A 27-year-old man is evaluated in the ICU for septic shock. For the past 3 months, he has received dialysis for end-stage kidney disease with a tunneled catheter because his arteriovenous fistula has not matured for use. He reports a 1-day history of fever and malaise.
On physical examination, temperature is 38.5 °C (101.3 °F), blood pressure is 90/50 mm Hg, pulse rate is 89/min, and respiration rate is 22/min. A right internal jugular tunneled hemodialysis catheter is in place with no erythema or discharge at the exit site. A normal-appearing and functioning left arteriovenous fistula is present. The remainder of the examination is normal.
Blood and urine cultures are obtained.
Cefepime and vancomycin are initiated, repeated fluid boluses are administered, and intravenous norepinephrine is started.
This is the next best step in management.
A 63-year-old woman is hospitalized for cardiac catheterization for unstable angina. History is significant for stage G3 chronic kidney disease attributed to diabetic nephropathy. Medications are heparin, metoprolol, losartan, amlodipine, atorvastatin, basal insulin, and prandial insulin.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. There is no jugular venous distension or lower extremity edema. The remainder of the examination is unremarkable.
Laboratory studies show a serum creatinine level of 2.4 mg/dL (212.2 µmol/L) and an estimated glomerular filtration rate of 24 mL/min/1.73 m2.
This is the most appropriate measure to prevent AKI.
What is pre- and post-procedure IV NS?
A 38-year-old woman is evaluated in the emergency department for a 4-hour history of left flank pain that radiates to the groin. She is otherwise well and takes no medications.
A noncontrast helical CT scan of the abdomen shows an 11-mm stone in the proximal ureter. There is dilation of the renal calyces.
Analgesics are initiated.
This is the most appropriate additional treatment.
What is lithotripsy?
A 34-year-old woman is evaluated for hypertension. During the past 3 months, two blood pressure measurements in health care settings averaged 150/90 mm Hg. During the same time period, three blood pressure measurements obtained outside of health care settings averaged 128/78 mm Hg. She has no other pertinent personal or family history. She takes no medications.
On physical examination, blood pressure is 144/92 mm Hg in both arms, pulse rate is 80/min, and respiration rate is 18/min. BMI is 22. The remainder of the examination is normal.
This is the most appropriate way to rule out or rule in the diagnosis of hypertension.
What is ambulatory BP monitoring?
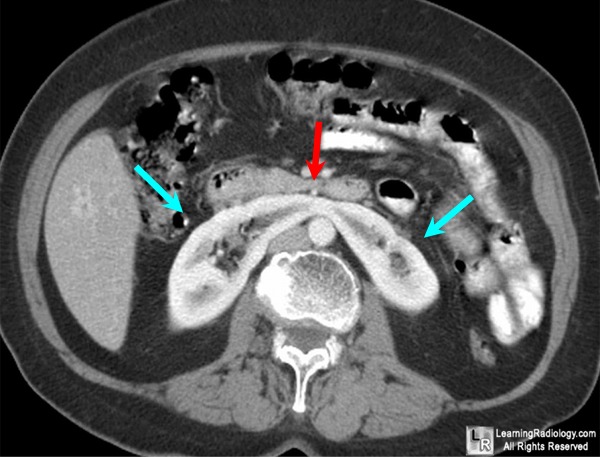
This is the congenital malformation shown in the CT scan above.
What is horseshoe kidney?
A 67-year-old man is evaluated during a follow-up visit for resistant hypertension. He was recently evaluated for primary hyperaldosteronism, and the screening plasma aldosterone concentration/plasma renin activity ratio was >20. A dedicated adrenal CT scan showed diffuse bilateral adrenal hyperplasia. The patient also has type 2 diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, coronary artery disease, and activity-limiting COPD. He does not want surgery under any circumstances. Medications are rosuvastatin, metformin, canagliflozin, amlodipine, enalapril, metoprolol, chlorthalidone, low-dose aspirin, albuterol, and tiotropium.
On physical examination, blood pressure is 160/94 mm Hg in both arms, pulse rate is 76/min, and respiration rate is 18/min. BMI is 24. Cardiac examination is notable for an S4. Pulmonary examination reveals occasional expiratory wheezing.
This class of medication is the most appropriate next step in management.
What are mineralocorticoid receptor antagoists?
A 28-year-old woman seeks preconception counseling. She has a 3-year history of primary hypertension. Medical history is otherwise unremarkable, and her only medication is ramipril.
