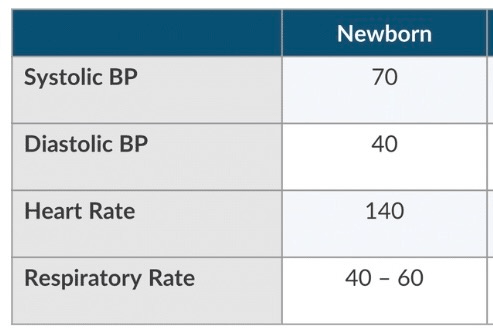
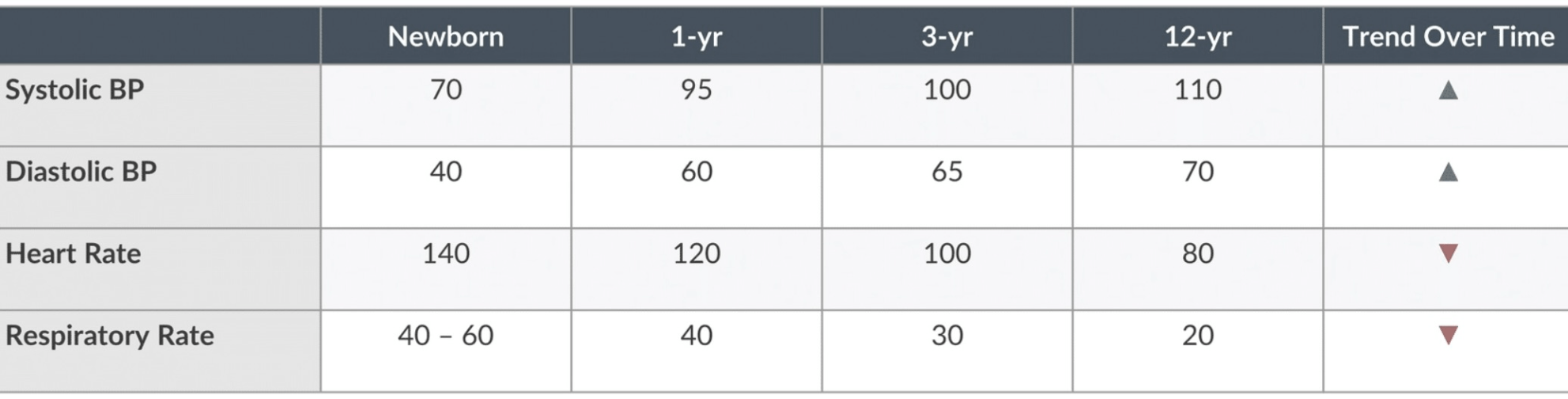
All of the following vital signs are consistent with term newborn except:
a. SBP 60
b. DBP 40
c. HR 140
d. Respiratory Rate 50
a. SBP 60
When compared to the adult patient, the newborn has a tendency to desaturate more quickly because:
1. They have a lower alveolar ventilation to FRC ratio
Or...
2. They have a higher alveolar ventilation to FRC ratio
2. They have a higher alveolar ventilation to FRC ratio
- Pediatric patients have an increased Oxygen Consumption rate
- Increased alveolar ventilation to increase oxygen supply
- Decreased FRC reflects a reduced oxygen reserve.
- All resulting causing the neonate to desaturate quicker.
- Increased ratio of alveolar ventilation relative to reduced FRC (fewer alveoli need to achieve a steady-state) also explains a faster inhalational induction in neonates when compared to adults.
HgbA begins to replace HgbF at __ months of life, and this process is completed at __ months of life.
✦ 2
✦ 6
True or False:Due to the neonates body habitus, the will experience a shorter duration of action of lipid-soluble drugs.
✦ False → Neonates have a greater percentage of total body water and lower percentage of body fat and muscle mass.
✦ Drugs that require fat for redistribution and termination of effect will have a longer duration of action.
Neonates produce heat by:
a. Shivering
b. Brown fat metabolism
c. Screaming and Crying
b. Brown fat metabolism
✦ Non-shivering thermogenesis a.k.a brown fat metabolism is the primary source of heat production in the neonate and is a function that persist up to 2 years of age.
__ is the primary determinant of cardiac output and systolic blood pressure in infants.
✦ Heart Rate
✦ A neonate is unable to increase contractility to overcome an increase in afterload
✦ The frank-Starling relationship is underdeveloped, therefore, the heart rate must be maintained to ensure adequate tissue perfusion & adequate oxygen delivery.
