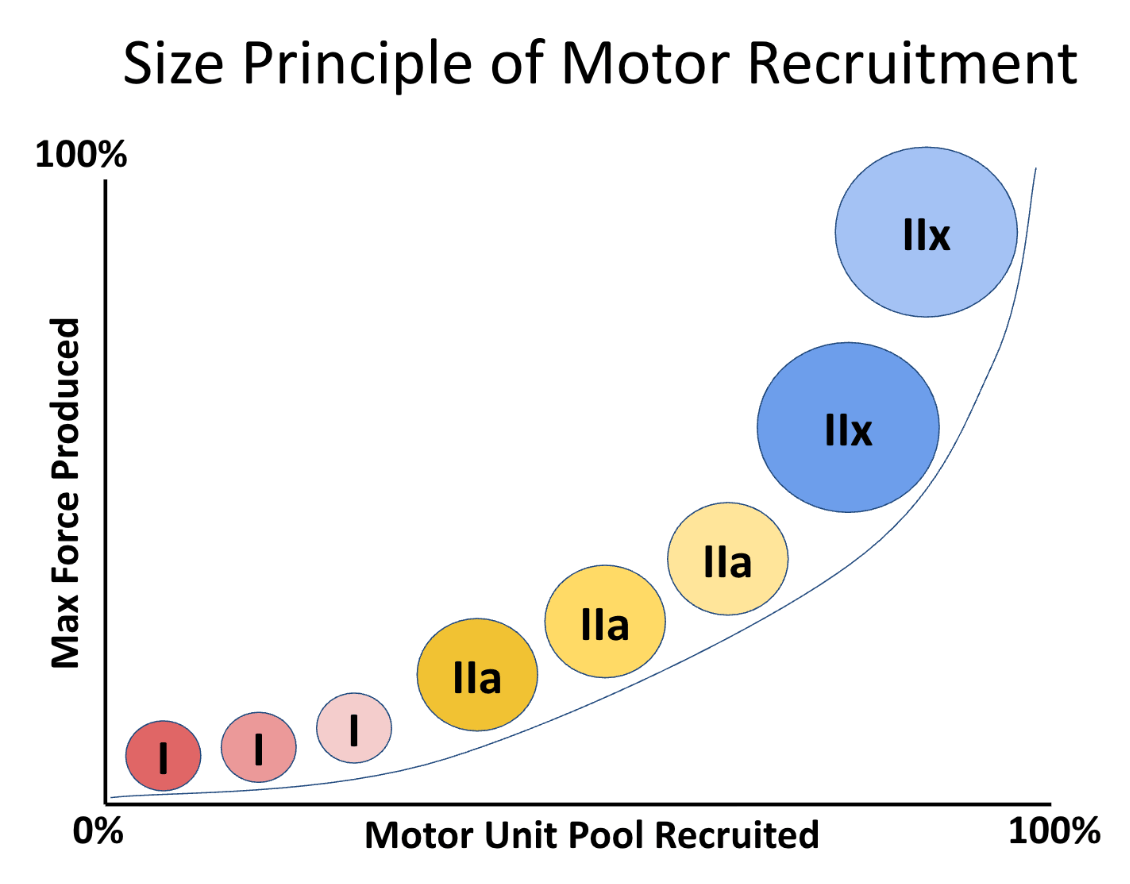
Explain the size principle of motor unit recruitment.
Motor units are recruited in order from smallest to largest in response to increasing demand for strength. Small, type I motor units are recruited first, followed by medium-sized, type IIa motor units, and large, type IIx motor units are recruited last.
What is this machine called, and what does it do?

Isokinetic dynamometer. It measures the force (torque) produced at different joint angles while moving at a constant rate.