Mohenjo-Daro was laid out in an organized pattern, with long, wide main streets and large rectangular blocks. Most of its houses were built with baked clay bricks of a standard size. At Harappa and other Indus sites, mud and unbaked bricks were also common building materials. In addition, Indus houses had complex plumbing systems, with baths, drains, and water chutes that led into sewers beneath the streets. Indus merchants used a uniform system of weights and measures. What claim can you draw about Mohenjo–Daro and Harappa based on the passage above?
(1) There was constant warfare between the cities.
(2) The cities were well-planned.
(3) They had well-organized nomadic tribes.
Base your answer to the question on the map below and on your knowledge of social studies.
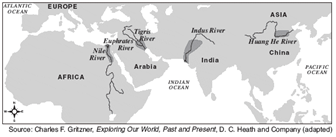
Source: Charles F. Gritzner, Exploring Our World, Past and Present, D.C. Health and Company (adapted) from the NYS Global History and Geography Regents Exam.
The main purpose of this map is to illustrate the location of
(1) overseas trade routes
(2) early belief systems
(3) river valley civilizations
(4) burial sites of ancient rulers
(3) river valley civilizations
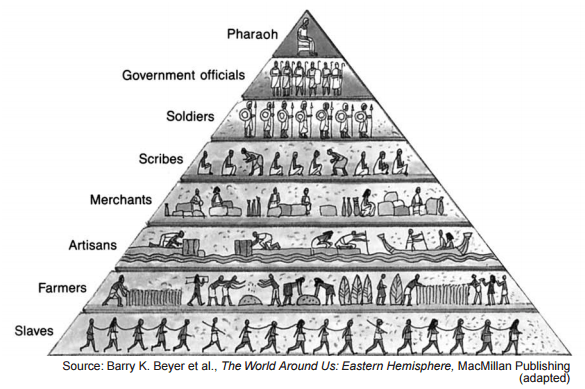
Which claim about the society is best supported by this illustration?
(1) The women had equal status to the men.
(2) The social structure was hierarchical.
(3) Social mobility was unrestricted.
(4) Soldiers had less power than farmers.
(2) The social structure was hierarchical.
Base your answer to the question on the passage below and your knowledge of social studies.
“If a seignior (noble) has knocked out the tooth of a seignior of his own rank, they shall knock out his tooth. But if he has knocked out a commoner's tooth, he shall pay one-third mina of silver.”
– Code of Hammurabi excerpt from the NYS Global History and Geography Regents Exam
What type of source does this quote come from?
- Letter
- Legal code
- Newspaper article
- Oral history
- Legal code
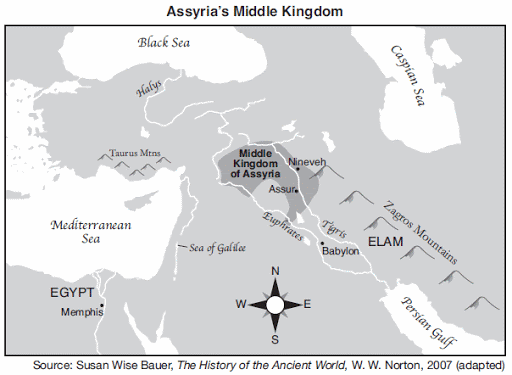
The Middle Kingdom of Assyria was located in an area also known as the
subcontinent
Holy Land
Fertile Crescent
rooftop of the world
Fertile Crescent
Mohenjo-Daro was laid out in an organized pattern, with long, wide main streets and large rectangular blocks. Most of its houses were built with baked clay bricks of a standard size. At Harappa and other Indus sites, mud and unbaked bricks were also common building materials. In addition, Indus houses had complex plumbing systems, with baths, drains, and water chutes that led into sewers beneath the streets. Indus merchants used a uniform system of weights and measures. What claim can you draw about Mohenjo–Daro and Harappa based on the passage above?
(1) There was constant warfare between the cities.
(2) The cities were well-planned.
(3) They had well-organized nomadic tribes.
(2) The cities were well-planned.

