What is the difference between DVT and PE?
DVT is in the deep, lower leg veins, whereas PE is in the lungs.
What should the nurse educate the patient on and why regarding hip fractures?
- mobilize sooner rather than later
- use walker to assist with mobility
- educate pt about how walkers provide support and prevent falls

Describe the presentation of rheumatoid arthritis.
Presentation is symmetrical
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues, particularly the synovium, which is the lining of joints

What are the s/s of VTE?
Homans' sign, lower leg swelling, calf tenderness, warmth, redness. HOMANS LOWER LEG AND CALF IS WARM AND RED.
What are some nursing interventions for external fixation?
Pin care
Infection risk
Pain control
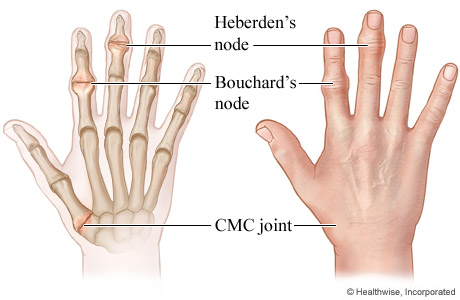
What are the deformities of OA?
DISEASE OF WEAR AND TEAR
Heberden’s nodes (familial, 40yrs/ distal interphalangeal joint)
- high up and on the finger
Buchards nodes (Proximal Interphalangeal joint)
- below
ASYMMETRIC
What are the early s/s of Fat Embolism Syndrome?
Hypoxemia, decreased O2, recent long bone/pelvic fracture
What are post reduction concerns?
1. Circulation is a major concern post reduction procedures, if circulation post fracture can not be felt upon palpation, nurse must attempt using a doppler.
2. Pain that is unrelieved by opioids is also a sign of more serious complication.
What is the cure for OA?
WRONG TRICKED YOU!!!
There is no cure, however, therapies to mange OA includes: weight mgmt, rest and joint protection, therapeutic exercise, and heat && cold.
What are the late s/s of Fat Embolism Syndrome?
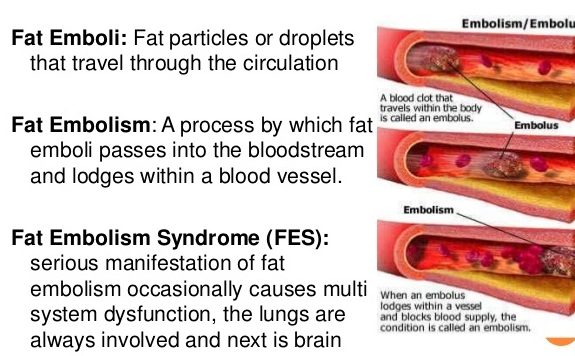 Possible petechial rash (late sign), change in LOC, tachypnea, SOB and chest pain(late sign), headache (late sign).
Possible petechial rash (late sign), change in LOC, tachypnea, SOB and chest pain(late sign), headache (late sign).
What is the criteria for cast removal?
Casts may be removed only after ends of bones are well joined.
Ossification is the final laying down of bone after the fracture has been bridged and the fragments are united.
Mature bone replaces the callus, and the fracture site feels firm and appears united on radiograph.
Remodeling takes place after ossification
What are the differences in the picture below?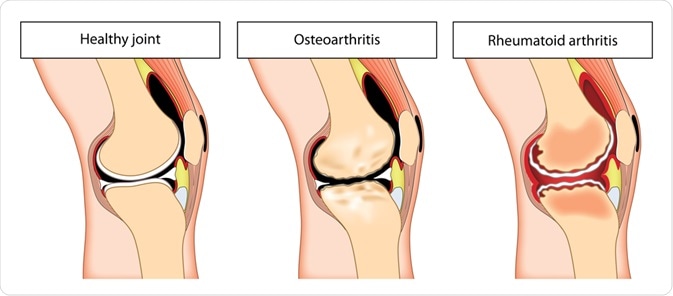
OA: thinned cartilage, bone ends rub together
RA: swollen inflamed synovial membrane
What are the s/s of Compartment Syndrome?
Compartment syndrome: swelling and increased pressure within a confined space
6 Ps
Pain: passive stretching of muscles within the compartment; out of proportion to the injury/ no relief after medication
Paresthesia: tingling; decreased sensation
Pressure: decreased power
Pallor
Paralysis
Pulselessness
Picture below is trx for compartment syndrome:

What are the phases of fracture healing?
1. Initial Injury (Fracture) phase
2. Inflammatory phase
3. Reparative phase
4. Remodeling Phase
Limit or avoid animal proteins (liver, kidney, beef, lamb and pork)
Limit intake of seafood, especially those high in purine such as shellfish, sardines and tuna
Avoid alcohol as it greatly increases the risk of gout attacks
Limit or avoid foods/drinks sweetened with fructose
Encourage foods that reduce the risk of attacks including: coffee, cherries and foods high in vitamin C
