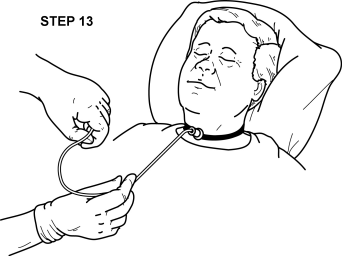
Endotracheal Tubes
In addition to HR, BP, RR, and temp; the nurse needs to assess a patient’s oxygen saturation (SaO₂). What procedure will best accomplish this?
- Incentive spirometry
- ABG
- Peak flow measurement
- Pulse oximetry

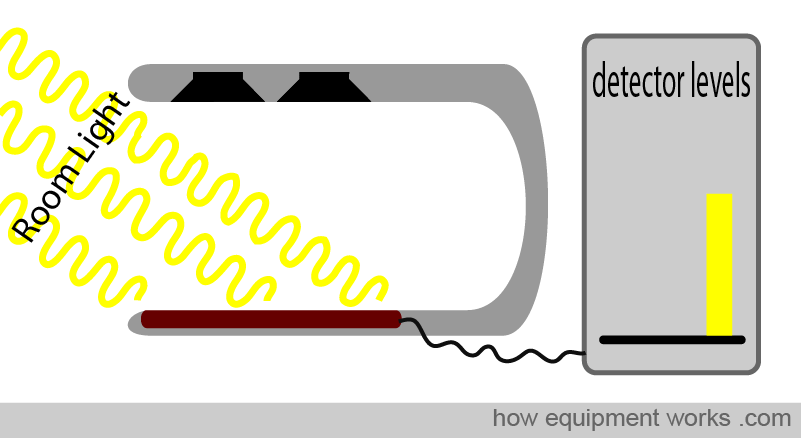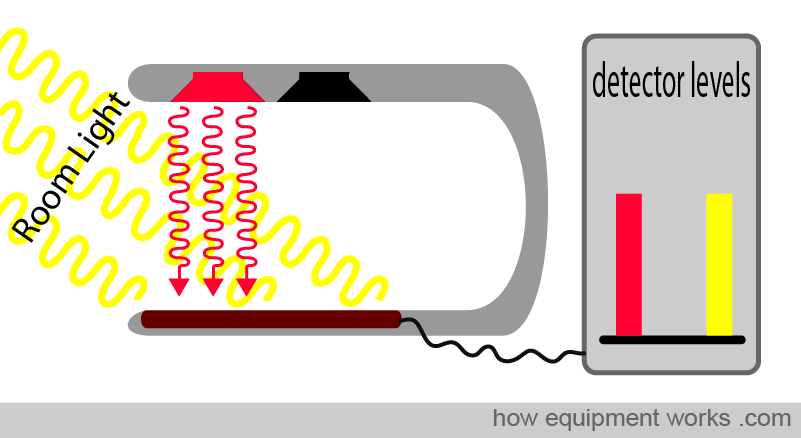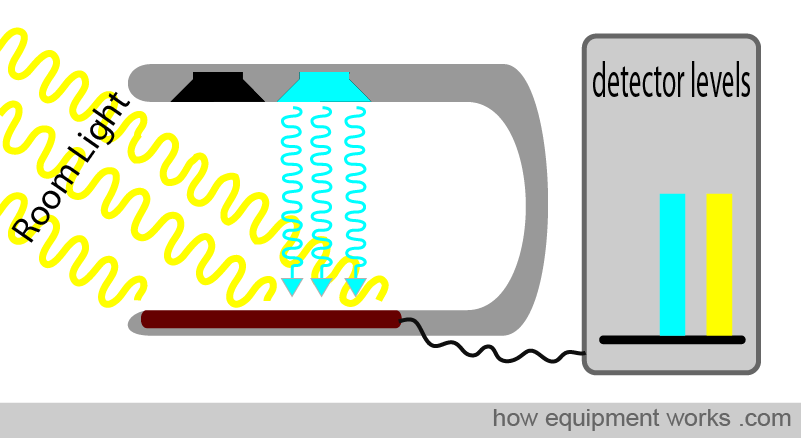
Pulse Oximetry= SaO₂
A client is diagnosed with a tension pneumothorax resulting from their chest hitting the steering wheel during an automobile accident. The ED nurse knows the highest priority is given to which intervention?
- Oxygenation
- Chest tube insertion
- ABGs
- Attaching a cardiac monitor
 reestablish thoracic negative pressure
reestablish thoracic negative pressure
An ED patient from a boating accident 3 hours ago presents with headache, fatigue, and the feeling that he “just can’t breathe enough”, also restless and tachycardic with elevated BP. The patient may be in the early stages of what respiratory problem?
- Hemodynamic shock
- Pleural effusion
- Acute respiratory failure
- Pneumonia