The historical development depicted in this map is an effect of
- The use of primary sources
- Judaism
- The Neolithic Revolution
- The Golden Age of Greece
- The Neolithic Revolution
“Praise to thee, O Nile, that flows out
of the Earth and comes to nourish
the dwellers of Egypt….
If the Nile is sluggish, the nostrils are
stopped up, and the people are
brought low;
The offerings of the gods are reduced,
and millions die.
When the Nile rises, the Earth is joyous
and everyone is glad; every jaw
laughs and every tooth is
uncovered.”
2a. Using document 2, explain the purpose of the Hymn to the Nile.
Base your answer to the question on the passage below and your knowledge of social studies.
“If a seignior (noble) has knocked out the tooth of a seignior of his own rank, they shall knock out his tooth. But if he has knocked out a commoner's tooth, he shall pay one-third mina of silver.”
– Code of Hammurabi excerpt from the NYS Global History and Geography Regents Exam
Which idea of Babylonian society does this portion of the Hammurabi code of law reflect?
- All men were equal under the law.
- Fines were preferable to corporal punishment.
- Divisions existed between social classes.
- Violence was always punished with violence.
- Divisions existed between social classes.
The ancient Sumerians modified their environment to increase food production by
building terraces
removing rain forests
digging irrigation canals
developing chinampas
digging irrigation canals
Mohenjo-Daro was laid out in an organized pattern, with long, wide main streets and large rectangular blocks. Most of its houses were built with baked clay bricks of a standard size. At Harappa and other Indus sites, mud and unbaked bricks were also common building materials. In addition, Indus houses had complex plumbing systems, with baths, drains, and water chutes that led into sewers beneath the streets. Indus merchants used a uniform system of weights and measures. The Indus merchants most likely developed a uniform system of weights and measures to —
(1) generate more money for the people of Harappa.
(2) make it easier and fairer to trade goods.
(3) raise money for the plumbing systems of Harappa.
(2) make it easier and fairer to trade goods.

Identify the best use of this map for a historian.
- To explore the religious beliefs of people living in Early River Valley Civilizations
- To compare the geographic context of Early River Valley Civilizations
- To compare the written languages of Early River Valley Civilizations
- To analyze trade routes between Early River Valley Civilizations
- To compare the geographic context of Early River Valley Civilizations
Base your answer to the question on the passage below and your knowledge of social studies.
The first successful efforts to control the flow of water were made in Mesopotamia and Egypt, where the remains of the prehistoric irrigation works still exist. In ancient Egypt, the construction of canals was a major endeavor of the pharaohs and their servants, beginning in Scorpio’s time. One of the first duties of provincial governors was the digging and repair of canals, which were used to flood large tracts of land while the Nile was flowing high. The land was checkerboarded with small basins, defined by a system of dikes. Problems regarding the uncertainty of the flow of the Nile were recognized. During very high flows, the dikes were washed away and villages flooded, drowning thousands. During low flows, the land did not receive water, and no crops could grow. In many places where fields were too high to receive water from the canals, water was drawn from the canals or the Nile directly by a swape or a shaduf. These consisted of a bucket on the end of a cord that hung from the long end of a pivoted boom, counterweighted at the short end. The building of canals continued in Egypt throughout the centuries.…
Source: Larry W. Mays, “Irrigation Systems, Ancient,” Water Encyclopedia online (adapted) from NYS Global History and Geography Regents, January, 2014.
Why did Ancient Egyptians build canals, systems of dikes, and tools like swapes and shadufs?
- Egyptians believed that the god of the Nile needed to be contained within the river’s banks.
- Egyptian farmers needed to flood their fields because they believed their crops grew best under water.
- The Pharaohs wanted water diverted to their royal baths.
- The Nile River’s water levels were difficult to predict and the water was needed to grow food.
4
Sections from the Code of Hammurabi (1754 BCE)
53. If any one be too lazy to keep his dam in proper condition, and does not so keep it; if then the dam break and all the fields be flooded, then shall he in whose dam the break occurred be sold for money, and the money shall replace the corn which he has caused to be ruined.
54. If he be not able to replace the corn, then he and his possessions shall be divided among the farmers whose corn he has flooded.
199. If [a free-born man] put out the eye of a man's slave, or break the bone of a man's slave, he shall pay one-half of its value.
202. If any one strike the body of a man higher in rank than he, he shall receive sixty blows with an ox-whip in public.
203. If a free-born man strike the body of another free-born man of equal rank, he shall pay one gold mina.
Source: “Code of Hammurabi,” 1780 BCE. adapted from STANFORD HISTORY EDUCATION GROUP sheg.stanford.edu
2a. Using document 2, explain Hammurabi’s purpose for writing the Code of Hammurabi. [1]
To provide rules and establish order in his empire.
Hammurabi wrote the Code of Hammurabi to establish the laws in the Babylonian Empire so everyone knows what the rules are and the punishments for breaking them.
Base your answer to the question on the map below and on your knowledge of social studies.

