A newborn presents with a prominent port wine stain over the right forehead. This is the ophthalmologic finding associated with this condition.
What is glaucoma (Sturge Weber - MRI for leptomeninges)
A term infant is born by STAT Cesarean section after cord prolapse. The infant has Apgar scores of 0 at 1 minute and 2 at 5 minutes. Cord gas is 6.9/-17. The infant is being transferred to a regional NICU. This treatment should by initiated by this time
What is therapeutic hypothermia and by 6 hours of life
A GBS positive mother delivers vaginally at 38 weeks gestation. ROM was 4 hours, no fevers. She received penicillin less than 1 hour prior to delivery. The infant is well appearing. The plan of care for this infant is
What is routine vitals
Compared to term infant formula, preterm formula has higher protein concentration, lower lactose concentration, and higher sodium content
What is true
Posterior auricular pits, omphalocele, ear lobe creases, macroglossia, hypoglycemia. This tumor is most commonly seen in these children.
What is Wilms tumor
A newborn LGA infant presents with paralysis of the right shoulder and arm. The right arm is held alongside the body in internal rotation. What is the diagnosis?
What is Erb's Palsy (5th and 6th cervical roots)
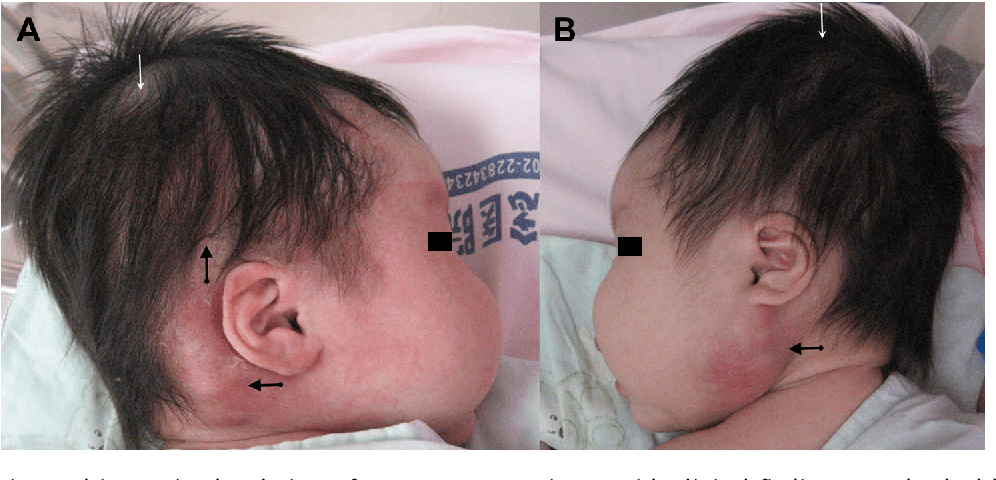
The vessel and affected space involved in this neonatal finding is
What are emissary veins and subgaleal space (potential space between galeal aponeurosis and periosteum)
A mother with no prenatal care delivers at home. The infant develops a maculopapular rash and persistent runny nose. On exam you note that the mother has a rash on her hands and you suspect this infection.
What is syphillis
These LCPUFAs present in human milk that have been found to accumulate rapidly in the fetal brain and retina
What are ARA and DHA
Autosomal dominant inheritance, bile duct paucity with cholestasis, triangular face, pulmonary valve stenosis. This is the most common eye finding.
Bonus points for diagnosis
Posterior embryotoxin
A term baby is referred from UCMC with failure to pass meconium in the first 3 days of life. A contrast enema is performed and results in the baby successfully passing meconium. No other abnormalities are detected on routine examination. The baby is breastfeeding and stooling normally. What is the most important investigation to arrange in the follow-up of this baby?
What is a sweat test for CF
A newborn infant appears 'floppy' with club feet. Pregnancy was complicated by polyhydramnios and preterm labor. The infant's breathing is shallow, he has a 'droopy' face with a mouth open in a 'tent' like appearance. The mother has temporal wasting, a long thin face with open mouth. After shaking your hand, you note that she has difficulty releasing. The dyad is affected by this
What is myotonic dystrophy (AD with anticipation - usually maternal inheritance)
An infant is admitted to the NICU for suspected sepsis. A CBC is obtained which shows a WBC of 22 (S50, B10, L23, M7, E4, meta 4, myelo 2). The IT ratio is
What is 0.24
These fat soluble vitamins are present in low quantities in human milk
What are Vit D and K
Craniosynostosis, hypertelorism, broad thumbs, syndactyly with fused nails are findings in an infant with this
What is Apert syndrome
Your patient is a term female infant who is 5 days old, being treated for NOWS on morphine. The nurse (their first day in the NICU!) is concerned about possible bleeding and is worried about a pink spot in the diaper. They show you the diaper, and upon inspection you clearly note a salmon-colored spot in the diaper. On physical examination, the infant is healthy-appearing, conjunctivae are pink. There is no blood noted at the vaginal introitus. Growth parameters are all at the 50th percentile, the child has a healthy appetite and breastfeeds well. A urine dip-stick shows no blood. The etiology of this is
What are urate crystals
This is the most common outcome in a very low birthweight infant with cystic periventricular leukomalacia
What is spastic diplegia
A pregnant patient at 37 weeks gestation has just been diagnosed with chickenpox. This period of time around delivery is the highest risk of infection for the newborn
The mother of a preterm infant born at 32 weeks gestation desires soy milk feedings for her infant at time of discharge. This would be a major concern about soy formula use in this patient population
What is osteopenia
This metabolic disease can cause subdural hematomas and retinal hemorrhages, which can be mistaken for child abuse
What is glutaric aciduria type 1
This reflex appears at 28 weeks gestational age, is established by 32 weeks gestation and disappears by age 2-4 months. If this reflex persists, it is characteristic of athetoid cerebral palsy.
What is the palmar grasp reflex
The specific EEG pattern seen in severe HIE and that strongly correlates with poor neurological outcome
What is burst suppression
A 28 week gestation infant, currently 3 weeks of age develops acute abdominal distention and bloody stools. An abdominal X-ray shows gas cysts in the submucosa of the bowel wall. The main component of the gas and the part of bowel most commonly affected
What is nitrogen, distal ileum, and proximal colon
An LGA term infant is being screened for hypoglycemia. Before feeding the blood sugar measurement is 35. Baby is otherwise asymptomatic and eating formula well. You decide to provide an IV dextrose. Does the infant need a D10W bolus? This is the GIR if the baby is 4kg and receives D10W at 10ml/hour
No
What is 4.2mg/kg/min
An infant fails the newborn hearing screen and on EKG has a very prolonged QT interval; this condition can cause these
What is Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome