This type of access is preferred for rapid volume resuscitation in an unstable pediatric patient
IO
The most common cause of maternal death worldwide
What is postpartum hemorrhage
In a crashing pediatric patient who is not breathing with a suspected tension pneumothorax, your first step would be _______
Perform needle decompression
This condition, characterized by ground-glass opacities on CXR, is common in premature neonates with underdeveloped lungs.
What is Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS)
This maneuver is used to relieve a shoulder dystocia during delivery
What is the McRoberts maneuver
The IV/IO dose for Epinephrine in neonatal resuscitation is
0.2ml/kg or 0.02mg/kg
What is the #1 cause of morbidity and mortality for women of New Mexico?
Sepsis
30-week gestation trauma patient arrives hypotensive with fetal bradycardia. This bedside maneuver should be performed immediately to improve uteroplacental perfusion.
What is left uterine displacement (or left lateral tilt)
A 4-month-old presents with nasal congestion, increased work of breathing, wheezing, crackles, and poor feeding after 3 days of upper respiratory symptoms. Cap refill is slightly delayed, and oxygen saturation is 88% on room air. This syndrome is most likely
What is bronchiolitis
This maternal condition, often asymptomatic, can cause neonatal sepsis, pneumonia, or meningitis if not treated during labor
What is Group B Streptococcus (GBS)
This is the most common pediatric lethal arrhythmia
Asystole
A maternal BP of 160/110 with proteinuria indicates this critical OB condition
What is severe preeclampsia
A neonate is delivered via emergent C-section after maternal eclampsia and presents with poor tone and no respiratory effort. This is the immediate procedural intervention
What is positive pressure ventilation (PPV)
This virus is the most common cause of bronchiolitis in infants under 1 year old
RSV
A laboring patient suddenly develops shortness of breath, hypotension, altered mental status, and massive bleeding. What is the most likely diagnosis?
What is amniotic fluid embolism (AFE)
Your pediatric patient requires an Epi 'spritzer' aka PDP. Your patient weighs 13kg. How much EPI do you put in a 10ml syringe?
1.3 ml, or .13mg
A pregnant patient with fever, tachycardia, uterine tenderness, and fetal tachycardia is likely experiencing this infection
What is chorioamnionitis
The antidote for Mag toxicity is _________ _________ and the dose is ___________.
Calcium gluconate 1gm IV
This electrolyte abnormality occurs in dehydrated infants due to poor feeding
What is hyponatremia
Maternal diabetes increases the risk of this neonatal metabolic disturbance after birth
What is neonatal hypoglycemia
A term neonate delivered via vacuum assistance presents with lethargy, seizures, a bulging fontanelle, and a midline shift on imaging. What do you see on imaging?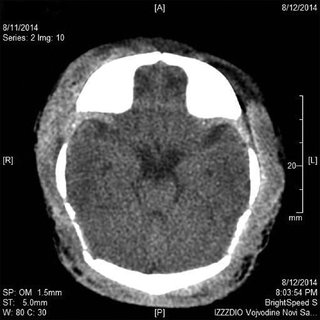
Severe neonatal subgaleal hemorrhage
This cardiac condition presents with dyspnea, fatigue, and signs of heart failure late in pregnancy or postpartum
What is peripartum cardiomyopathy
Daily Double!
To decrease the incidence of death or disability in infants, CST can provide cooling therapy during transport. This infant has the following S/S: Cord prolapse SVD at 36 5/7 weeks, 2 hours of life, apgars 25 410 415, initial pH 6.8. Does this patient meet HIE cooling therapy guidelines?
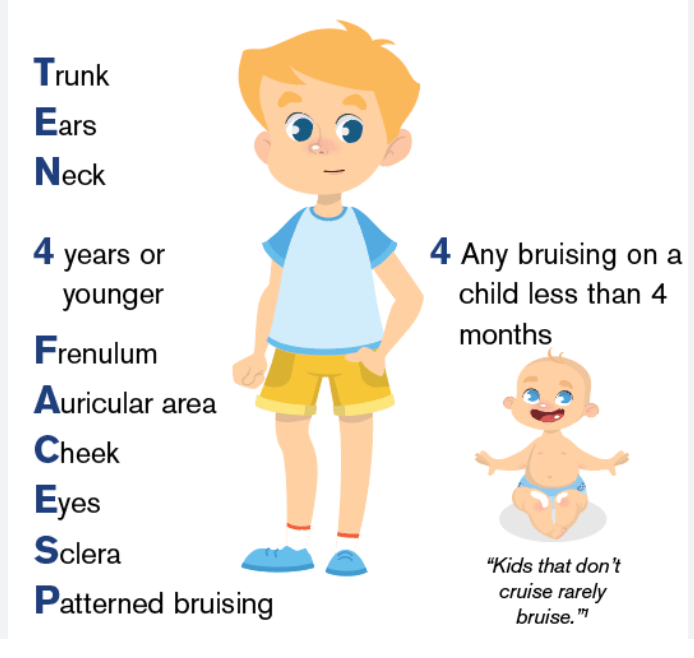
Bruising in these three areas in a non-mobile child should raise concern for abuse
What are the torso, ears, and neck (TEN-4 rule)
A mother with a history of cocaine use during pregnancy presents with sudden, severe abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding. Fetal heart tones are absent on ultrasound. What is this condition?
What is placental abruption leading to fetal demise