Name the 4 nucleic bases AND their pairing.
What are Adenine with Thymine and Guanine with Cytosine.
What molecule unzips the hydrogen bonds in DNA replication?
What is helicase
Molecule that pairs RNA nucleotides with the DNA nucleotides.
RNA polymerase.
What is translation?
the conversion of mRNA into the amino acid sequence of protein.
Define mutation
What is a change in a base sequence of the DNA or RNA.
What is a nucleotide?
Sugar, phosphate and base- create the monomer of the nucleic acids
What is the complimentary base sequence of the following DNA strand:
TACGGATACCCAAATTGAATT
ATGCCTATGGGTTTAACTTAA
What is the complimentary mRNA strand from the following DNA strand?
TACGGATACCCAAATTGAATT
AUGCCUAUGGGUUUAACUUAA
What enzyme binds the appropriate amino acid and tRNA?
200 extra points if you can draw a tRNA (2D format) and indicate where the amino acid is attached and where the anticodon is located.
tRNA activating enzyme. (or more specifically an aminoacyl-tRNA-synthetase)
For 200 extra points... 100 for drawing it correctly & 100 for identifying the anti-codon and a.a. attachment site. 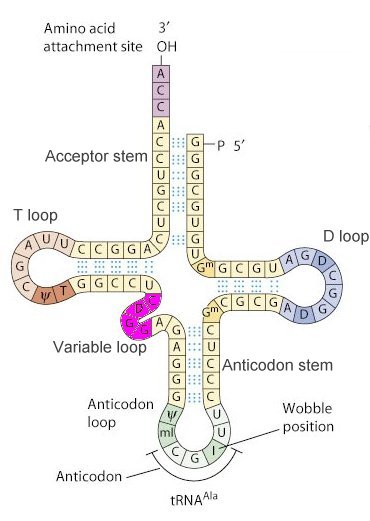
Briefly describe the 4 protein folding stages.
Primary structure- amino acid chain
Secondary structure- alpha helixes & beta sheets (held together by hydrogen bonds
Tertiary structure- R groups of amino acids cause the structure to fold. Hydrophobic R groups moving inside and hydrophillic R groups moving outward. +/- R groups attached and Cystine groups form sulfur bridges.
Quaternary structure- multiple folded tertiary structures added together. (may or may not be needed for a functional protein)
What are the STRUCTURAL (2) similarities and (3) differences between DNA and RNA?
Similarities: both are helical, both made of nucleotides, guanine, adenine, and cytosine are common, both contain phosphates Differences: DNA is double stranded- RNA single stranded, DNA had thymine- RNA has uracil, DNA has deoxyribose sugar- RNA has ribose sugar
Distinguish between the 2 types of DNA polymerases.
DNA polymerase III- adds the bases during replication,
polymerase I- replaces the RNA primers with DNA
How do promoters and enhancers help to regulate transcription?
Promoters and enhancers are non-coding DNA. Promoters are closer to the gene and enhancers further downstream. Transcription factors bind the promoter which allows the RNA polymerase to be captured. Co-activator molecules also bind which allows the activator proteins, bound to the enhancer sequence, to initiate transcription. Depending on the type of activator protein, transcription can be sped up, slowed down, or stopped all together.
What is the appropriate amino acid sequence for the following mRNA sequence?
AUG CCU AUG GGU UUA ACU UAA

met- pro- met- gly- leu- thr- stop
Why do most mutations commonly go unnoticed in the human body?
What are 3 answers: 1) have no affect due to multiple codons coding for the same amino acid 2) occur only in 1 cell of the body so have no affect because they are not passed on 3) not detrimental to the livelihood of the cell or organism.
Describe the Hershey and Chase Experiment AND it's conclusion.
Hershey and Chase's experiment concluded that DNA not protein carried the genetic information.