On physical examination, blood pressure is 138/78 mm Hg. Average blood pressure with home blood pressure monitoring is 136/72 mm Hg. Other vital signs are normal. BMI is 30. The remainder of the examination is normal.
Previous evaluation revealed no evidence of retinopathy, left ventricular hypertrophy, or kidney disease.
This is the most appropriate next step in this patient's care.
What is discontinue ramipril?
An 87-year-old man is evaluated in the emergency department for a 36-hour history of lower abdominal discomfort, urinary frequency, and nocturia. He has no other symptoms. Medical history is significant for type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and IgG4-related autoimmune pancreatitis. Medications are metformin, hydrochlorothiazide, and rituximab. He began taking over-the-counter chlorpheniramine last week for symptoms related to seasonal allergies.
On physical examination, he is afebrile. Blood pressure is 158/64 mm Hg, and pulse rate is 78/min. There is tenderness to palpation of the lower abdomen. The prostate is diffusely enlarged.
Laboratory studies show a BUN of 50 mg/dL and a serum creatinine of 2.4 mg/dL. Urinalysis shows a specific gravity of 1.012, 1+ blood, 1+ protein, 1+ leukocytes, 3 nondysmorphic erythrocytes/hpf, 1-3 leukocytes/hpf, and no casts.
This is the most appropriate next step in management.
What is bladder ultrasound (to diagnose postrenal obstructive uropathy 2/2 BPH)?
A 46-year-old woman is evaluated for a serum creatinine level of 2.6 mg/dL (229.8 µmol/L). Her baseline serum creatinine level 3 months ago was 0.9 mg/dL (79.6 µmol/L). She has no symptoms. Two years ago, she started losartan and amlodipine for hypertension. One year ago, she started omeprazole for gastroesophageal reflux disease and naproxen for knee osteoarthritis. Eight months ago, she began atorvastatin for hyperlipidemia.
Vitals are stable.
Urinalysis shows the following: specific gravity 1.015; pH 5.5; 1+ erythrocytes; 3+ leukocytes; 1+ leukocyte esterase; no nitrates; and >100 leukocytes/hpf with leukocyte and granular casts.
The following medication(s) will be discontinued.
What is omeprazole and naproxen?
A 25-year-old woman is evaluated for a 6-month history of fatigue, joint pain, sun sensitivity, and pleuritic chest pain. Medications are an oral contraceptive pill and as-needed naproxen.
On physical examination, temperature is 38.2 °C (100.8 °F), blood pressure is 142/90 mm Hg, and pulse rate is 100/min. The fingers and wrist joints are tender, but there is no synovitis. The remainder of the examination is normal.
Laboratory studies show a serum creatinine level of 1.4 mg/dL (123.8 µmol/L); dipstick urinalysis shows 2+ blood, 3+ protein, positive leukocyte esterase, and no nitrites.
Urine microscopy is shown.
 This is the most appropriate diagnostic test.
This is the most appropriate diagnostic test.
What is a kidney biopsy (to diagnose glomerulonephritis)?
A 36-year-old woman is evaluated during a routine follow-up visit for stage G4 chronic kidney disease. Her estimated glomerular filtration rate is 22 mL/min/1.73 m2. Medications are lisinopril, sevelamer, and sodium bicarbonate. She has selected hemodialysis for her renal replacement therapy, and an arteriovenous fistula will eventually be placed in her nondominant left arm.
Three weeks later, the patient is hospitalized with septic shock secondary to community-acquired pneumonia. Venous access for the administration of fluids, vasopressors, and antibiotics is urgently needed.
This is the most ideal venous access for this patient.
What is central venous catheter in internal jugular vein?
A 63-year-old man is evaluated during a follow-up visit for gastroesophageal reflux disease and heartburn. His symptoms are worse after large meals and when lying down and have significantly decreased the quality of his life and disrupted his sleep. He also has stage 4 chronic kidney disease, obesity, and hypertension. Medications are atenolol, lisinopril, and nifedipine.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. BMI is 38. The remainder of the examination is normal.
Laboratory studies show an estimated glomerular filtration rate of 29 mL/min/1.73 m2.
Weight loss and other lifestyle management modifications for gastroesophageal reflux disease are discussed.
This is the class of medications that should be started as an additional therapy.
What are H2 blockers?
A 59-year-old man is evaluated for recently discovered normochromic, normocytic anemia and an elevated serum creatinine level. He is otherwise well and takes no medications.
All physical examination findings, including vital signs and neurologic examination, are normal.
