I tried to tell a joke about chemistry but there was no reaction.
Treatment of symptomatic isovolemic hypotonic hyponatremia
100-mL bolus of 3% saline
Disorder defined by low serum bicarbonate
Primary metabolic acidosis
Acid Base disorder: decrease in PCO2, an increase in pH, and a slight decrease in bicarbonate
Respiratory alkalosis
Alkalemia is defined as a pH >7.44
Metabolic alkalosis = [HCO3] >[***]mEq/L. Respiratory alkalosis = arterial PCO2 <[***] mm Hg.
Metabolic alkalosis = [HCO3] >26 mEq/L. Respiratory alkalosis = arterial PCO2 <36 mm Hg.
Name the Artist:
Lyrics: "All about that bass, 'bout that bass, no treble."
Meghan Trainor
Therapeutic goal for chronic isovolemic hypotonic hyponatremia is an increase in serum sodium by (#) to (#) mEq/L in a 24 hour period
4-6 mEq/L
( not to exceed 8.0 mEq/L in 24 hours)
Most common cause of increased anion gap metabolic acidosis
Lactic acidosis
Most common causes of metabolic alkalosis (3)
Vomiting, nasogastric suction, and diuretic use
(low urine chloride and chloride depletion)
Salicylate intoxication presents in its early phase
Respiratory alkalosis and an increased anion gap metabolic acidosis
Name the Artist:
Song Lyrics: "Pump up the bass! Pump up the bass!" – Clue a 1988 hit from this electronic music act.
Technotronic
Replacement fluid for hypernatremia due to intravascular volume depletion
Isotonic saline
(otherwise, a hypotonic solution (half [0.45%] normal saline) can be used)
Serum Anion Gap (formula and assessment)
If Metabolic acidosis (unmeasured organic anion)
Anion Gap = Serum Sodium (mEq/L) − (Serum Chloride [mEq/L] + Serum Bicarbonate [mEq/L]) )
Acid-base disorder with hypertension, hypokalemia, euvolemia, and an elevated urine chloride
(Type and *cause)
Metabolic alkalosis from mineralocorticoid excess
Expected Compensation: Expected change in PaC02 for Acute Metabolic acidosis
Metabolic acidosis Acute:
Δ arterial PCO2 = (1.5)[HCO3–] + 8 ± 2
alkalosis: 0.7 mm Hg ↑ in PaCO2 for each 1 mEq/L ↑ in [HCO3–]
Name the Artist:
Song Lyrics: "With a taste of your lips, I’m on a ride. You're toxic..."
Britney Spears
Antagonizes the effects of hyperkalemia on the cardiac membrane
Intravenous administration of calcium gluconate
Delta-delta (Δ-Δ) ratio of <0.5 to 1
Indicates the presence of (General Disorder)
Presence of an increased anion gap metabolic acidosis
Expected Compensation:
Acute and Chronic Respiratory acidosis ( [mEq/L] change in HCO3 - for each 10 mm Hg ↑ in PaCO2 )
Acute: 1 mEq/L ↑ in [HCO3–] for each 10 mm Hg ↑ in arterial PCO2
Chronic: 3.5 mEq/L ↑ in [HCO3–] for each 10 mm Hg ↑ in arterial PCO2
Anion Gap and Osmolar gap (alcohol)
Methanol
Ethylene glycol
(Possible AG) Ethanol
Before modern dialysis, doctors used this time-intensive, laborious procedure—essentially an early peritoneal dialysis technique—to remove toxins from patients in renal failure.
Leech Therapy or Peritoneal Lavage
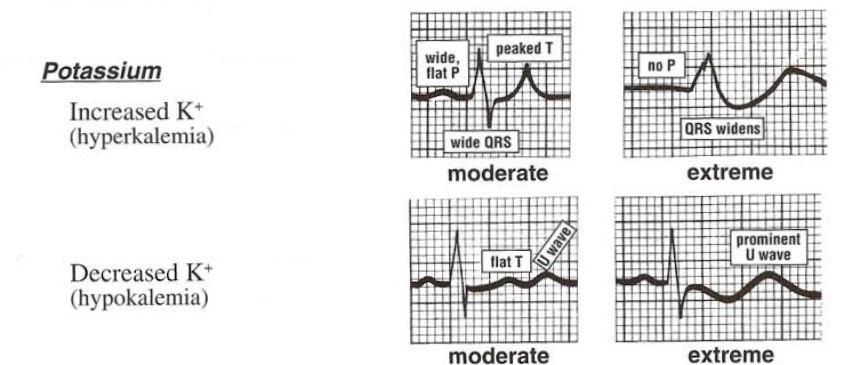
ECG manifestations of hypokalemia
ST-segment depression, decreased T-wave amplitude, and increased U-wave amplitude.
