Who was the first female composer in European written history that was a nun, a psychic, philosopher, and the author/artist of the universe called Scivias, which is Latin for "Know the Ways of the Lord" ?
Who is Hildegard of Bingen (1098-79)
These are key components of which Musical Era?
Humanism: Emphasis on human potential and creativity, moving away from medieval religious focus.
Art and Architecture: Revival of classical styles, realism, and perspective, exemplified by artists like da Vinci, Michelangelo, and Raphael.
Scientific Advancements: Focus on observation and experimentation, leading to breakthroughs in fields like astronomy and anatomy.
Literary Developments: Growth of literature in vernacular languages, featuring writers like Dante and Shakespeare.
Patronage System: Wealthy patrons and the Church funding artists and scholars.
City-States: Emergence of influential city-states such as Florence and Venice that nurtured cultural growth.
What is the Renaissance (1450-1600)
A musical dramatic work for singers and instrumentalists, typically performed in theaters.
What am I?
What is Opera
What is form in music?
-Multiple answers accepted-
organizing principle in music
•work’s structure or shape
•repetition and contrast: unity and variety
•variation: only some aspects of music altered
What do you remember about the relationship between text and music?
HINT: Week 2 lecture
Text within music helps tell the story.
The melodic and harmonic components add to this.
Composers/Artists when writing music compose the music to follow along with the words and to reflex what the words are saying.
Nothing is “on a count of because” to the idea of music with text.
Which composer is considered the father of opera, was born in Cremona, Italy in 1567, was court position to duke of Mantua, and choirmaster at St. Mark’s in Venice for thirty years?
HINT: composed Si ch’io vorrei morire (Truly I want to die) (Published 1603)
Who is Claudio Monteverdi (1567–1643)
These are key components of which Musical Era?
Monophonic Singing: Predominantly single melodic lines without harmony (unison).
Gregorian Chant: Dominant sacred music form linked to the Catholic Church, featuring simple, unaccompanied Latin melodies.
Early Notation Systems: Musicians developed "neumes" to indicate pitch direction without exact values.
Liturgical Music: Composed primarily for church services and religious ceremonies.
Secular Music: Performed by traveling musicians (troubadours and trouveres), often centered on courtly love and chivalry.
Modes: Utilized systems of modes distinct from modern scales, shaping the music's sound.
What is the The Medieval Era, or Middle Ages! This lasted from approximately 476 AD to 1400-1450 AD
What is a composition for an instrumental soloist, often with a piano accompaniment, typically in several movements with one or more in sonata form?
What is a Sonata
Define strophic form
the same melody with each stanza of text
What is the structure of melody and how can one define it?
HINT:
Can have multiple answers
- Influenced by object size; shorter objects create higher frequencies.
- Finger placement alters vibrating length and pitch.
- Staff symbols indicate frequency and duration.
Timbre: Unique sound quality or tone color.
Melody: A sequence of pitches.
Range: Distance between lowest and highest notes—narrow (children’s songs), medium, wide.
Contour: Shape—ascending, descending, arch, wave, static.
Melodic Movement:
Interval: Distance between pitches.
Conjunct Melodies: Small intervals.
Disjunct Melodies: Larger intervals.
Components:
Phrase: Unit within a melody.
Cadence: Ends a phrase, providing a resting point.
This composer (very famous) was a Baroque innovator and master of counterpoint. Some say the Mass in B Minor is a summation of his art, with sections that weren't usually part of church services at the time. Who is he?
HINT: The "Coffee Cantata"!
Johann Sebastian Bach (1685-1750)
Key factors of this era include:
- Simplicity: Characterized by straightforward melodies and a more simplified style than the preceding Baroque period.
- Homophony: Music features a primary part supported by smaller components for a more harmonious sound.
- Sonata: The solo keyboard sonata was a crucial musical form.
- Variation: Composers frequently developed and varied themes within their works.
- Orchestra: The orchestra was a prominent ensemble of the time.
- Symmetry and Balance: Compositions displayed symmetry and balance.
- Clear Divisions: Distinct divisions between parts, typically with a single melody and accompanying chords.
- Brighter Contrasts: Employed brighter contrasts and diverse tone colors.
What is this Musical Era?