The nurse prepares to suction a vent patient’s ETT. Which vent setting is adjusted by the nurse before and after the procedure
- Tidal volume
- Respiratory rate
- Fraction of inspired oxygen (FIO₂)
- Flow

The nurse observes a student provide tracheostomy care and determines care is appropriate if the patient is placed in what position?
- Semi-Fowler
- Supine
- Prone
- Trendelenburg
Which of the following therapies may be ordered to increase oxygen-carrying capacity?
a. Blood transfusion
b. Corticosteroids
c. Bronchodilators
d. Sedatives

Hemoglobin
A client has a pleurovac drainage system in place to correct a hemothorax. Which action does the nurse take when providing care for this client?
- Assesses the client’s respiratory status frequently
- Loops any extra tubing to keep it off the floor
- Maintains an open drainage system
- Keeps the client in a supine position

If a DNR patient with end stage advanced COPD presents to the ED in acute respiratory failure. Which of the following treatments might be indicated to facilitate ventilation?
- Mechanical ventilation via an endotracheal tube
- Noninvasive positive pressure ventilation
- Emergency tracheostomy and mechanical ventilation
- Oxygen at 100% via bag-valve mask device
The physician orders the following mechanical ventilation settings for a patient. The patient’s spontaneous RR is 22. What ABG abnormality may occur if the patient continues to be tachypneic at these ventilator settings?
Settings: Tidal Volume 800 ml; FIO₂ 0.50%; Respiratory rate 14 breaths/per min; Mode Assis/control; Positive end-expiratory pressure 10cm
A. Metabolic acidosis
B. Metabolic alkalosis
C. Respiratory acidosis
D. Respiratory alkalosis
 patient will ventilate 22 complete breaths == respiratory alkalosis
patient will ventilate 22 complete breaths == respiratory alkalosis
When the ventilator alarm sounds, the nurse finds the patient lying in bed holding the endotracheal tube (ETT). The first intervention by the nurse is to
a. Position the patient in a left lateral position
b. Call the health care provider immediately to reinsert the tube
c. Activate the hospital’s rapid response team
d. Manually ventilate the patient with 100% oxygen
Your patient’s (PaO2) arterial blood gas levels indicate hypoxemia. The first intervention to relieve hypoxemia is:
A. Endotracheal suctioning
B. High tidal volume
C. Supplemental oxygen
D. Positive end-expiratory pressure PEEP
Apply supplemental oxygen
An adult is in a motorcycle accident and sustains 3 fractured ribs and a pneumothorax. A chest tube is inserted. The nurse should take which of the following actions?
- Monitor the fluctuations in the tube
- Pin the tubes to the sheets
- Clamp the tubes when transferring the patient to bed
- Empty the bottles every 8 hours
cessation of fluctuation may indicate blockage of the tube, or that the lung has re-expanded therefore fluctuation should be monitored
Which assessment information obtained by the nurse when caring for a patient receiving mechanical ventilation indicates the need for suctioning?
- The patient has not been suctioned for the last 6 hours
- The lungs have occasional audible expiratory wheezes
- The respiratory rate is 32 breaths/minute
- The pulse oximeter shows an SaO₂ of 95%
The nurse expects which mode of mechanical ventilation to be prescribed for a client with severe Guillain-Barre syndrome?
- Controlled mechanical ventilation (CMV)
- Assist-Control ventilation (AC)
- Synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (SIMV)
- Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP)
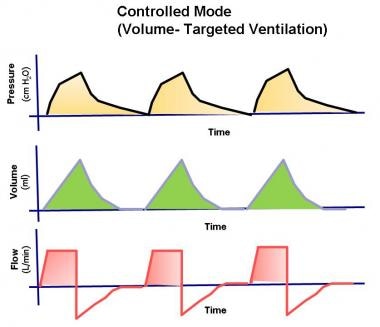
Neuro Muscular disease Guillain-Barre patient's can not breathe
The outer cannula of a client’s trach tube is accidentally expelled 36 hours after surgery. Which action does the nurse take first?
- Contacts the health care provider
- Cuts the trach nec ties
- Inserts the emergency outer tube that is taped to the HOB
- Ventilates the client using a manual resuscitation bag