Infants less than 60 weeks PCA are at risk for ___ following surgery with general anesthesia.
✦ Apnea
✦ 24-hr observation is needed postoperatively to observe for apnea
✦ Prophylactic caffeine (10mg/kg IV) may reduce the risk of postoperative apnea after general anesthesia.
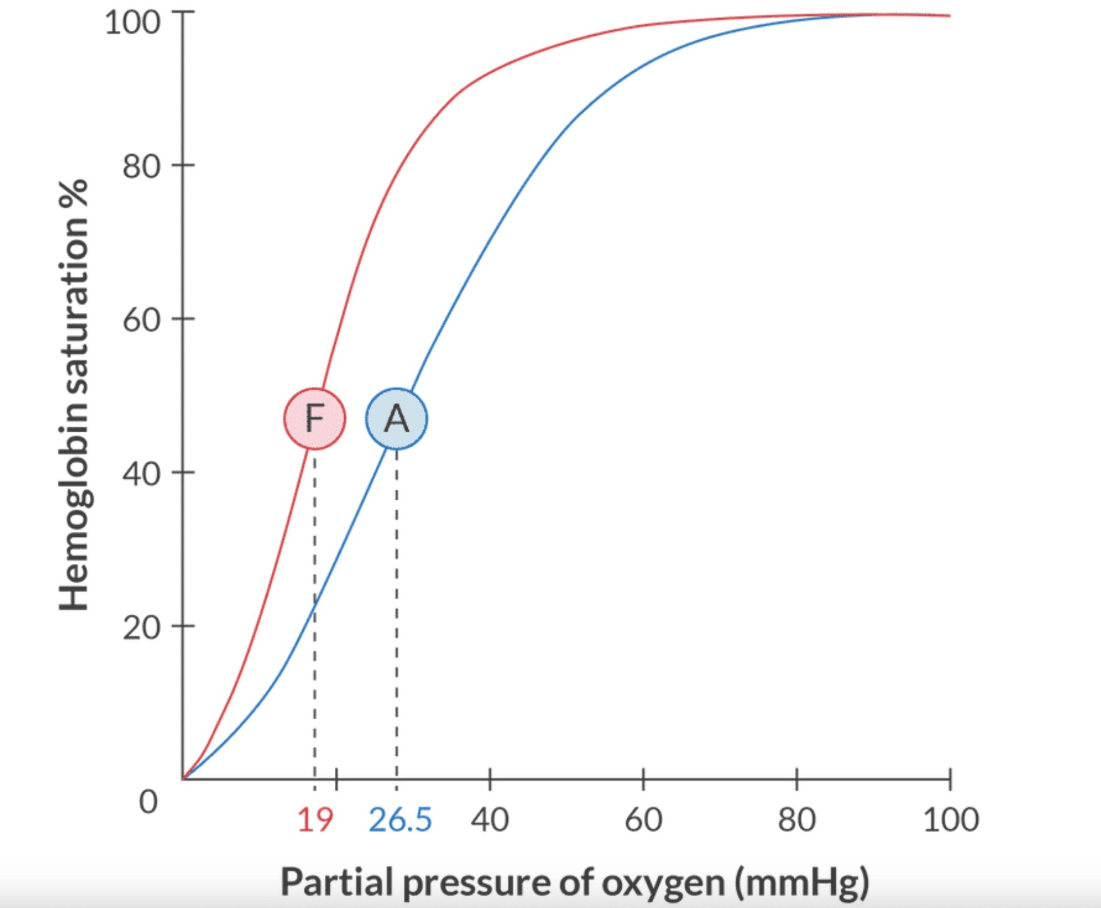
Fetal hemoglobin shifts the oxyhemoglobin curve to the ___.
✦ Left
✦HgbF: P50 = 19.5mmHg
✦HgbA: P50 = 26.5 mmHg
The newborn has a cardiac output of about __ mL/kg/min, causing drugs to be delivered and removed from the body at a ___ rate when compared to the adult patient.
✦ 200 ml/kg/min
✦ Faster
Physiologic anemia of the infant occurs between __ to __ months.
✦ 2 to 3 months

True or False: In the newborn, phenylephrine is a first-line treatment for hypotension.
✦ False → Neonates have a poorly compliant ventricle, so the heart is unable to increase contractility to enough to overcome and elevated afterload.
True or False: The neonates respiratory rate and tidal volume are both equally increased when compared to the adult.