Renal tubular acidosis(type), impaired distal hydrogen ion excretion causes citrate reabsorption and increases the risk for nephrocalcinosis
In type 1 (hypokalemic distal)
Expected Compensation:
Acute and Chronic Respiratory alkalosis ( [mEq/L] change in HCO3 - for each 10 mm Hg ↓ in PaCO2 )
Acute: 2 mEq/L ↓ in [HCO3–] for each 10 mm Hg ↓ in arterial PCO2
Chronic: 4-5 mEq/L ↓ in [HCO3–] for each 10 mm Hg ↓ in arterial PCO2
Non-Anion Gap and Osmolar gap (alcohol)
Isopropyl Alcohol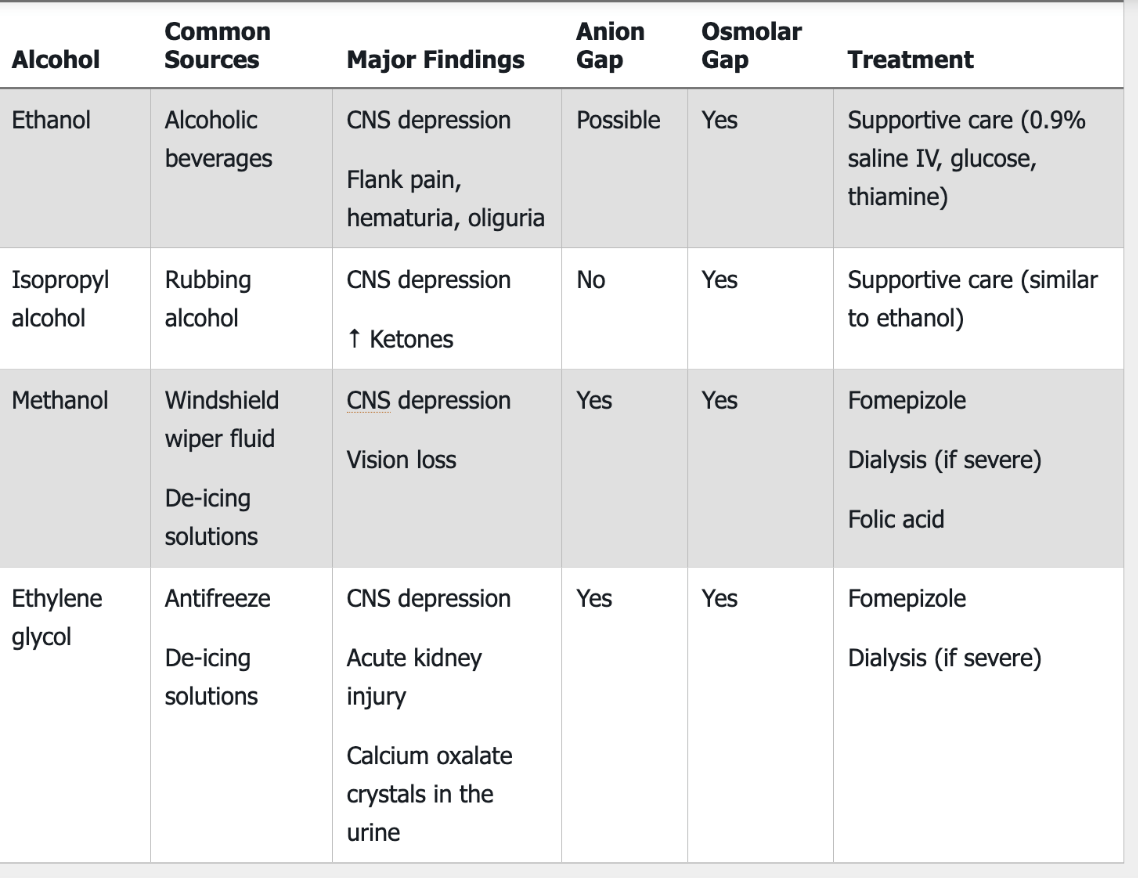
This children’s science show host, played by Bob Newhart, was a childhood hero to Sheldon Cooper and made multiple appearances as a ghostly mentor.
Professor Proton