The nurse understands the physiological state r/t the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve in a patient with normal Hgb, but with significant ↓ SaO₂ and PaO₂ is
a. The patient’s tissue demands may be met, but they will be unable to respond to physiological stressors
b. The patient’ short-term oxygen needs will be meet, but they will be unable to expel sufficient CO₂
c. The patient will experience tissue hypoxia with no sensation of SOB or labored breathing
d. The patient will experience respiratory alkalosis with no ability to compensate

no reserve oxygen supply for additional needs
A client with a chest tube asks the nurse about the intermittent bubbling seen in the water seal drainage equipment
- “It’s supposed to do that”
- “It shows your lung has not yet re-expanded”
- “it indicates that the drainage system needs to be replaced”
- “What do you think it means?”
 air leak indicated with bubbling in water seal drainage chamber
air leak indicated with bubbling in water seal drainage chamber
Which of the following statements about mechanically ventilated patient’s is true?
a. Some patients are able to write notes as a means of communication
b. Patients must always have their wrists restrained to avoid self-extubating
c. Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease COPD wean easily from mechanical ventilation
d. Controlled ventilation is the preferred mode for most patients
A client requires respiratory support with SIMV. The nurse understands which to be the primary mechanism of action
- The delivery of breaths is synchronized with the R wave of the client
- A set tidal volume is delivered at a set rate regardless of client’s breathing efforts
- Positive pressure is intermittently exerted at the end of ventilator breaths
- Ventilator breaths are correlated with client breathing and the client can breathe naturally in between.
 patient can breathe naturally in-between preset machine breaths
patient can breathe naturally in-between preset machine breaths
A client requires an emergency tracheostomy. When caring for the trach the nurse
- Suctions the trach every hour
- Cleans the inner cannula after suctioning
- Cleans the site every four hours
- Hyperextends the client’s neck to maintain patency
The respiratory nurse knows primary oxygenation clinical problems that may improve with increased oxygen supplements include which of the following
- Atelectasis
- Opioid sedation
- Pneumothorax
- Pneumonia