✦ False → Oxygen consumption and carbon dioxide production doubles when compared to the adult patient.
✦ In the newborn, the alveolar ventilation must increased → it is more efficient to increase respiratory rate than it is to increase tidal volume.
✦This explains why newborns have a high respiratory rate, yet a tidal volume that is comparable to the adult (6mL/kg).
The potential complications the neonate may experience after receiving massive transfusion (Select 2):
a. Hypocalcemia
b. Hypercalcemia
c. Metabolic alkalosis
d. Respiratory acidosis
a. Hypocalcemia
c. Metabolic alkalosis
Massive transfusion for the neonate is associated with:
Alkalosis → Due to citrate metabolism to bicarbonate in the liver
Hypothermia → Due to transfusion of cold blood
Hyperglycemia → Due to dextrose additive to stored blood
Hypocalcemia → Due to the binding of calcium by citrate
Hyperkalemia → Due to the administration of older blood
Infant 1 to 6 months of age: MAC is ___ than the adult.
a. Higher
b. Lower
a. Higher
✦ Minimum alveolar concentration varies with age.
✦ Neonate (0-30 days): MAC is lower than the infant
✦ Premature: MAC is lower than the neonate
✦ Infant 1-6 months: MAC is higher than adults
✦ Infant 2-3 months: MAC peaks at its highest level
MAC for sevoflurane differs:
✦ 0 days to 6 months: MAC is higher → 3.2%
✦ 6mo to 12 years: MAC is lower, however still higher than when compared to adults → 2.5%
The newborn's kidneys tend to:
a. Excrete sodium
b. Reabsorb sodium
c. Reabsorb water
d. Do nothing
a. Excrete sodium
✦ The newborn's kidneys are not fully developed, therefore its concentrating mechanism is minimal → Sodium is excreted
✦ Renal tubular function continues to improve shirtly after birth, but does not achieve its full concentrating ability until 2 years of age.
The respiratory rate for a new born ranges between __ - __ breaths per minute.
✦ 40-60 breaths per minute
The statement most that most describes the infants airway (Select 2)
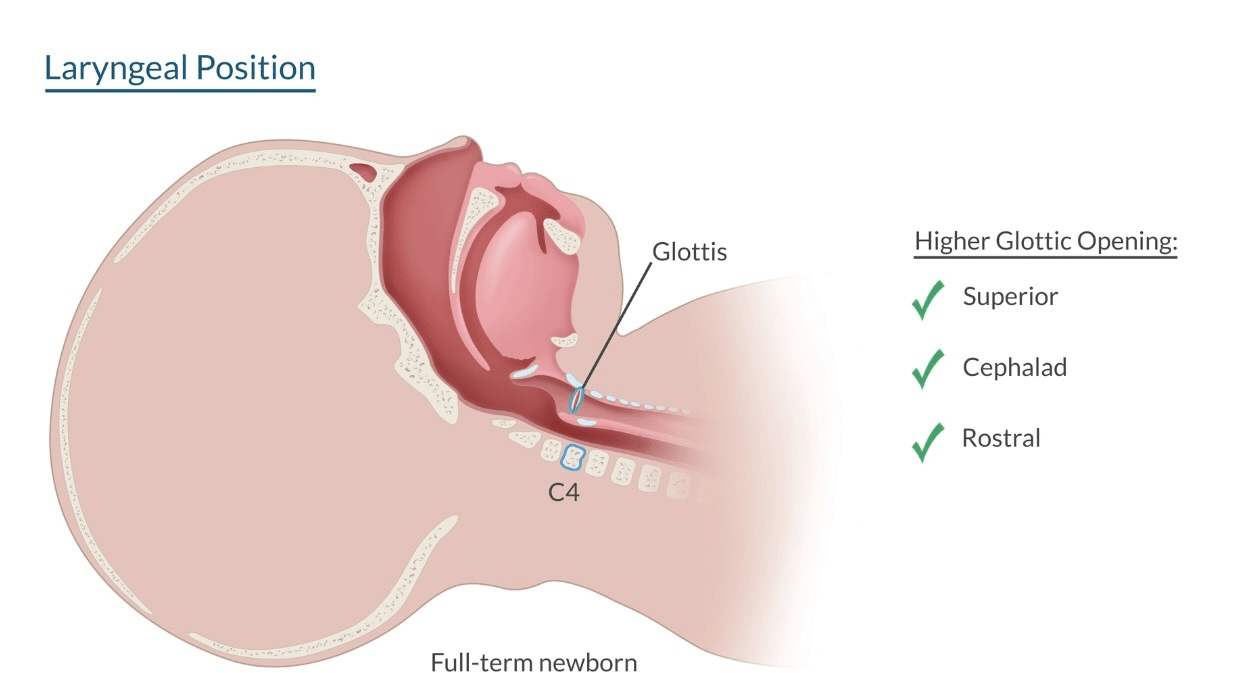
a. The glottic opening is more cephalad
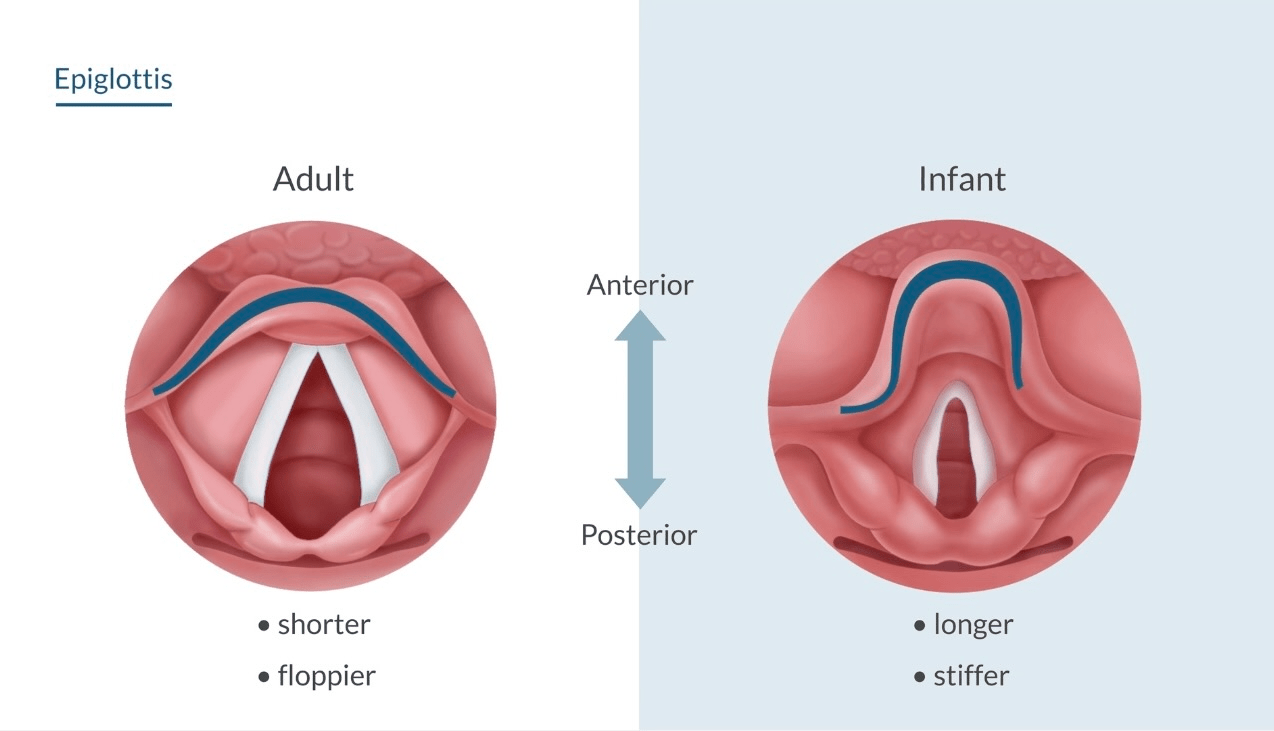
b. The epiglottis is floppy
c. The vocal cords position is at C3-C4
d. Like the adult, the left and right mainstem bronchi take off at different angles
a. The glottic opening is more cephalad
c. The vocal cords position is at C3-C4
✦ The left and right mainstem bronchi take off at the same angle( Up to 3 years of age @ 55 degrees)
✦ The epiglottis is long and stiff
✦ The larynx is more superior, cephalad & rostral. But is it not anterior. A neonates airway can only be considered anterior during neck flexion.