Source: Charles F. Gritzner, Exploring Our World, Past and Present, D.C. Health and Company (adapted) from the NYS Global History and Geography Regents Exam.
Identify the best use of this map for a historian.
- To explore the religious beliefs of people living in Early River Valley Civilizations
- To compare the geographic context of Early River Valley Civilizations
- To compare the written languages of Early River Valley Civilizations
- To analyze trade routes between Early River Valley Civilizations
The yellow river was called the "river of sorrows" because...
flooding

Which innovation most contributed to the development of the civilizations depicted in the map?
- Paper
- Irrigation
- The compass
- Gunpowder
- Irrigation
Base your answer to the question on the passage below and your knowledge of social studies.
The first successful efforts to control the flow of water were made in Mesopotamia and Egypt, where the remains of the prehistoric irrigation works still exist. In ancient Egypt, the construction of canals was a major endeavor of the pharaohs and their servants, beginning in Scorpio’s time. One of the first duties of provincial governors was the digging and repair of canals, which were used to flood large tracts of land while the Nile was flowing high. The land was checkerboarded with small basins, defined by a system of dikes. Problems regarding the uncertainty of the flow of the Nile were recognized. During very high flows, the dikes were washed away and villages flooded, drowning thousands. During low flows, the land did not receive water, and no crops could grow. In many places where fields were too high to receive water from the canals, water was drawn from the canals or the Nile directly by a swape or a shaduf. These consisted of a bucket on the end of a cord that hung from the long end of a pivoted boom, counterweighted at the short end. The building of canals continued in Egypt throughout the centuries.…
Source: Larry W. Mays, “Irrigation Systems, Ancient,” Water Encyclopedia online (adapted) from NYS Global History and Geography Regents, January, 2014.
What effect did the water control methods described in the passage have in Ancient Egypt if they worked properly?
- Priests performed mummification ceremonies with more frequency.
- Crop yields increased and floods were controlled.
- There were fewer slave riots.
4. Trade in fish from the Nile increased between Egypt and civilizations in Mesopotamia.
- Crop yields increased and floods were controlled.
Base your answer to the question on the map below and on your knowledge of social studies.

Source: Charles F. Gritzner, Exploring Our World, Past and Present, D.C. Health and Company (adapted) from the NYS Global History and Geography Regents Exam.
Which innovation most contributed to the development of the civilizations depicted in the map?
- Paper
- Irrigation
- The compass
- Gunpowder
- Irrigation
The river valleys of the Tigris-Euphrates, the Nile, and the Indus were centers of civilization because they
had rich deposits of iron ore and coal
were isolated from other cultural influences
were easy to defend from invasion
provided a means of transportation and irrigation
provided a means of transportation and irrigation
Name one achievement of Ancient China Civilization.

The Middle Kingdom of Assyria was located in an area also known as the
(1) subcontinent
(2) Holy Land
(3) Fertile Crescent
(4) rooftop of the world
(3) Fertile Crescent
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the model below and your knowledge of social studies.
1. An examination of this model would suggest that
(1) peasants are excluded from political activity
(2) this society lacks a social class system
(3) art can provide an understanding of history
(4) everyday life is based on religious beliefs
- 3) art can provide an understanding of history
Base your answer to the question on the passage below and your knowledge of social studies.
“If a seignior (noble) has knocked out the tooth of a seignior of his own rank, they shall knock out his tooth. But if he has knocked out a commoner's tooth, he shall pay one-third mina of silver. ”
- Code of Hammurabi excerpt from the NYS Global History and Geography Regents Exam
What type of source does this quote come from?
- Letter
- Legal code
- Newspaper article
- Oral history
- Legal code
The early civilizations of the Nile River Valley, Mesopotamia, and the Yellow River Valley were similar because they were
industrialized societies
monotheistic
dependent on fertile land
dependent on each other for trade