primary ventilation problems do not respond to increased oxygen
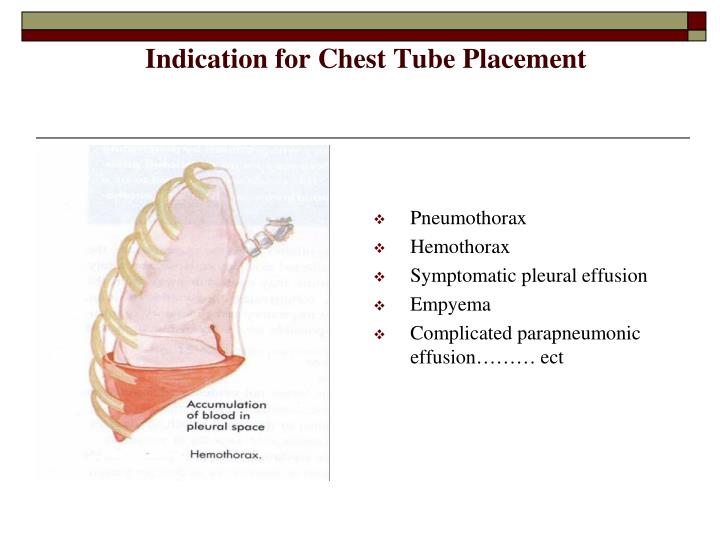
A nurse educator is reviewing the indications for chest drainage systems with a group of medical nurses. What indications should the nurses identify?
- Post thoracotomy, Pleurisy and Spontaneous Pneumothorax
- Spontaneous Pneumothorax
- Need for postural drainage, Pleurisy and Chest trauma resulting in Pneumothorax
- Chest trauma Pneumothorax, Spontaneous Pneumothorax and Post thoracotomy
When the nurse is weaning a patient who has COPD from mechanical ventilation, which patient assessment indicates that the weaning protocol should be discontinued?
a. The patient’s heart rate is 98 beats/min
b. The patient respiratory rate is 35 breaths/min
c. The patient’s oxygen saturation is 91%
d. The patient’s spontaneous tidal volume is 500 ml
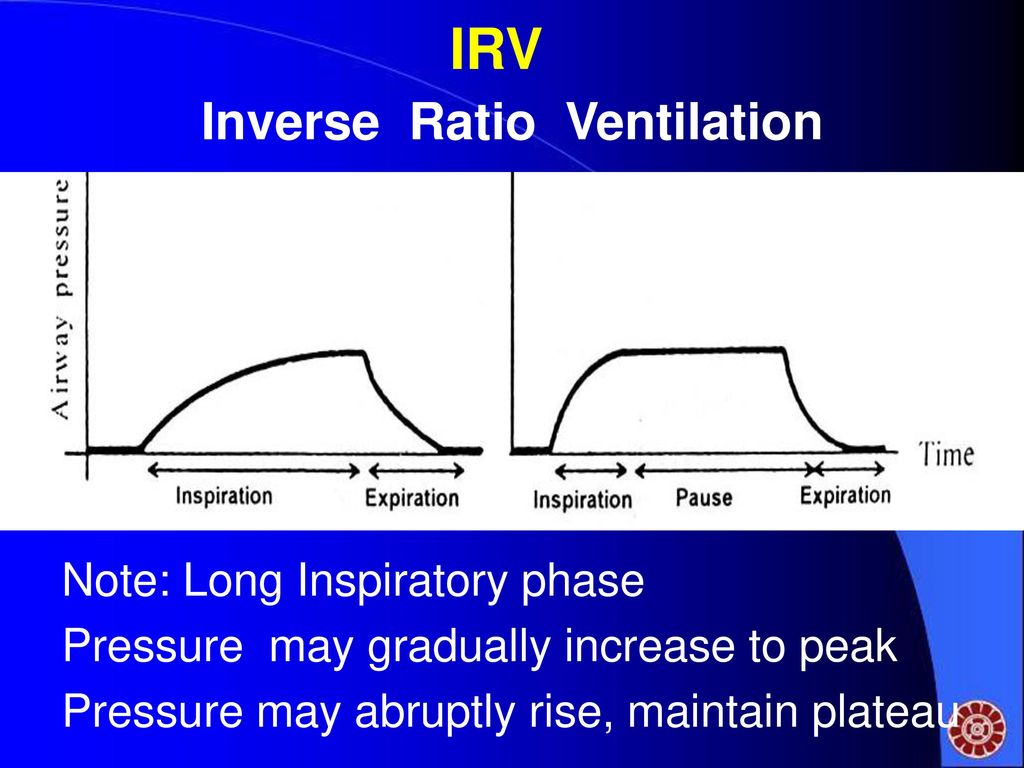
Conventional therapy has been used to treat a patient with acute respiratory distress syndrome, but the patient remains hypoxemic. Which of the following might be ordered?
a. Helium instead of oxygen through the ventilator circuit
b. Pressure-control, inverse-ration ventilation
c. Supine positioning
d. Synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation at a rate of 10 breaths/min
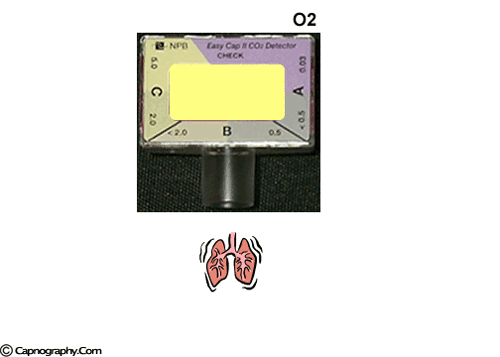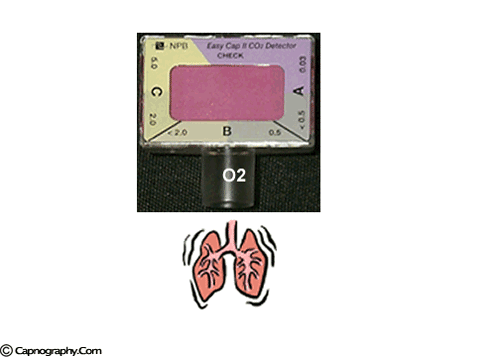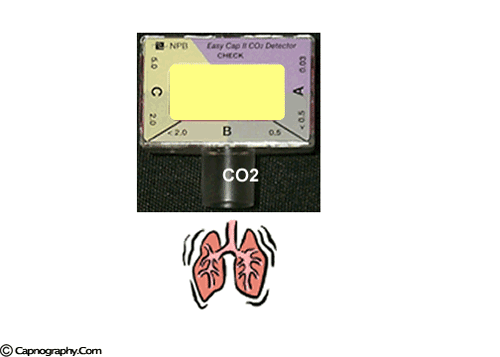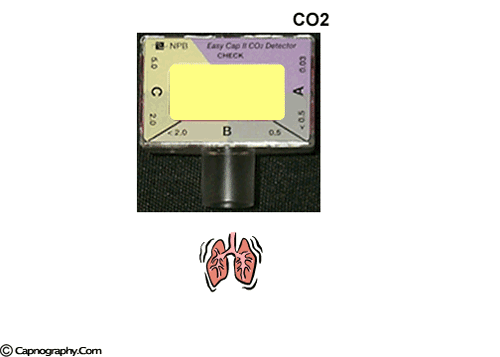
To verify the correct placement of an endotracheal tube (ETT) after insertion, the best initial action for the nurse to take is…
- Obtain a portable chest radiograph to check tube placement
- Auscultate for the presence of bilateral breath sounds
- Use an end-tidal CO₂ monitor to check for placement in the trachea
- Observe the chest for symmetrical movement with ventilation