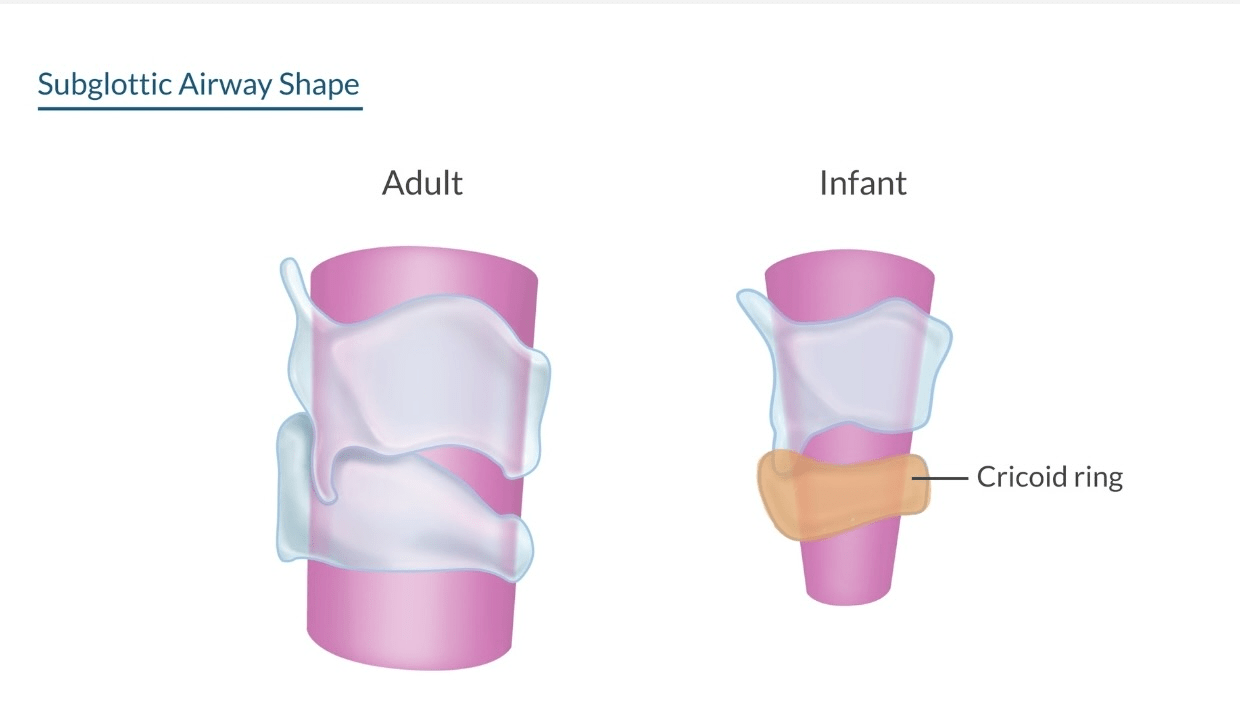
✦ Narrowest FIXED region of glottic opening: Cricoid Ring (Funnel-Shaped)
✦ Narrowest DYNAMIC region of glottic opening: Vocal Cords
Calculate the hourly maintenance rate for a pediatric patient weighing 15kg.
✦ 50 mL
✦ 4:2:1 Rule !!
- 4 ml/kg/h for the 1st 10 kg → 4x10 = 40
- 2 ml/kg/h for the 2nd 10 kg → 2x5 = 10
- 1 ml/kg/h for the remaining kg
✦ 40 + 10 = 50 mL
True or False: Neonates require a larger dose of succinylcholine when compared to the adult patient.
✦ True → NMB are highly water-soluble. In combination of an increase ECF and normal sensitivity to succinylcholine, the neonate requires an increased dose (2mg/kg)
The neonate is at risk of postoperative apnea. Prophylactic caffeine is not available at the pharmacy. What is the alternative medication that can be administered?
✦ Theophylline
✦ Caution must be taken when administered due to its increased risk of toxicity when compared to caffeine administration.
Select the statement that accurately reflect the cardiovascular system in the neonate (Select 2)
a. Heart rate is the primary determinant of blood pressure
b. Stress is more likely to activate the sympathetic nervous system
c. Stress is more likely to activate the parasympathetic nervous system
d. Hypotension is defined as a SBP < 70 mmHg
a. Heart rate is the primary determinant of blood pressure
c. Stress is more likely to activate the parasympathetic nervous system
When compared to the adult:
1. The diaphragm has more type 1 than type 2 muscle fibers
Or...
2. The diaphragm has more type 2 than type 1 muscle fibers
2. The diaphragm has more type 2 than type 1 muscle fibers
✦ The neonate has more type 2 (fast-twich) fibers and less type 1 (slow-twitch) fibers → This is the cause of neonates to experience respiratory fatigue at a quick rate.