Serum labs show hgb 9.2, cr 3.0, UA shows trace protein only, urine protein to creatinine ratio is 2500.
This is the most appropriate test to perform next.
What is urine protein electrophoresis?
A 28-year-old man with PMH of IgA nephropathy is evaluated for hematuria that he noted on awakening and a 3-day history of fever, runny nose, and cough. He has no other medical problems and takes no medications.
On physical examination, temperature is 37.9 °C (100.2 °F), and blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg; other vital signs are normal. The nasal mucosa is edematous, with serous discharge. Examination of the oropharynx reveals erythema without exudate. There is no lymphadenopathy. The remainder of the examination is unremarkable.
Laboratory studies show a serum creatinine level of 0.9 mg/dL; urinalysis shows 3+ blood, trace protein, too numerous to count erythrocytes, and no casts. Streptococcal rapid antigen test is negative.
This is the most appropriate management for this patient.
What is clinical observation only?
A 70-year-old woman is evaluated for right flank pain and dysuria. She has a 20-year history of type 2 diabetes mellitus with neurogenic bladder and recurrent urinary tract infections. Medications are metformin and simvastatin.
On physical examination, temperature is 38.3 °C (100.9 °F); other vital signs are normal. There is tenderness to palpation over the right flank. The remainder of the examination is normal.
Urinalysis shows cloudy urine with a specific gravity of 1.010, pH of 8.0, 1+ blood, trace protein, 3+ leukocyte esterase, and positive nitrites. Microscopic urinalysis reveals 1-2 erythrocytes/hpf, 20-25 leukocytes/hpf, and crystals (shown)
 This organism is the most likely infective agent.
This organism is the most likely infective agent.
What is proteus mirabilis?
A 32-year-old man is evaluated for end-stage kidney disease due to congenital reflux nephropathy. He began hemodialysis at age 21 years. He is on the kidney transplant list. He also has hypertension. Medications are amlodipine, calcitriol, lisinopril, and sevelamer carbonate.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. There is a left upper extremity arteriovenous fistula with strong thrill. The remainder of the examination is normal.
Kidney ultrasound shows small kidneys with multiple cysts bilaterally. A few cysts have internal septations. There are no solid components or evidence of vascular flow within the cysts.
This is the most appropriate management of this patient's acquired kidney cysts.
What is annual kidney US (to screen for RCC)?
A 41-year-old woman is evaluated during a follow-up visit for stage 2 hypertension confirmed by daytime ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. She also has a 10-year history of type 2 diabetes mellitus and hyperlipidemia. Medications are atorvastatin, metformin, and empagliflozin.
On physical examination, blood pressure is 142/92 mm Hg, and pulse rate is 72/min; other vital signs are normal. BMI is 28. The remainder of the examination is unremarkable.
Laboratory studies show a serum creatinine level of 0.9 mg/dL (79.6 µmol/L). Urine dipstick reveals no blood or protein.
The patient is instructed in lifestyle modifications for blood pressure control.
This is the next best step in management of this patient's blood pressure.
A 22-year-old woman participating in a marathon is evaluated in the medical tent for headache, confusion, and disorientation after she stopped running at mile 20.
On physical examination, temperature is 38.0 °C (100.4 °F), blood pressure is 110/72 mm Hg, pulse rate is 110/min, and respiration rate is 20/min. The patient is confused. The remainder of the examination is normal.
Laboratory studies show a serum sodium level of 130 mEq/L (130 mmol/L).
This is the most appropriate management.
What is 3% saline bolus?
A 38-year-old woman seeks treatment for polyuria and nocturia that began 6 weeks ago after starting lithium for bipolar disorder. Medical history is otherwise unremarkable. Her only other medication is olanzapine.
Physical examination findings, including vital signs, are normal.
Laboratory studies show a serum sodium level of 145 mEq/L (145 mmol/L) and a urine osmolality of 200 mOsm/kg H2O.
This medication is the most appropriate in managing this patient's condition?
What is amiloride (for nephrogenic diabetes insipidus)?
A 31-year-old woman is evaluated for lower extremity edema, a rash over both legs, and fatigue that have worsened during the past 3 months. She has no other medical problems and takes no medications. The patient was born in Egypt and moved to the United States at 20 years of age.
On physical examination, the patient is afebrile, and blood pressure is 147/96 mm Hg. There is 1-mm pitting edema through the mid-shins bilaterally.
 Serum studies are positive for cryoglobulins and rheumatoid factor while UA is positive for 3+ blood and 3+ proteins.