What is the Classical Era (1750-1820)
a group of instrumentalists, especially one combining string, woodwind, brass, and percussion sections and playing classical music.
typically in front of the stage and on a lower level than the audience.
What is an Orchestra
Define through-composed form.
no main section of music or text repeated
What do you remember about the conversation of female composers in written history? Give an example!
Female Composers are historically overlooked due to sexism, elitism, and laws limiting their autonomy. For instance, Mozart's sister Maria, a child prodigy, has no surviving music.
Any other hint given that is relevant can also gain these points.
After early success, this Italian Romantic Composer suffered a serious car accident that resulted in severe leg injuries, delaying his opera "Madama Butterfly." While recovering, his wife Elvira accused their servant, Doria Manfredi, of infidelity, leading to public humiliation and Doria's suicide by poisoning. Despite evidence of her innocence, Elvira was later convicted of slander and sentenced to prison.
Can you name the composer involved in this scandal?
Who is Giacomo Puccini (1858–1924)
Ornamentation: Features intricate sound embellishments.
Contrast: It contrasts dynamics, tempos, and instrument timbres.
Movement: This period is defined by dynamic musical movement.
Sonorous bass line: A continuous bass line supports higher voices.
Key transitions: Frequent shifts occur between closely related keys.
Instrumental use: Instrumental music flourished, with the harpsichord as a key instrument.
Hierarchy of beats: The first beat is emphasized as the strongest.
Cantatas: Vocal compositions set to sacred or secular texts.
Sonatas: Multi-movement works for one or more instruments with basso continuo.
Which Era is this?
What is the Baroque Era (1600-1750). The Baroque style originated in Rome in the early 17th century and spread to other parts of Europe.
a set of related songs, often on a romantic theme, intended to form a single musical entity.
Often connected by poetry, or musical ideas.
What is an Art Song cycle
Define the difference between
-Binary (two-part) form: (A-B)
•statement and departure
-Ternary (three-part) form: (A-B-A)
•statement, departure, and return of original statement
Any answer that is basically this can be counted as points.
What is this Instruments?
HINT: WEEK 2 lecture on world instruments
What is a Bowl Harp or Chelys.
- Bowl harps or Chelys or have been made using tortoise shells and calabashes as resonators since prehistory.The chelys is an ancient Greek bowl harp made from tortoise shell with wooden, bone, ivory, or metal arms and gut strings. Known as the original lyre, it was played by both genders in various musical contexts. Legend attributes its invention to Hermes, who used a tortoise shell and cane wood. The chelys, alongside the barbitos—which has longer arms for deeper tones—distinguishes itself by being strummed rather than plucked, with hand movements shaping the sound.
This composer, celebrated on December 17 for his Catholic baptism, has an unknown birth date. A notable figure of the Classical era, he wrote the Piano Concerto No. 1 in C Major. Despite having dyscalculia, he produced mathematically complex compositions and shocked contemporaries with his experimental masterpieces. Even after becoming deaf, he composed by relying on imagination, sound recollection, ear trumpets, and tactile feedback from the piano. He rejected traditional classical norms to express emotion, known for his loud and unruly demeanor, wild hair, and often unkempt attire. Tall and socially disadvantaged, he struggled with love, ultimately remaining unmarried and dying from illness. Who is this composer?
Ludwig van Beethoveen (1770-1827)
- Long melodies
- Dramatic
- Nationalistic undertones
- A return to the past
- Starving Artist
- An awe of nature
- The celebration of the individual
- The glorification of nature
What musical era is this?
What is the Romantic Era (1820-1900)
A musical composition for a solo instrument or instruments accompanied by an orchestra, especially one conceived on a relatively large scale.
What is a Concerto
Pick out someone from your team to write out either
5-part Rondo
or
Sonata Rondo
Use letters to help write it out
-double points if you do both! -
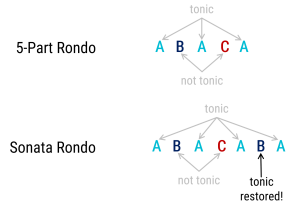
Someone from your group go up and play something on the piano for DOUBLE POINTS!!!!
OR
Sing a random song off the top of your head for DOUBLE POINTS!!!!
Double points achieved!