Functions
Miscellaneous
Two hemispheres of gray matter connected by this intermediate mass
Thalamus
This region controls the unconscious coordination of skeletal muscles for balance and muscle tone
Cerebellum
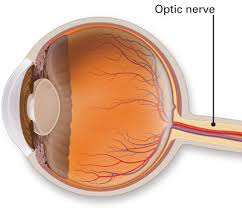
The number of this cranial nerve.
II or 2.
The muscles controlled by the accessory nerve
Trapezius and sternocleidomastoid
The two hemispheres of the cerebellum
Cerebral cortex and arbor vitae
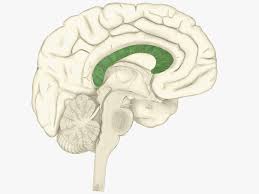
The name of structure highlighted green.
Corpus callosum
This structure relays sensory and motor information to the cerebral cortex
Thalamus
This nerve innervates the masseter and temporalis muscles
Trigeminal nerve
True or false:
The gray matter of the cerebrum is mostly comprised of cell bodies (nulcei)
True
Looks like the "adam's apple" of the brain
Pons
Regulates heartbeat, breathing, and sleeping
The brainstem
Nerve IV (4)
Trochlear nerve
The nerve responsible for eye movement and pupil control
Oculomotor nerve
Does the arbor vitae of the cerebellum comprise white matter or gray matter?
White matter.
The connective tissue membranes that cover the brain
Meninges
This structure secretes melatonin
Pineal gland
The number of cranial nerves
12 pairs
The muscle controlled by the trochlear nerve.
Superior oblique muscle.
The number of lobes in the cerebrum
Five
Hypothalamus
The two centers that the medulla oblongata controls.
Respiratory and Cardiovascular
True or false:
The cranial nerves arise from the base of the brain
True
This nerve travels through the superior orbital fissure of the sphenoid bone
Trochlear nerve
The four regions of the diencephalon
Thalamus, hyphothalamus, pineal gland, optic chiasma