A 6 kg term neonate is scheduled for surgery. Preoperative hematocrit is 60%. What is the maximum allowable blood loss to maintain a hematocrit of 50%?
✦ What is the range? __ - __ mL
✦ 80 - 90 mL
1. Determine the Estimated Blood Volume 
✦ Term neonate weighting 6 kg: EBV 480-540 mL
2. Maximum allowable blood loss formula:
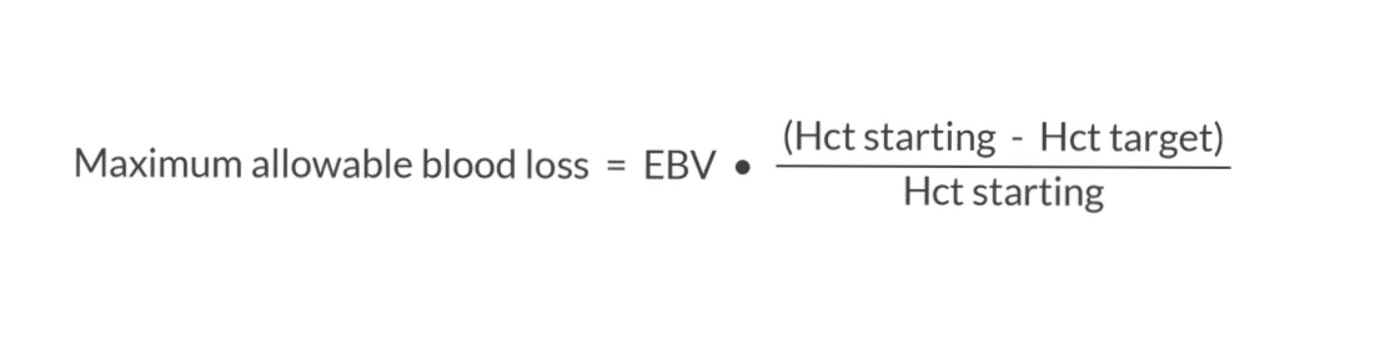
3. 480-540 x (60 - 50) / 60 = 80-90 mL
In children less than 5 years of age, succinylcholine may cause ___.
a. Junctional rhythm
b. Tachycardia
c. Bradycardia
d. PVC's
c. Bradycardia
✦ Succinylcholine may cause bradycardia or asystole in children less than 5 years of age.
✦ Increased risk after repeated administration
✦ Atropine pre-treatment (0.02mg/kg) IV will mitigate this response.
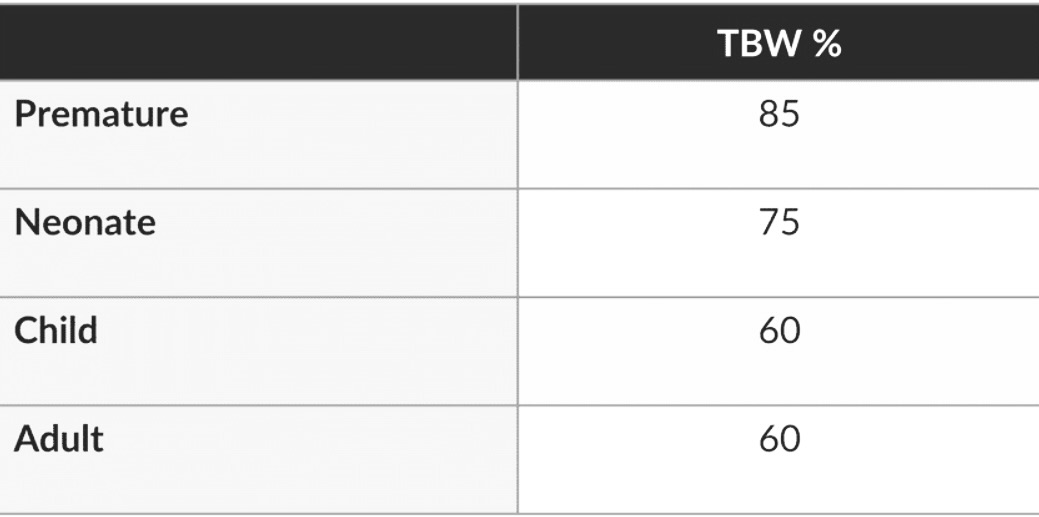
Total body water in the neonate is __ %.
✦ 75%