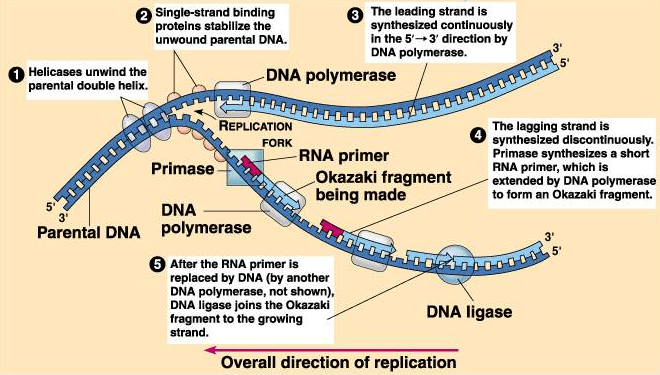
What is the reason for the leading and lagging strands in DNA replication?
DNA polymerase can only add based 5' --> 3', because the two strands run anti-parallel to each other, the polymerase must run against the direction of replication on one strand creating the lagging strand.
Name and describe the purpose of both types of post-transcription modification of mRNA.
What is DNA splicing and the addition of the 5' cap and 3' poly A tail. DNA splicing allows for one gene to make multiple different proteins (increases the functionality of the gene). 5' cap and 3' poly A tail prevent degradation of the mRNA strand and help the ribosome to recognize the mRNA to be translated in the cytoplasm.
Explain the process of Translation: Initiation, Elongation and Termination.
Initiation: binding of the mRNA to small ribosome subunit, AUG in the P site, binds the appropriate tRNA, Large subunit of ribosome binds.
Elongation: next tRNA complimentary to the next codon in the A site binds. A peptide bond is formed between the two amino acids. The entire ribosome shifts moving the original tRNA into the E site and releasing it. The A site tRNA moves into the P site. The process repeats until the stop codon is reached.
Termination: When the stop codon is reached in the P site, a tRNA that codes for NO amino acid is attached. This ends the elongation phase and the present tRNAs are released and the ribosome disassembled.
Explain the cause and consequences of sickle cell anemia.
Sickle cell anemia is caused by a base substitution (or point mutation) of the codon GAA to GUA. This changes the amino acid from Glutamine to Valine (a movement from basic to hydrophobic amino acid). This is a severe change.
This causes the red blood cells to become sickle shaped instead of round and carry oxygen less efficiently around the body. It often leads to pain, clogged arteries, and even infection due to the sickle shape of the cells.
Draw the structure of DNA. Label the following parts: nucleotide, G, T, A, C, Phosphate, specific sugar, covalent bond, hydrogen bond.
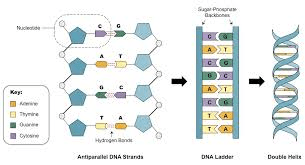
Extra 100 points if you demonstrated the anti-parallel nature of the molecule as well.
Draw the process of Replication. Label the following: direction or replication, helicase, gyrase, polymerase I and III, leading and lagging strands, Primase, RNA primer, okazaki fragments, DNA ligase
Explain the importance of methylation in transcription regulation.
Nucelosomes (8 histones with wrapped DNA twisted around each other) tightly coil DNA. When methylated they remain coiled. When aceytlated they unravel and allow transcription to occur. A gene that is attached to a methylated histone or nucleosome would be unable to be transcribed hence regulating it's expression. 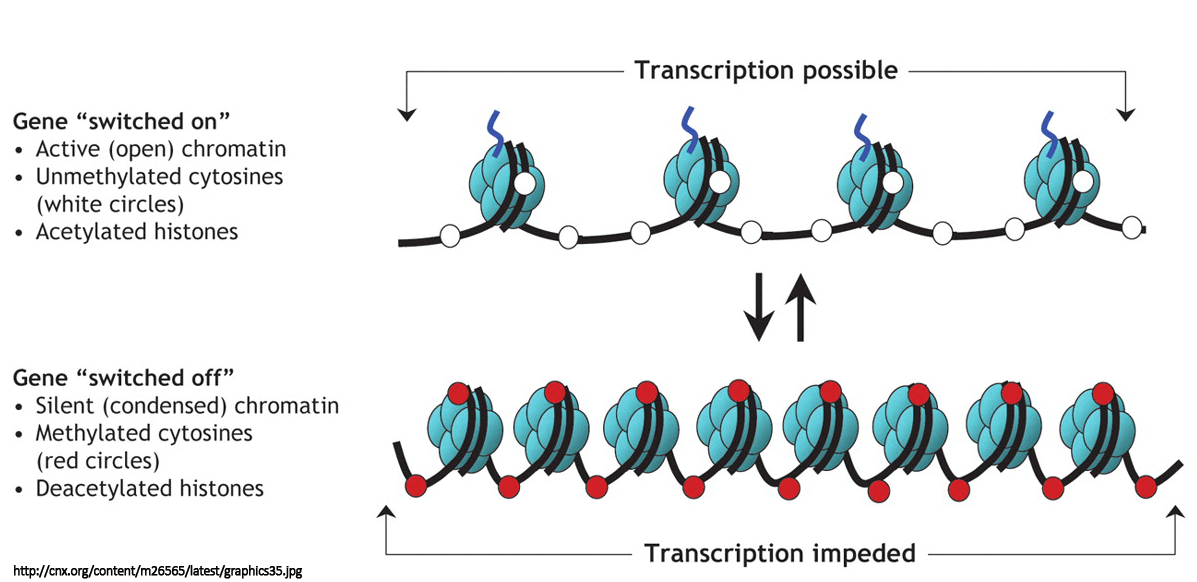
Draw and label the diagram of translation- label mRNA, codon, anticodon, tRNA, amino acids, ribosome, peptide bond

Of the 5 types of mutations (point mutations, insertions, deletions, inversions, and translocations) which would you consider to have the severest affects? Use evidence and reasoning in your answer.
Answers will vary but should indicate a level of understanding concerning how mutations affect DNA and that not all mutations are bad but even small ones can cause problems. Placement and significance of where the mutation occurs should be indicated.