If a = b, then a + c = b + c
Addition Property of Equality
if vec(AB) cong vec(CD)
then AB = CD
Definition of Congruent
If ∠ABC is a right angle, then m∠ABC = 90o
Definition of right angle
If bar(AB) bot bar (BC) , then m∠ABC = 90o
Definition of Perpendicular
If a(b + c) = d, then ab + ac = d
Distributive Property
if B is the midpoint of bar(AC) then AB = BC
Definition of Midpoint
If mangleC=mangleB, then, angleCcongangleB
Definition of Congruent
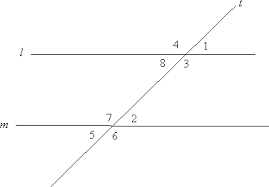
If l || m, then ∠2 and ∠3 are supplementary
Consecutive Interior Angle Theorem
If a = b, then b = a
Symmetric Property
If A is between C and F, then CA + AF = CF
Segment Addition Postulate
If vec(LM) bisects ∠AMC, then ∠AML ≅ ∠LMC
Definition of Angle Bisector
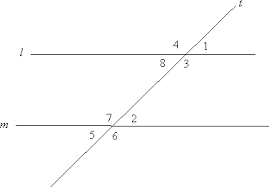 If ∠1 ≅ ∠5, then l || m
If ∠1 ≅ ∠5, then l || m
Converse of Alternate Exterior Angles Theorem
Substitution Property
If AB + BC = AC and AD + DC = AC,
then AB + BC = AD + DC
Transitive Property
If C is in the interior of ∠XYZ, then
m∠XYC + m∠CYZ = m∠XYZ
Angle Addition Postulate
If point B is on the perpendicular bisector of bar(CD) then BC = BD
Perpendicular Bisector Theorem
If a * b = c * b, then a = c
If 2(AB) = AB + EF, then AB = EF
Subtraction Property of Equality
If ∠A is supplementary to ∠B and ∠C is supplementary to ∠A, then ∠B ≅ ∠C
Congruent Supplements Theorem
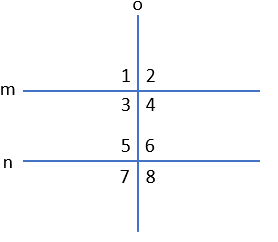 If o⊥m and o⊥n, then m||n
If o⊥m and o⊥n, then m||n
Converse of Perpendicular Transversal Theorem