Serum studies are positive for cryoglobulins and rheumatoid factor while UA is positive for 3+ blood and 3+ proteins.
This viral study will support the most likely diagnosis.
What is hep c virus antibody testing?
A 35-year-old woman is evaluated during a follow-up visit for recurrent microscopic hematuria without proteinuria. Family history is significant for microscopic hematuria in her brother and mother; her two other siblings have no urinary abnormalities. There is no family history of chronic kidney disease or end-stage kidney disease. Her medical history is otherwise unremarkable, and she takes no medications.
Physical examination findings, including vital signs, are normal.
Laboratory studies show a serum creatinine level of 0.7 mg/dL; urinalysis shows 2+ blood, no protein, and 20-30 erythrocytes/hpf.
Kidney ultrasound shows normal-sized kidneys with no masses or stones.
This is the most likely diagnosis.
What is thin glomerular basement membrane disease?
A 26-year-old man is referred for an elevated serum creatinine level of 1.4 mg/dL (123.8 µmol/L) that was measured when he presented to an urgent care center for flank pain. The flank pain was determined to be musculoskeletal and caused by a weight-lifting injury. A subsequent urinalysis was normal, and a random urine albumin-creatinine ratio was 10 mg/g. He reports that he takes no creatine supplements but is evasive when questioned about anabolic steroid use. His medical history is otherwise unremarkable, and he takes no prescribed medications.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. BMI is 29. The patient is muscular, with no evidence of subcutaneous fat. He has mild muscle tenderness in the right lower back. The remainder of the examination is unremarkable.
This serum marker should be used to most accurately measure kidney function.
What is cystatin C?
A 62-year-old man is evaluated in the emergency department for abrupt onset of sharp chest pain radiating to his upper back that started 90 minutes ago. Medical history includes difficult-to-control hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Medications are metformin, empagliflozin, rosuvastatin, amlodipine, hydrochlorothiazide, and lisinopril.
On physical examination, blood pressure is 210/120 mm Hg in the right arm and 180/100 mm Hg in the left arm, pulse rate is 118/min, respiration rate is 20/min, and oxygen saturation is 97% with the patient breathing ambient air. The patient is diaphoretic and in distress. Cardiac examination reveals tachycardia with a 3/6 diastolic murmur heard along the upper left sternal border. Lungs are clear to auscultation. The remainder of the examination is unremarkable.
This is the most likely diagnosis and this is the first line drug class (given IV) to be used as its treatment.
What is ascending aortic dissection and beta blockers?
A 54-year-old man is evaluated for the nephrotic syndrome 10 days after undergoing a kidney biopsy. He reports normal urine volume and no hematuria. He has noticed mild bilateral flank aches during the past 2 days. Prebiopsy serum creatinine level was 0.9 mg/dL (79.6 µmol/L). Medical history is also significant for hyperlipidemia. Medications are furosemide and atorvastatin.
On physical examination, temperature is 37.0 °C (98.6 °F), blood pressure is 148/88 mm Hg, and pulse rate is 72/min. Bilateral costovertebral angle tenderness is noted. There is 2+ lower extremity edema. The remainder of the examination is normal.
Laboratory studies show a serum creatinine level of 3.2 mg/dL (282.9 µmol/L). Urinalysis shows a specific gravity of 1.012; pH of 5.0; 3+ blood; 3+ protein; 1+ leukocytes; >100 erythrocytes/hpf; occasional leukocytes; and no casts.
Kidney biopsy shows membranous nephropathy with minimal interstitial fibrosis and no glomerulosclerosis.
This is next best step for establishing a diagnosis.
What is renal US w/ doppler (to diagnose renal vein thrombosis)?
A 72-year-old man is evaluated for an ulcerating, painful lesion on his left calf that began as a patch of red skin 2 to 3 weeks ago. He has dialysis-dependent end-stage kidney disease, atrial fibrillation, and hypertension. Medications are amlodipine, calcium acetate, calcitriol, insulin, and warfarin. There have been no recent changes in his medications.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. Skin findings are shown.
 A skin punch biopsy shows calcifications in the subcutaneous tissue within necrotic lipocytes and within the walls of small blood vessels. There is confluent epidermal necrosis.
A skin punch biopsy shows calcifications in the subcutaneous tissue within necrotic lipocytes and within the walls of small blood vessels. There is confluent epidermal necrosis.
Serum labs show INR 2.5, Ca 9.6, Phos 3.1, and PTH 361.
This is the most likely diagnosis.
What is calciphylaxis?